Root Causes of Chronic Diseases
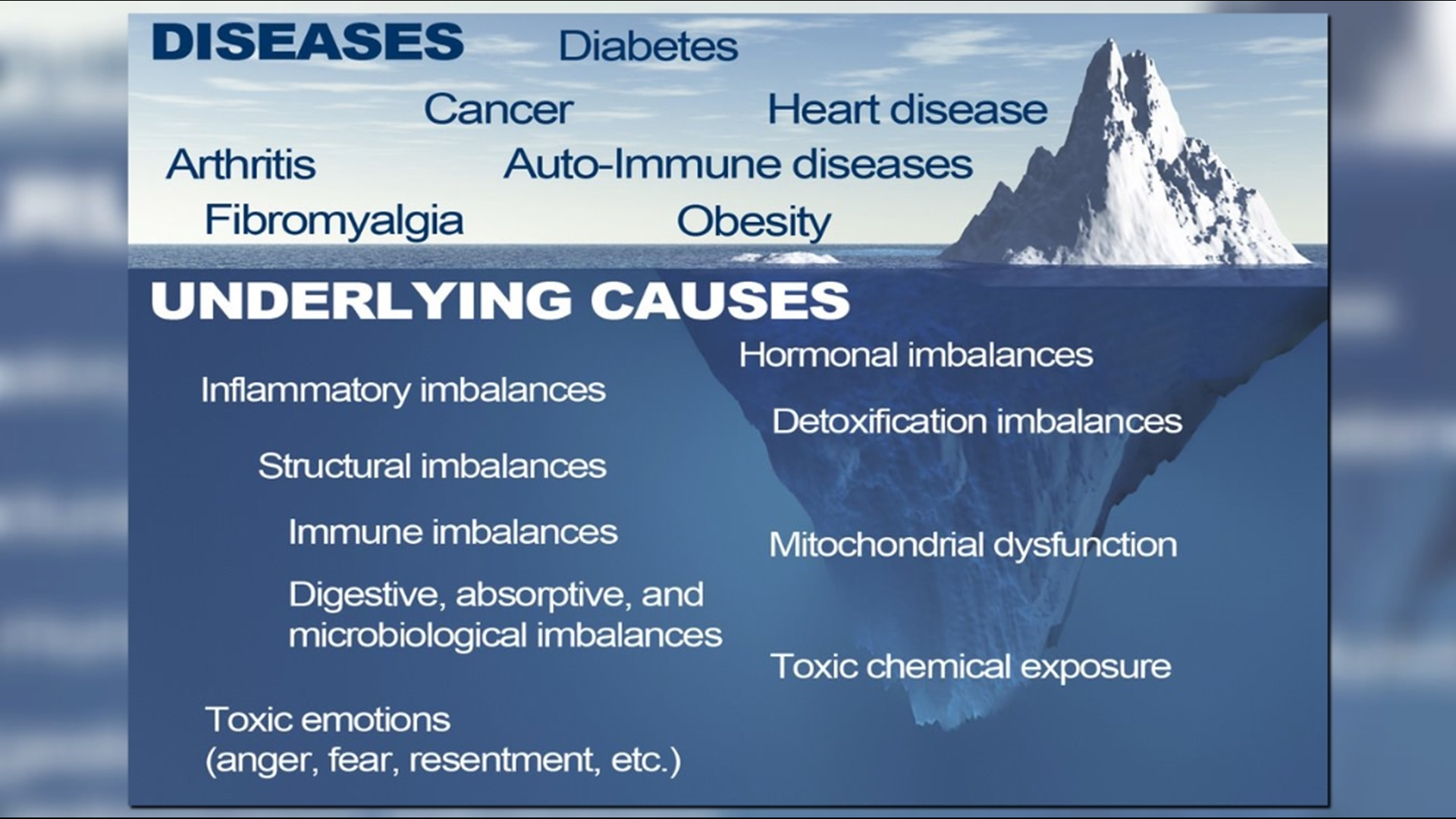
Root Causes of Chronic Diseases are the fundamental dysfunctions or risk factors that lead to the onset and progression of long-lasting health conditions. Addressing these root causes involves identifying why a specific individual develops a particular illness and targeting the underlying issues rather than merely managing symptoms
Root Causes of Chronic Diseases: A Comprehensive Overview
Chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and chronic respiratory diseases, significantly impact global health and quality of life[4][6]. While managing symptoms is essential, identifying and addressing the root causes of these conditions can lead to more effective treatments and prevention strategies[4]. Chronic diseases often result from a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental, and behavioral factors[1].
