Phantom Limb Pain (PLP)
Phantom Limb Pain (PLP)
Phantom Limb Pain (PLP) is the perception of pain in a limb or part of a limb that has been amputated or is no longer physically present. Despite the absence of the limb, the pain felt is real and can range from mild to severe, lasting seconds to years.
Causes and Mechanisms
PLP is complex and involves multiple overlapping mechanisms:
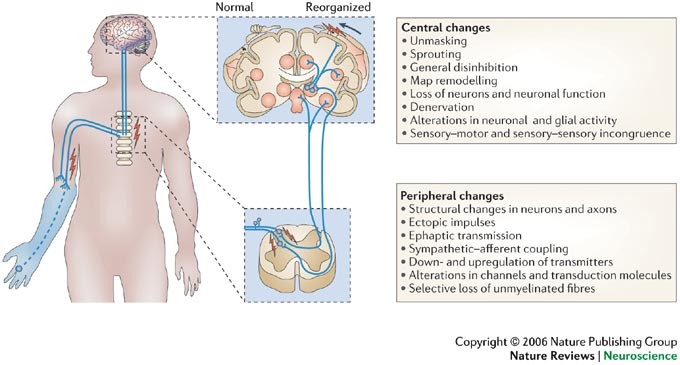
- Peripheral Mechanisms:
After amputation, nerve endings in the residual limb can form neuromas-abnormal nerve growths that generate spontaneous and abnormal nerve signals perceived as pain. - Central Nervous System Changes:
Brain imaging shows activity in the somatosensory and motor cortex areas corresponding to the missing limb, indicating cortical reorganization. Neighboring brain regions may take over the area previously representing the amputated limb, leading to altered sensory processing and pain.
Central sensitization in the spinal cord also increases neural excitability and pain perception. - Maladaptive Neuroplasticity:
The brain and spinal cord adapt to the loss of sensory input by rewiring, which may cause persistent pain signals despite no peripheral input. - Psychological Factors:
Anxiety, depression, and stress can exacerbate PLP, contributing to chronic pain syndromes.
Symptoms
- Pain sensations described as burning, shooting, stabbing, cramping, squeezing, tingling, or pins and needles.
- Sensations often localize to the distal parts of the limb (e.g., fingers, toes).
- Pain can be intermittent or continuous, triggered by pressure on the residual limb, temperature changes, or emotional stress.
- Phantom sensations (non-painful awareness of the missing limb) may coexist with PLP.
Epidemiology
- PLP affects approximately 60% to 85% of amputees.
- More common following upper limb amputations than lower limbs.
- Can begin immediately after amputation or years later.
- Risk factors include vascular disease, trauma, cancer-related amputations, and pre-existing chronic pain or psychological conditions.
Diagnosis
- Primarily clinical, based on patient history and description of pain in the absent limb.
- Important to differentiate PLP from residual limb pain (pain in the remaining part of the limb).
- Physical exam includes inspection for wounds or infection, sensory testing, and evaluation of the joint above the amputation site.
- Imaging (MRI, PET) may support diagnosis by showing cortical changes.
Treatment
- Multimodal approach including medications (antidepressants, anticonvulsants, opioids), nerve blocks, mirror therapy, physical therapy, and psychological support.
- Addressing psychological factors improves outcomes.
- Novel treatments target central sensitization and cortical reorganization.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Pain perceived in an amputated or missing limb |
| Mechanisms | Peripheral neuromas, central cortical reorganization, spinal sensitization, psychological factors |
| Symptoms | Burning, shooting, cramping, tingling, intermittent or continuous pain |
| Prevalence | 60–85% of amputees; more common in upper limb amputations |
| Diagnosis | Clinical history, exam, differentiate from residual limb pain |
| Treatment | Medications, physical and mirror therapy, nerve blocks, psychological interventions |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Phantom Limb Pain (PLP) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Cleveland Clinic. Phantom Limb Pain: What It Is, Causes, Treatment & Prevention.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12092-phantom-limb-pain - StatPearls. Phantom Limb Pain. 2023.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448188/ - WebMD. Phantom Limb Pain After Amputation: Causes & Treatments. 2024.
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/phantom-limb-pain - Healthline. Phantom Pain Symptoms, Causes, Medications, and Treatments.
https://www.healthline.com/health/phantom-pain - Wikipedia. Phantom pain. 2025.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phantom_pain - Physiopedia. Phantom Limb Pain.
https://www.physio-pedia.com/Phantom_Limb_Pain
Phantom limb pain is a real and complex pain syndrome arising from both peripheral nerve changes and central nervous system reorganization after limb loss. Effective management requires a comprehensive approach addressing both physical and psychological components.















