T-cell subsets (TCS)
T-Cell Subsets (TCS): Overview, Types, Functions, and Importance
What are T-Cell Subsets?
T-cells Subsets (TCS) are a diverse group of white blood cells that play central roles in the adaptive immune system. T-cell subsets are specialized types of T-cells distinguished by their surface markers, functions, and cytokine profiles. These subsets work together to identify, target, and eliminate pathogens, regulate immune responses, and maintain immune homeostasis.
Major T-Cell Subsets and Their Functions:
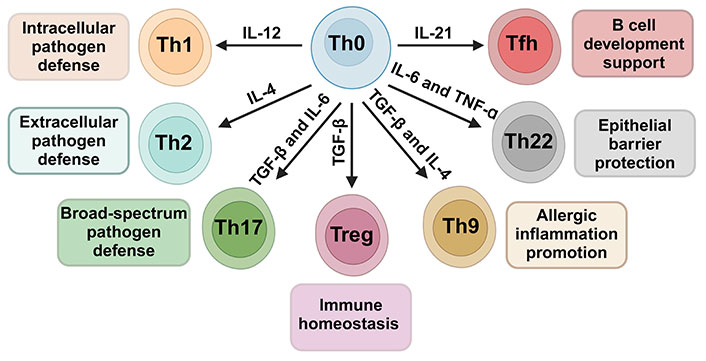
Helper T Cells (CD4+ T Cells)
- These cells facilitate the immune response by recognizing antigens and releasing cytokines that direct other immune cells to fight infections.
- Subtypes include Th1 (promote inflammation and defense against intracellular pathogens), Th2 (activate B cells for antibody production), Th17 (important in defense against extracellular pathogens and inflammation), and T follicular helper cells (support B cell maturation in germinal centers)456.
Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8+ T Cells)
- These cells directly kill infected or cancerous cells by recognizing antigen presented with MHC class I molecules and releasing cytotoxic substances, such as perforin and granzymes7.
Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
- These cells suppress the immune response to prevent overactivation and autoimmune diseases by maintaining immune tolerance and controlling inflammation.
Naïve and Memory T Cells
- Naïve T cells are mature but inexperienced cells that circulate in lymphoid organs waiting to encounter their specific antigen. Upon activation, they proliferate and differentiate into effector or memory T cells.
- Memory T cells provide rapid and enhanced responses upon re-exposure to the same pathogen, supporting long-term immunity123.
Importance of T-Cell Subsets
The balanced function of these T-cell subsets is critical for effective immune defense against infections, tumor surveillance, and prevention of autoimmunity. Dysregulation of T-cell subsets is associated with various diseases including infections, cancers, autoimmune disorders, and inflammatory conditions9.
Clinical Relevance
Understanding T-cell subsets supports the development of targeted immunotherapies, such as CAR-T cell therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, and aids in diagnosing and treating immune-related diseases.
Key Points
- T-cell subsets include helper, cytotoxic, regulatory, naïve, and memory T cells.
- Helper T cells coordinate immune responses via cytokine release.
- Cytotoxic T cells kill infected and abnormal cells.
- Regulatory T cells maintain immune tolerance and prevent autoimmunity.
- Naïve and memory T cells contribute to immune surveillance and long-term immunity.
- Proper T-cell subset balance is essential for immune health and disease prevention.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For detailed evaluation of immune function or immunotherapy options related to T-cell subsets, consult with our specialists for personalized assessment and treatment planning.
References:
- Immunopaedia. Overview of T Cell Subsets. 2018. Available at: https://www.immunopaedia.org.za/immunology/basics/5-overview-of-t-cell-subsets/
- Nature. T cells in health and disease. 2023. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01471-y. Available at: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01471-y
- PMC. Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions. 2016. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC/… (provide full article link if known)















