Sacroiliac (SI) Joints
Sacroiliac (SI) Joints: Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Significance
What are the Sacroiliac Joints?
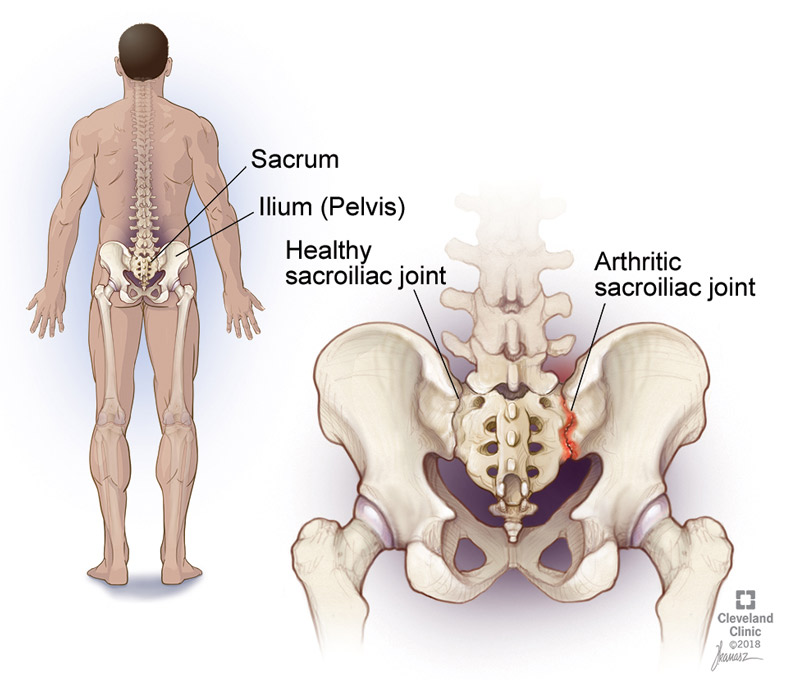
The sacroiliac (SI) joints are paired synovial joints that connect the sacrum—the triangular bone at the base of the spine—to the ilium bones of the pelvis. Positioned deep in the pelvis on either side of the lower spine, these joints play a vital role in transmitting forces between the upper body and the lower limbs.
Anatomy
Each sacroiliac joint has a complex structure:
- Articular Surfaces: The joint surfaces form a C-shaped connection where the convex ilium meets the concave sacrum. The surfaces are covered with thick hyaline cartilage on the ilium side and fibrocartilage on the sacral side, adapted to withstand the stresses and compression that occur in this region.
- Ligaments: The joints are stabilized by strong ligaments, including the anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments, sacrotuberous ligament, and sacrospinous ligament, which help maintain stability while allowing slight movement.
- Innervation and Blood Supply: The SI joints receive nerve innervation primarily from the S1-S3 spinal nerves and are supplied by branches of the iliolumbar and superior gluteal arteries.
Function
The sacroiliac joints serve several essential biomechanical and physiological functions:
- Force Transmission: They transfer weight and forces from the upper body to the hips and legs during standing, walking, and other activities.
- Shock Absorption: The SI joints help absorb and distribute forces generated by movements and impacts, protecting the lower spine and pelvis.
- Mobility and Stability: While their movements are limited, they allow slight gliding and rotational motions, accommodating changes in posture and supporting activities like walking, sitting, and childbirth in women. A unique “self-locking” mechanism enhances stability when weight is transferred from one leg to the other during gait.
Clinical Significance
Dysfunction or inflammation of the SI joints (sacroiliitis) can cause lower back, pelvic, or leg pain, often mimicking other spine or hip pathologies. SI joint pain diagnosis involves clinical examination, imaging, and sometimes diagnostic injections. Treatment includes physical therapy, medications, and interventional procedures for pain relief.
Key Points
- The sacroiliac joints connect the sacrum to the pelvis and support weight transfer.
- They combine stability with limited mobility through strong ligaments and cartilage surfaces.
- Functions include shock absorption, facilitating posture changes, and aiding locomotion.
- SI joint dysfunction can lead to pain necessitating specialized evaluation and care.
- Proper joint function is essential for mobility, load distribution, and pelvic health.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For evaluation and treatment of sacroiliac joint disorders or pelvic and lower back pain, consult with our multidisciplinary team offering comprehensive diagnostic and therapeutic services using Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells.
References:
Vleeming A, Schuenke MD, Masi AT, Carreiro JE, Danneels L, Willard FH. The sacroiliac joint: an overview of its anatomy, function, and potential clinical implications. J Anat. 2012 Sep;221(6):537-67. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01564.x. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2012.01564.x















