Pineal Gland
The pineal gland is a small, pinecone-shaped endocrine gland located deep in the center of the brain, between the two cerebral hemispheres, attached to the posterior wall of the third ventricle near the superior colliculi of the midbrain367. It measures approximately 5–8 mm in humans and weighs about 100–150 mg356.
Structure and Cells
- The gland is composed mainly of pinealocytes, which are the hormone-secreting cells, and glial cells that provide support35.
- It is highly vascularized and lacks a typical blood-brain barrier, receiving rich blood supply primarily from branches of the posterior cerebral artery6.
- With age, the pineal gland often undergoes calcification, visible on radiographs and CT scans as “brain sand” or acervuli356.
Function
- The primary function of the pineal gland is the synthesis and secretion of melatonin, a hormone derived from serotonin that regulates the body’s circadian rhythm—the sleep-wake cycle12345678.
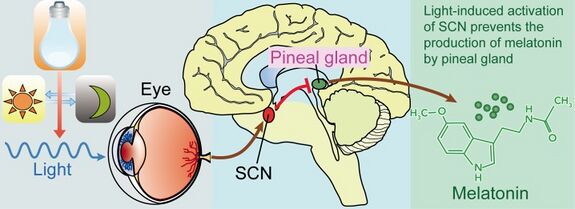
- Melatonin secretion is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light, with levels rising at night to promote sleep and falling during daylight12367.
- The gland acts as a neuroendocrine transducer, converting photic information received from the retina (via the suprachiasmatic nucleus and sympathetic pathways) into hormonal signals568.
- Melatonin also influences reproductive hormones by inhibiting secretion of gonadotropins (FSH and LH) from the anterior pituitary, thus affecting reproductive function26.
- Additional roles of melatonin include modulation of cardiovascular health, bone metabolism, immune function, and possibly neuroprotection267.
Regulation
- Light detected by retinal photoreceptors signals the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the body’s master circadian clock, which then modulates sympathetic input to the pineal gland via the superior cervical ganglia6.
- This neural pathway regulates melatonin synthesis through norepinephrine release acting on pinealocytes568.
Clinical Significance
- Dysfunction or tumors of the pineal gland can disrupt circadian rhythms, leading to sleep disorders.
- Calcification of the pineal gland increases with age and is generally considered physiological but may be associated with certain neurological conditions35.
- Melatonin supplements are widely used to treat sleep disorders, jet lag, and circadian rhythm disruptions.
Summary Table
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Midline brain, posterior to third ventricle, between cerebral hemispheres |
| Size | ~5–8 mm length, 100–150 mg weight |
| Cell Types | Pinealocytes (hormone-secreting), glial cells |
| Main Hormone | Melatonin (regulates circadian rhythm and reproductive hormones) |
| Blood Supply | Choroidal branches of posterior cerebral artery |
| Regulation | Light-dark cycle via retinal input → SCN → sympathetic nervous system → pineal gland |
| Functions | Sleep-wake cycle regulation, reproductive hormone modulation, cardiovascular and bone health |
| Clinical Notes | Calcification common with age; melatonin used therapeutically for sleep disorders |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Pineal Gland or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- A comprehensive review of the pineal gland’s structure, vascularization, cellular composition, calcification, and its central role in melatonin-mediated circadian rhythm regulation is provided in “The morphological and functional characteristics of the pineal gland” (DOI: 10.1016/j.aanat.2019.151421).
The pineal gland plays a central role in synchronizing the body’s internal clock to the external light-dark environment through melatonin secretion, influencing sleep, reproduction, and other physiological processes.















