Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA)
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA): Understanding Its Role and Applications
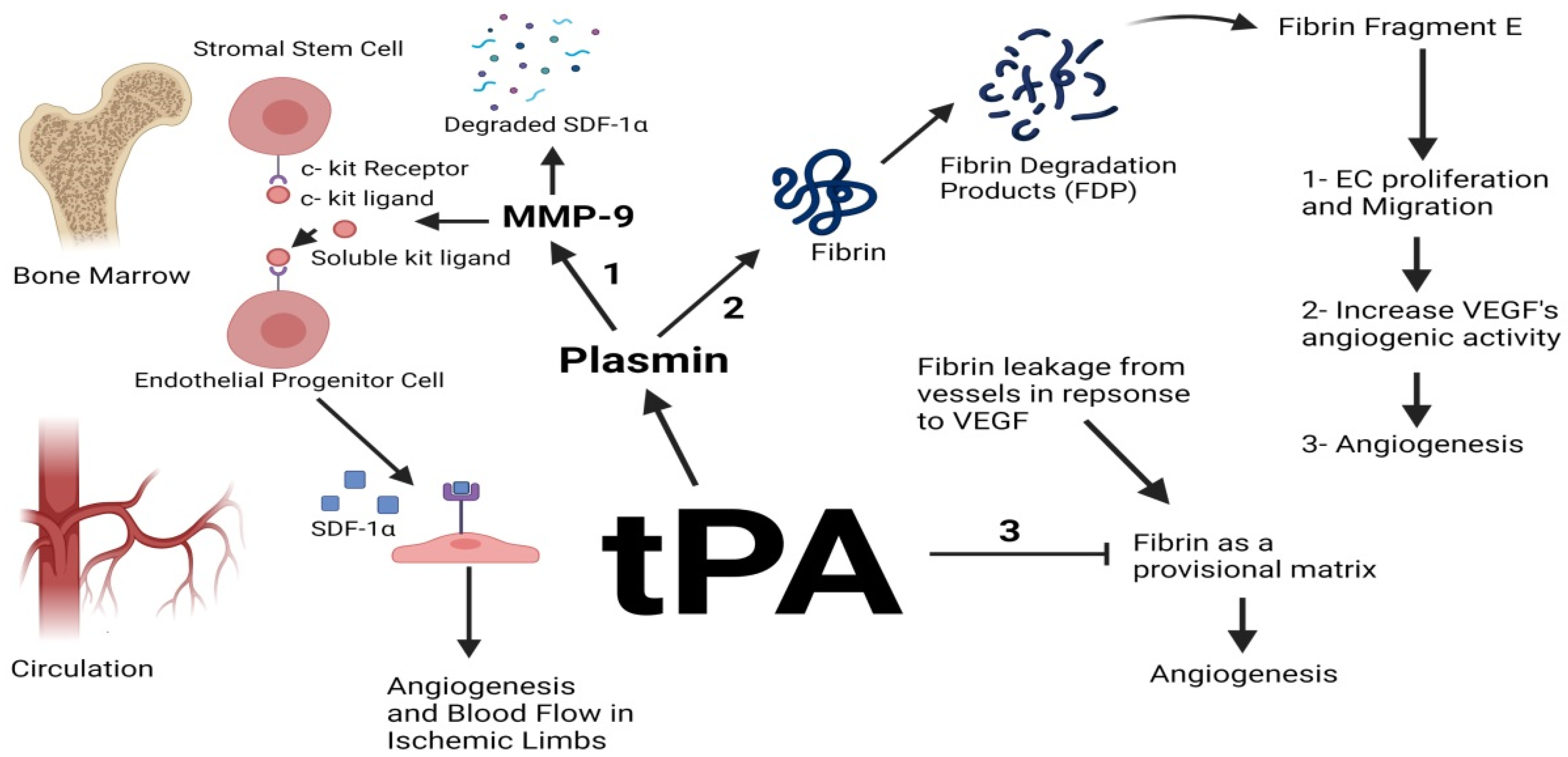
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a serine protease enzyme that plays a crucial role in the breakdown of blood clots by converting plasminogen into plasmin, the primary enzyme responsible for clot dissolution. This process is essential for maintaining vascular health and preventing thrombotic events.
Mechanism of Action
tPA acts by cleaving the Arg561-Val562 peptide bond in plasminogen, converting it into its active form, plasmin. This conversion is highly efficient in the presence of fibrin, as fibrin provides binding sites that enhance the interaction between tPA and plasminogen, facilitating clot breakdown123.
Clinical Applications
- Ischemic Stroke:
tPA is used to treat acute ischemic stroke by dissolving blood clots and restoring blood flow to the brain. It is most effective when administered within a few hours of symptom onset36. - Myocardial Infarction:
tPA is indicated for acute myocardial infarction, particularly when there is a delay in performing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)3. - Pulmonary Embolism:
It is used in cases of massive pulmonary embolism to reduce clot burden and improve hemodynamic stability3. - Deep Vein Thrombosis:
tPA can be used for thrombolysis in deep vein thrombosis, although its use is less common compared to other conditions3.
Recombinant Forms
Recombinant tissue plasminogen activators (rtPA), such as alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase, are manufactured using biotechnology techniques. These drugs have varying pharmacokinetic profiles and are used in different clinical scenarios:
- Alteplase (Activase):
FDA-approved for ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, and pulmonary embolism14. - Reteplase:
Used for acute myocardial infarction, offering faster thrombolysis compared to alteplase1. - Tenecteplase:
Indicated for acute myocardial infarction with fewer bleeding complications1.
Conclusion
tPA is a vital enzyme in the fibrinolytic pathway, and its recombinant forms are critical in managing thrombotic conditions. Understanding its mechanism and clinical applications is essential for effective treatment strategies.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing cardiovascular and brain health. If you have questions about tPA or would like more information on our services related to cardiovascular and brain care, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Wikipedia: Tissue-type Plasminogen Activator
Discusses the role of tPA in fibrinolysis and its recombinant forms. - DiaPharma: Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Highlights tPA’s function in clot breakdown and its structure. - PubMed: Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Explains tPA’s mechanism and clinical indications. - DrugBank: Alteplase
Details the mechanism of action of alteplase, a recombinant tPA. - StatPearls: Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Discusses tPA’s role in thrombolysis. - Bumrungrad: Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Stroke
Highlights tPA’s use in ischemic stroke treatment. - MedLink Neurology: Tissue Plasminogen Activator
Explains tPA’s role in clot breakdown. - Verywell Health: tPA for Stroke
Discusses tPA’s use in stroke management.















