Pulmonary Hemorrhage (PH)
Pulmonary Hemorrhage (PH): Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Management
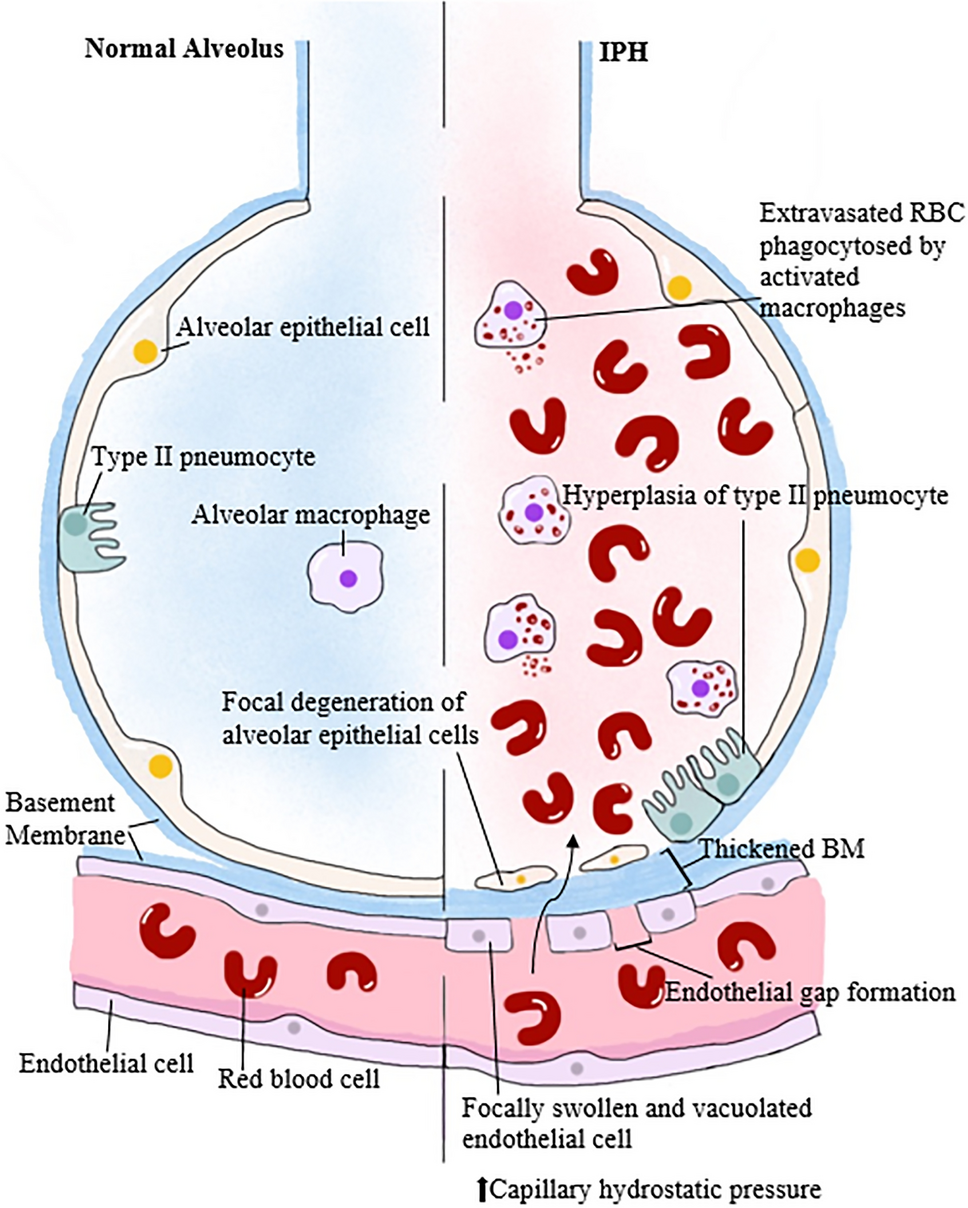
Pulmonary hemorrhage (PH) refers to acute bleeding from the lungs or respiratory tract, ranging from mild hemoptysis to life-threatening alveolar hemorrhage. It can occur in neonates, children, and adults, often requiring urgent intervention to prevent respiratory failure.
Causes
Pulmonary hemorrhage arises from diverse etiologies:
- Neonates:
- Adults:
- Autoimmune: Vasculitis (e.g., ANCA-associated), Goodpasture syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus24.
- Cardiac: Mitral stenosis, pulmonary veno-occlusive disease4.
- Coagulation Disorders: Thrombocytopenia, anticoagulant use4.
- Infections: Tuberculosis, hantavirus, fungal pneumonia14.
- Toxic/Drug-Induced: Cocaine, pesticides, amiodarone, nitrofurantoin4.
- Procedural: ECMO, cardiopulmonary bypass, pulmonary endarterectomy3.
Symptoms
- Common: Hemoptysis (coughing blood), dyspnea, hypoxemia, cyanosis14.
- Neonates: Acute respiratory deterioration, bloody endotracheal secretions, anemia5.
- Atypical: Up to 30% of patients lack hemoptysis, presenting with anemia or respiratory failure4.
Diagnosis
- Imaging:
- Laboratory Tests:
- Anemia, elevated D-dimer, coagulation studies, autoimmune markers (ANCA, anti-GBM)4.
- Bronchoscopy:
- Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) showing hemosiderin-laden macrophages confirms DAH4.
- Biopsy:
- Histopathology distinguishes capillaritis (immune-mediated) from bland hemorrhage2.
Treatment
Immediate Stabilization:
- Airway Management: Endotracheal suction, mechanical ventilation with PEEP, bronchial blockers for localized bleeding13.
- Supportive Care: Oxygen, blood transfusions, coagulopathy reversal14.
Targeted Therapies:
- Autoimmune Causes:
- High-dose corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, rituximab, or plasma exchange4.
- Severe Bleeding:
Neonatal Management:
- Surfactant therapy, sepsis treatment, PDA closure, and ventilator strategies5.
Prognosis
- Neonates: Mortality rates reach 50–68%, often due to prematurity complications5.
- Adults: Mortality depends on etiology; autoimmune DAH has better outcomes with immunosuppression4.
- Complications: Respiratory failure, pulmonary fibrosis, chronic lung disease24.
Conclusion
Pulmonary hemorrhage demands rapid diagnosis and tailored interventions to address underlying causes. Early use of immunosuppressants for autoimmune cases and advanced respiratory support (e.g., ECMO) can improve survival.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we provide advanced diagnostics and multidisciplinary care for complex pulmonary conditions. For personalized management of pulmonary hemorrhage, consult our specialists today for Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells!