Key Categories of Root Causes of Chronic Diseases
- Behavioral Risk Factors:
- Poor Diet: Unhealthy eating habits are major contributors to chronic diseases[5].
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity increases the risk of various chronic conditions[5][2].
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is associated with numerous chronic diseases, including cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory illnesses[3][2].
- Heavy Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol use can lead to liver disease, cardiovascular problems, and other chronic conditions[5][2].
- Intermediate Risk Factors:
- Raised Blood Pressure (Hypertension): High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke[2].
- Elevated Blood Lipids: High cholesterol levels contribute to cardiovascular diseases[2].
- Overweight/Obesity: Excess weight increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers[2].
- Pre-diabetes: Elevated blood glucose levels that are not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes can lead to type 2 diabetes[2].
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:
- Age: The risk of many chronic diseases increases with age[1][2].
- Sex: Some diseases are more prevalent in one sex than the other[1][2].
- Genetics: Family history and genetic predispositions can increase the risk of certain chronic conditions[1][4].
- Social Determinants:
- Socioeconomic Factors: Conditions such as poverty, employment status, and family composition can impact health[2].
- Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions like climate and air pollution play a role in disease development[2].
- Cultural Factors: Practices, norms, and values within a community can influence health behaviors and outcomes[2].
- Access to Resources: Limited access to resources such as money, education, status, power, and social connections can negatively impact health[3].
- Infectious Etiologies:
- Infections: Certain chronic diseases have links to infectious agents[8].
- The importance of Root Cause Analysis:
- A functional medicine approach considers diet, lifestyle, gut health, and stress levels to uncover the root causes of chronic diseases[4].
- Advanced diagnostic tests, such as genetic testing, hormonal assays, and microbiome analysis, can help identify specific factors contributing to chronic diseases[4].
Finding the Root Cause
- Comprehensive Medical History: A thorough review of medical history helps identify potential genetic and environmental factors[4].
- Functional Medicine Approach: This approach views the body as a whole system, considering various factors to uncover root causes[4].
- Advanced Testing: Genetic testing, hormonal assays, and microbiome analysis can pinpoint specific contributors to chronic diseases[4].
- Lifestyle Modifications: Identifying and modifying lifestyle factors such as diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management is crucial[4].
- Osteopathic Medicine: Focuses on improving how all systems within the body function as a whole through manipulative techniques and treatments[5]. Can provide additional benefits to health when used together with traditional medicine[5].
DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand‘s Approach
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we recognize the importance of identifying and addressing the root causes of chronic diseases. Our approach includes:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: A thorough review of medical history, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
- Advanced Diagnostic Testing: Utilizing state-of-the-art testing to identify underlying imbalances and contributing factors.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring treatment strategies to address the specific root causes identified in each patient.
- Holistic Approach: Integrating lifestyle modifications, nutritional support, and regenerative therapies to promote overall health and well-being.
By focusing on the Root Causes of Chronic Diseases, we aim to provide our patients with more effective, long-lasting solutions that improve their quality of life.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
[1] Chronic Diseases | Chester County, PA – Official Website. https://www.chesco.org/357/Chronic-Diseases
[2] Chronic Disease Risk Factors – Canada.ca. (2008, July 10). https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/chronic-diseases/chronic-disease-risk-factors.html
[3] The Social Determinants of Chronic Disease – PMC. (2016, August 16). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5328595/
[4] The Importance of Finding the Root Cause of Your Chronic Disease. (2024, November 13). Rapid City Healthcare. https://rapidcitycare.com/the-importance-of-finding-the-root-cause-of-your-chronic-disease/
[5] Causes of Chronic Disease – Fontaine Center. Fontaine Center. https://www.fontainecenter.com/blog/440795-causes-of-chronic-disease
[6] Chronic Diseases and Conditions. NYS Department of Health. https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/chronic/
[7] Chronic Disease – Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Chronic_Disease
[8] OVERVIEW – The Infectious Etiology of Chronic Diseases – NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83680/















