Small Vessel Disease (SVD)
Small Vessel Disease (SVD)
Small vessel disease (SVD) refers to pathological processes affecting the small arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and venules, leading to impaired blood flow and tissue damage. It is a systemic condition impacting organs with rich microvascular networks, especially the brain, heart, kidneys, and retina.
Types and Affected Organs
- Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (CSVD):
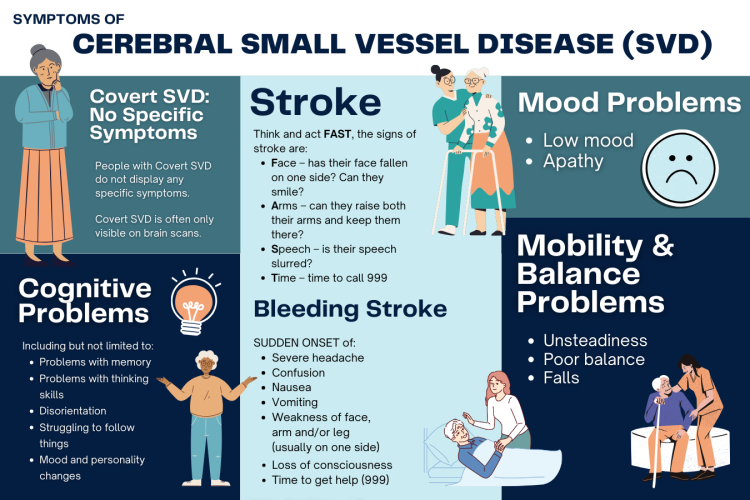
Affects small vessels in the brain, causing white matter lesions, lacunar infarcts, microbleeds, and brain atrophy. It is a major contributor to stroke, cognitive impairment, gait disturbances, depression, and vascular dementia. - Coronary Microvascular Disease:
Involves dysfunction of small coronary arteries, leading to reduced oxygen delivery to the heart muscle, causing angina and ischemia despite normal large coronary arteries. - Renal and Retinal SVD:
Contributes to kidney failure and vision loss, respectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Traditional vascular risk factors:
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Other contributors:
- Aging
- Estrogen deficiency (especially in women)
- Insulin resistance
- Poor sleep patterns
- Depression (recognized as a vascular risk factor)
- Pathophysiology involves endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, lipohyalinosis, and arteriolosclerosis, leading to vessel wall thickening, lumen narrowing, and impaired vasomotor regulation.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
- Heart: Chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, dizziness, and symptoms mimicking heart attack.
- Brain: Cognitive decline, stroke symptoms, gait disturbances, mood disorders, and dementia.
- Kidneys and Retina: Progressive organ dysfunction leading to renal failure and vision impairment.
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation based on symptoms and risk factors.
- Imaging modalities:
- Brain MRI for cerebral SVD (detects white matter hyperintensities, lacunes, microbleeds).
- Cardiac MRI, CT angiography, PET scans for coronary microvascular disease.
- Functional tests such as exercise stress tests and electrocardiograms (EKG) for cardiac involvement.
- Laboratory tests to evaluate vascular risk factors.
Management
- No specific cure; treatment focuses on controlling vascular risk factors to slow progression.
- Lifestyle modifications: smoking cessation, exercise, weight control, healthy diet.
- Pharmacologic therapy: antihypertensives, statins, antiplatelet agents, diabetes management.
- Addressing inflammation and other emerging targets is under investigation.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Pathologic processes damaging small arteries, arterioles, capillaries, and venules |
| Affected Organs | Brain (cerebral SVD), heart (coronary microvascular disease), kidneys, retina |
| Causes/Risk Factors | Hypertension, diabetes, aging, smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, estrogen deficiency, depression |
| Symptoms | Angina, chest pain, cognitive impairment, stroke, gait disturbance, renal failure, vision loss |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT, PET, EKG, clinical assessment, lab tests |
| Treatment | Risk factor control, lifestyle changes, medications (antihypertensives, statins), symptom management |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Small Vessel Disease (SVD) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
Reference with DOI
Wardlaw JM, Smith C, Dichgans M. Small vessel disease: mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019 Jul;18(7):684-696.
DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30079-1
Small vessel disease is a systemic microvascular disorder with significant impact on multiple organs, especially the brain and heart. Early identification and management of vascular risk factors are crucial to mitigate its debilitating consequences.















