Variceal Bleeding: Overview, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
What is Variceal Bleeding?
Variceal bleeding refers to bleeding from varices, which are abnormally dilated and fragile veins that develop due to increased pressure in the portal venous system (portal hypertension). These varices commonly occur in the esophagus, stomach, and less commonly in the rectum or abdominal wall. When these fragile veins rupture, they cause potentially life-threatening gastrointestinal bleeding.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Portal Hypertension: The primary cause of varices and variceal bleeding, usually due to liver cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis: Liver scarring from hepatitis B or C, alcohol abuse, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hemochromatosis, or other chronic liver diseases.
- Other causes: Portal vein thrombosis, congestive heart failure, arteriovenous malformations.
- Risk factors for bleeding: Large varices, presence of red wale signs on varices, advanced liver disease (high Child-Pugh score), ongoing alcohol use.
Symptoms of Variceal Bleeding
- Vomiting bright red blood or “coffee-ground” material.
- Passing black, tarry stools (melena) or blood in stools.
- Signs of blood loss: lightheadedness, weakness, pale skin, low blood pressure.
- Associated signs of liver disease: ascites, jaundice, hepatic encephalopathy, splenomegaly.
Diagnosis
- Endoscopy: The gold standard for detecting varices and active bleeding. It also allows for therapeutic interventions.
- Clinical presentation: History of liver disease and signs of GI bleeding.
- Imaging: Ultrasound or CT to assess portal hypertension and liver status.
- Laboratory tests: Evaluate hemoglobin, coagulation profile, liver function tests.
Treatment
Acute Management
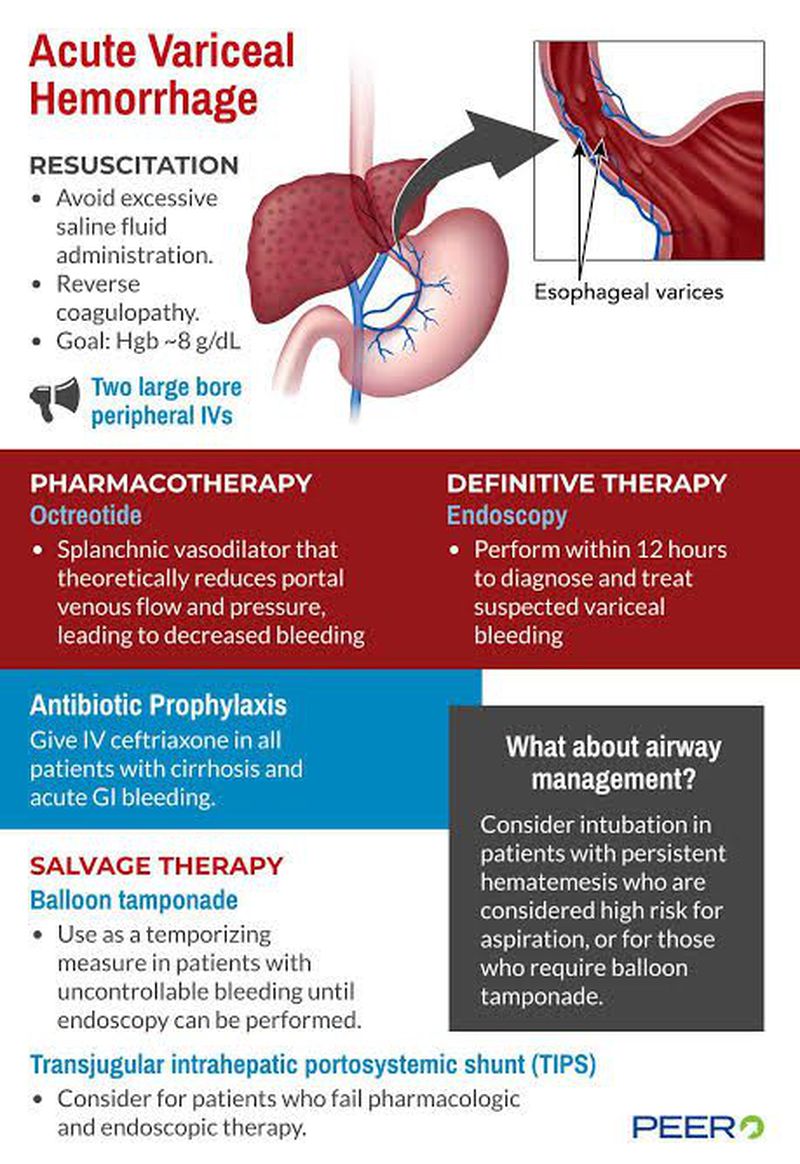
- Stabilization: Fluid resuscitation, blood transfusion as needed, airway protection.
- Pharmacological therapy:
- Vasoactive drugs: Terlipressin, octreotide, or somatostatin reduce portal pressure and control bleeding. Terlipressin is preferred due to mortality benefit and fewer cardiovascular side effects.
- Antibiotics: Prophylactic antibiotics reduce infection risk and improve survival.
- Endoscopic therapy:
- Endoscopic variceal ligation (banding): The first-line treatment to stop bleeding by placing rubber bands on varices.
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of clotting agents or glue, mainly for gastric varices.
- Balloon tamponade: Temporary measure to control bleeding if endoscopy is delayed or unsuccessful.
Preventing Rebleeding
- Combination of vasoactive drugs and endoscopic band ligation.
- Non-selective beta-blockers (e.g., propranolol) to reduce portal pressure.
- Regular surveillance endoscopy for variceal monitoring.
Advanced Interventions
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt): A shunt placed to reduce portal pressure in refractory cases.
- Liver transplantation: For patients with decompensated liver disease.
Prognosis
- Variceal bleeding has a high mortality rate (15-20% within 6 weeks).
- Early and combined therapy improves survival.
- Recurrence of bleeding is common without preventive treatment.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Bleeding from dilated portal hypertension-induced veins (varices) in GI tract |
| Main Cause | Portal hypertension secondary to liver cirrhosis |
| Symptoms | Vomiting blood, melena, lightheadedness, signs of liver disease |
| Diagnosis | Endoscopy (gold standard), imaging, lab tests |
| Acute Treatment | Resuscitation, vasoactive drugs (terlipressin), antibiotics, endoscopic band ligation |
| Prevention | Beta-blockers, repeated band ligation, TIPS in refractory cases |
| Mortality | 15-20% at 6 weeks; higher in advanced liver disease |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Variceal Bleeding or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References:
- Cleveland Clinic 2
- Mayo Clinic 3
- Liver Canada 46
- British Liver Trust 7
- PMC Article on Management of Acute Variceal Bleeding 8
In summary:
Variceal bleeding is a life-threatening complication of portal hypertension, requiring prompt diagnosis and combined pharmacological and endoscopic treatment to control bleeding and prevent recurrence. Early intervention and management of underlying liver disease are critical to improving outcomes.















