Scurvy (ScV)
Scurvy (ScV): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Scurvy (ScV) is a condition caused by a severe deficiency of vitamin C (ascorbic acid), an essential nutrient for collagen synthesis, iron absorption, wound healing, and immune function. Though rare in developed countries, it can still occur in individuals with poor dietary habits or limited access to fresh fruits and vegetables.
Causes of Scurvy
Scurvy results from prolonged insufficient intake of vitamin C. Risk factors include:
- Diets lacking fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Eating disorders or restrictive diets.
- Alcohol or drug abuse.
- Smoking, which reduces vitamin C absorption.
- Medical conditions like malabsorption syndromes (e.g., Crohn’s disease).
- Increased vitamin C needs during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
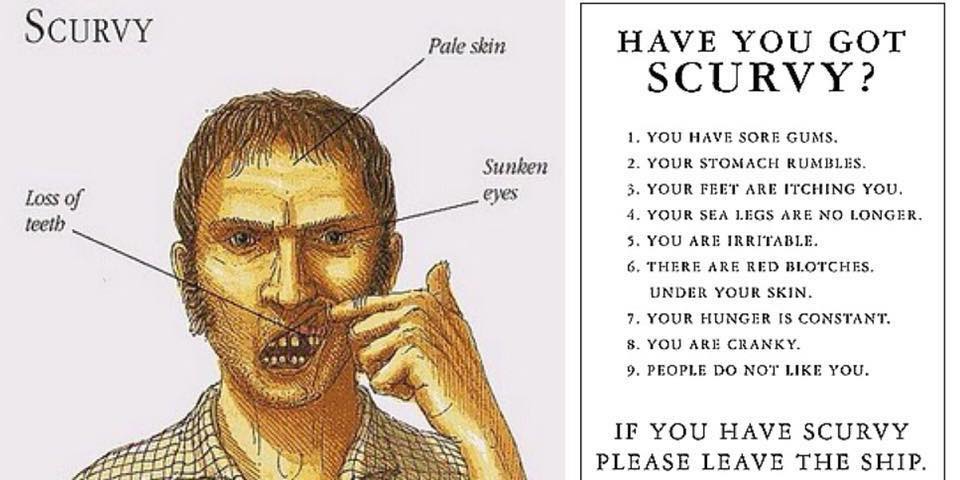
Symptoms of Scurvy
Symptoms typically appear after 1–3 months of severe vitamin C deficiency and include:
- Early Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Irritability and malaise.
- Advanced Symptoms:
- Swollen, bleeding gums and tooth loss.
- Bruising and petechiae (small red or purple spots).
- Joint pain and swelling.
- Poor wound healing and skin breakdown.
- Anemia due to impaired iron absorption.
- Severe Cases:
- Internal bleeding.
- Neurological symptoms like confusion.
- Potentially life-threatening complications if untreated.
Diagnosis
Scurvy is diagnosed based on:
- Clinical History: Dietary habits and symptoms.
- Physical Examination: Signs like Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease), bruising, and fatigue.
- Blood Tests: Low vitamin C levels or anemia.
Treatment
Treatment is simple and highly effective:
- Vitamin C Supplementation:
- Oral vitamin C (100–500 mg daily) leads to rapid improvement within days.
- Severe cases may require intravenous vitamin C.
- Dietary Changes:
- Incorporating vitamin C-rich foods like citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwis, bell peppers, broccoli, tomatoes, and leafy greens.
Most people recover fully within 1–2 weeks of treatment.
Prevention
Preventing scurvy involves maintaining a diet rich in vitamin C. Recommended daily intake varies by age and condition:
- Adults: 75–90 mg/day.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Higher requirements.
Conclusion
Though rare today, scurvy remains a preventable condition with proper nutrition. Early recognition and treatment are crucial to avoid serious complications.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Scurvy or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















