Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
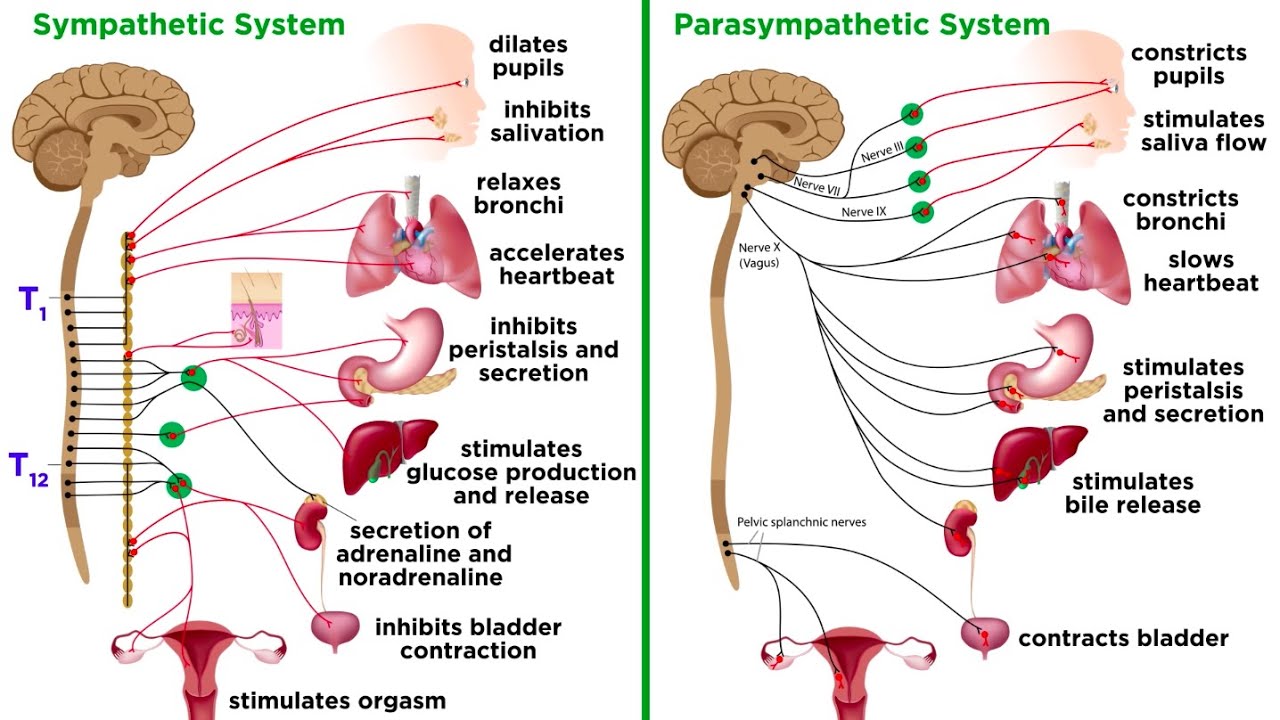
The Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, alongside the parasympathetic and enteric nervous systems. It primarily governs the body’s involuntary “fight or flight” response to stress, preparing the body for rapid action by regulating multiple organ systems135.
Anatomy and Structure
- The SNS originates from the thoracolumbar region of the spinal cord, specifically from the intermediolateral cell columns of spinal segments T1 to L2 or L317.
- It consists of two types of neurons:
- Neurotransmitters:
- Preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine, activating nicotinic receptors on postganglionic neurons.
- Postganglionic neurons mostly release norepinephrine, which acts on adrenergic receptors in target tissues.
- Exceptions include sweat glands (postganglionic neurons release acetylcholine) and the adrenal medulla, where preganglionic neurons stimulate chromaffin cells to release epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream1.
Functions
The SNS regulates many physiological responses, especially under stress:
| Organ/System | Sympathetic Effect |
|---|---|
| Eye | Pupil dilation (mydriasis) to enhance vision |
| Heart | Increased heart rate and force of contraction to boost cardiac output |
| Lungs | Bronchodilation to increase airflow |
| Blood vessels | Vasodilation in skeletal muscles; vasoconstriction in gastrointestinal organs and skin |
| Sweat glands | Activation of sweating (thermoregulation) |
| Digestive tract | Inhibition of peristalsis and digestive secretions |
| Kidneys | Increased renin secretion to regulate blood pressure |
| Reproductive organs | Promotes emission phase of ejaculation; no role in erection |
It maintains homeostasis at baseline but is strongly activated during acute stress, producing the fight-or-flight response characterized by rapid mobilization of energy and cardiovascular adjustments135.
Physiological Role and Clinical Relevance
- The SNS is essential for survival, enabling rapid responses to threats or physical activity.
- It modulates blood glucose levels, body temperature, immune function, and alertness.
- Chronic overactivation (e.g., due to stress) can contribute to hypertension, hyperglycemia, and cardiovascular disease35.
- Dysfunction can lead to disorders such as autonomic neuropathy or dysautonomia.
Summary Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Origin | Thoracolumbar spinal cord (T1-L2/L3) |
| Neuron Types | Preganglionic (short), postganglionic (long) |
| Neurotransmitters | Preganglionic: acetylcholine; Postganglionic: mainly norepinephrine; exceptions include sweat glands (acetylcholine) and adrenal medulla (epinephrine/norepinephrine release) |
| Primary Function | Fight-or-flight response; regulation of cardiovascular, respiratory, metabolic, and other systems |
| Effects | Pupil dilation, increased heart rate, bronchodilation, vasoconstriction/vasodilation, sweating, decreased digestion |
| Clinical Importance | Stress response, blood pressure regulation, metabolic control, implicated in hypertension and metabolic diseases |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Sympathetic Nervous System or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Sympathetic nervous system – Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sympathetic_nervous_system - Neuroanatomy, Sympathetic Nervous System – StatPearls – NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542195/ - Sympathetic nervous system | Britannica
https://www.britannica.com/science/sympathetic-nervous-system - Sympathetic Nervous System: What to Know – WebMD
https://www.webmd.com/brain/sympathetic-nervous-system-what-to-know - Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System – StatPearls – NCBI
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539845/ - Sympathetic nervous system: Definition, anatomy, function – Kenhub
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/sympathetic-nervous-system
The sympathetic nervous system is a crucial autonomic division orchestrating the body’s immediate and sustained responses to stress, regulating cardiovascular, respiratory, metabolic, and other vital functions to maintain homeostasis and ensure survival.















