Sagging (Sg)
Sagging (Sg): Causes, Characteristics, and Treatments
What is Sagging (Sg)?
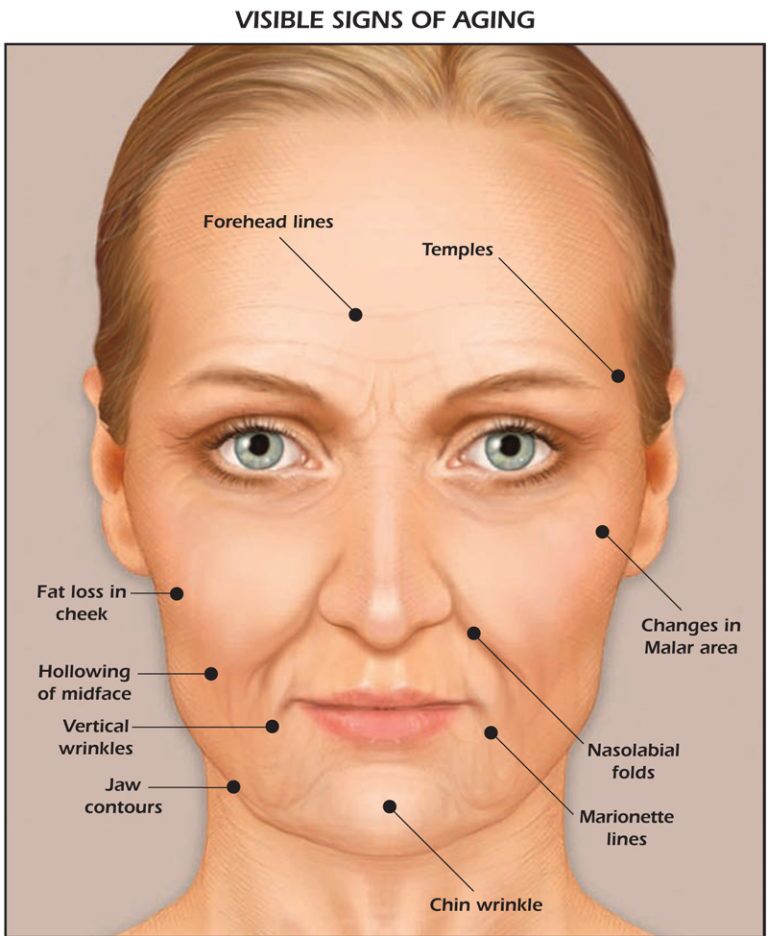
Sagging (Sg) refers to the loosening or drooping of the skin and underlying tissues commonly seen with aging. It results in a loss of firmness and elasticity, causing areas like the cheeks, jawline, neck, and eyelids to appear loose or droopy. Sagging skin contributes significantly to an aged or tired facial appearance.
Causes of Sagging
- Natural aging: Decreased production of collagen and elastin fibers in the skin reduces structural support.
- Volume loss: Reduction in facial fat and bone density results in diminished underlying support.
- Gravity: Continuous downward pull exacerbates tissue descent.
- Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation damages skin proteins leading to premature loss of elasticity.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, poor diet, dehydration, and repetitive facial movements accelerate sagging.
- Weight fluctuations: Rapid weight loss can stretch skin beyond its ability to snap back.
- Genetics: Some people are predisposed to sagging earlier or more prominently.
Symptoms of Sagging
- Hollowing and loss of plumpness in cheeks and temples
- Deepening of facial lines like nasolabial folds and marionette lines
- Appearance of jowls along the jawline
- Loose skin on the neck and under the eyes
Treatment Options for Sagging
Non-invasive and Minimally Invasive
- Dermal fillers: Restore lost volume to lift sagging areas and smooth folds.
- Facial peels and microneedling: Stimulate collagen production for firmer skin.
- Radiofrequency and ultrasound therapies: Deliver heat energy to deeper skin layers to tighten tissues and increase collagen.
Surgical
- Facelift and neck lift surgeries: Remove excess skin and tighten underlying muscles for dramatic and long-lasting rejuvenation.
- Body contouring surgery: For sagging skin after significant weight loss (e.g., tummy tuck, arm lifts).
At-Home Care
- Facial exercises may modestly improve skin firmness.
- Use of topical retinoids and antioxidants to promote collagen.
- Sun protection and hydration to prevent further damage.
Key Points
- Sagging is caused by aging, volume loss, gravity, sun damage, and lifestyle factors.
- It results in loose skin and deep folds that affect facial contours.
- Treatments range from skincare and non-invasive procedures to surgery.
- Early intervention and tailored treatment plans improve effectiveness.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For personalized management of sagging skin, consult our dermatologists and plastic surgeons who provide a full spectrum of treatments, from non-invasive to surgical, customized to your needs.
References:
Quan T, Fisher GJ. Molecular Mechanisms of Dermal Aging and Antiaging Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 9;20(9):2126. doi:10.3390/ijms20092126. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6540032/















