Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKI)
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKI): Mechanisms, Applications, and Clinical Impact
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) are a class of pharmaceuticals that block the activity of tyrosine kinases, enzymes critical for signaling pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation, and survival. By inhibiting these enzymes, TKIs disrupt abnormal signaling in diseases like cancer and inflammatory disorders. Below is a detailed overview of TKIs, including their mechanisms, therapeutic uses, and challenges.
Mechanisms of Action
Targeting ATP-Binding Sites:
- Most TKIs compete with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) at the kinase’s active site, preventing phosphorylation and downstream signaling[1][3].
- Examples include imatinib, which binds the ATP pocket of Bcr-Abl in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)[5].
Allosteric Inhibition:
- Some TKIs bind outside the active site, inducing conformational changes that disable kinase activity[1].
Degradation via Chaperone Disruption:
- TKIs like geldanamycin derivatives destabilize kinases by blocking their interaction with Hsp90, leading to proteasomal degradation[1].
Anti-Angiogenic Effects:
- Drugs like sunitinib and sorafenib inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs), reducing tumor blood supply[3].
Clinical Applications
Cancer Treatment:
- CML: Imatinib revolutionized CML management, converting it into a chronic condition with long-term survival[5].
- Solid Tumors: Gefitinib and erlotinib target EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)[2][6].
- Renal Cell Carcinoma: Sunitinib and pazopanib inhibit VEGFR/PDGFR, improving progression-free survival[3][6].
- Non-Cancer Conditions:
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Nintedanib slows disease progression by targeting fibrotic signaling pathways[1].
Key Examples of TKIs
| Drug | Target | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Imatinib | Bcr-Abl, PDGFR, c-KIT | CML, gastrointestinal stromal tumors[1][5] |
| Sunitinib | VEGFR, PDGFR, c-KIT | Renal cell carcinoma, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors[3][6] |
| Erlotinib | EGFR | NSCLC, pancreatic cancer[2][6] |
| Sorafenib | VEGFR, Raf kinase | Hepatocellular carcinoma, thyroid cancer[3][6] |
| Nintedanib | VEGFR, FGFR, PDGFR | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[1] |
Resistance Mechanisms
Mutation-Driven Resistance:
- Secondary mutations (e.g., T790M in EGFR) reduce drug binding affinity[2].
Alternative Pathway Activation:
- Tumors may upregulate parallel signaling (e.g., PI3K/Akt) to bypass inhibition[3].
Pharmacokinetic Issues:
- Poor drug penetration into tumors or increased efflux via transporters[2].
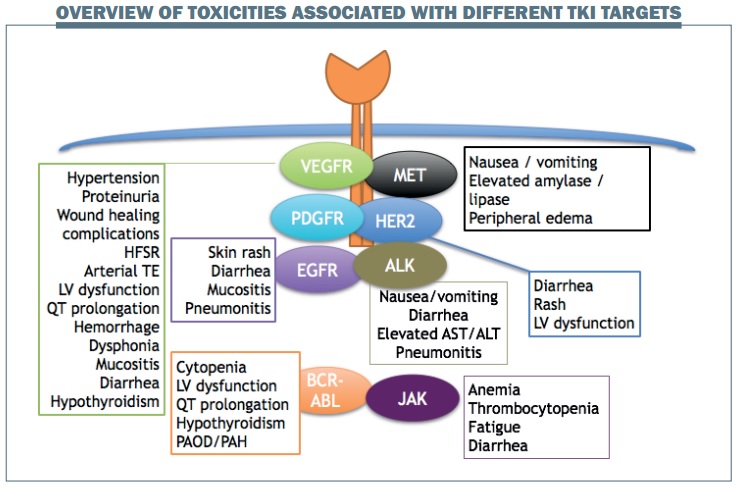
Side Effects
- Common: Fatigue, diarrhea, skin rash, hypertension[5].
- Severe: Cardiotoxicity (sorafenib), Steven-Johnson syndrome (erlotinib), and myelosuppression[5][6].
Conclusion
TKIs represent a cornerstone of targeted cancer therapy, offering significant survival benefits in diseases like CML and NSCLC. Their ability to selectively inhibit dysregulated kinases minimizes harm to healthy cells, though resistance and toxicity remain challenges. Ongoing research aims to develop next-generation TKIs with improved specificity and combinatorial strategies to overcome resistance.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Neuromodulation Programs (NMP) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References:
- DOI: 10.1038/s41571-023-00512-9
Summary: Explores the molecular mechanisms underlying resistance to TKIs, including secondary mutations and tumor microenvironment factors, and discusses strategies to overcome these challenges. - Title: Advances in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Development for Cancer Treatment
DOI: 10.1016/j.cancer.2023.04.003
Summary: Reviews the latest advancements in TKI development, focusing on next-generation inhibitors with improved specificity and reduced side effects. - Title: Multi-Target Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology: Clinical Applications and Future Directions
DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1008321
Summary: Discusses the role of multi-target TKIs in treating complex cancers with multiple signaling pathway dysregulations, emphasizing their therapeutic potential.















