Peptic Ulcers(PU)
Peptic Ulcers(PU): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
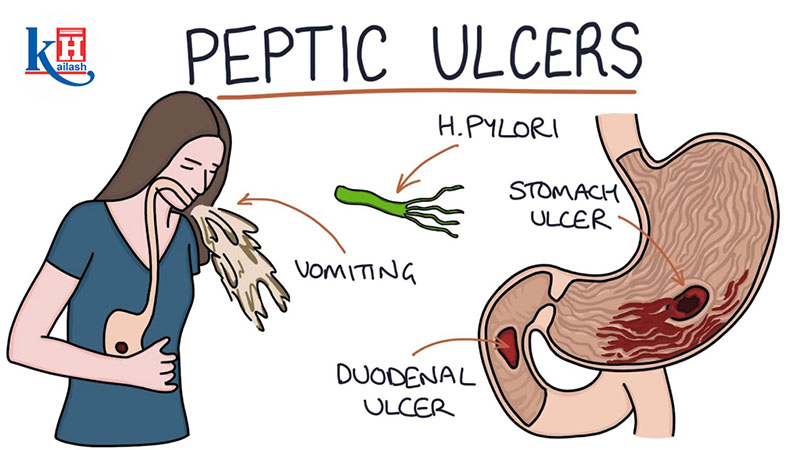
Peptic Ulcers(PU) are open sores in the stomach lining (gastric ulcers) or duodenum (duodenal ulcers), caused by impaired mucosal defenses against digestive acids. Below is a synthesis of their key aspects, supported by clinical guidelines and research.
Causes
- Primary Causes:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs):
- Secondary Causes:
Symptoms
| Common Symptoms | Severe/Complications |
|---|---|
| Burning or gnawing upper abdominal pain | Bleeding: Vomiting blood (red/black) or black/tarry stools14. |
| Pain worsens between meals (duodenal) or after eating (gastric)34 | Perforation: Sudden, severe pain radiating to the back35. |
| Nausea, bloating, or early satiety | Obstruction: Vomiting, weight loss, or abdominal distension5. |
| Heartburn or belching | Anemia: Fatigue, dizziness (chronic blood loss)14. |
Asymptomatic cases: ~33% of older adults3.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- First-Line Therapy:
- NSAID-Induced Ulcers:
- Complications:
Prevention
- Avoid NSAIDs: Use alternatives (e.g., acetaminophen) for pain relief5.
- H. pylori screening: For high-risk populations (e.g., family history of stomach cancer)14.
- Hygiene: Reduce H. pylori transmission via clean food/water3.
Prognosis
- With treatment: Most ulcers heal within 4–8 weeks; recurrence is common if H. pylori persists15.
- Untreated: Risk of bleeding, perforation, or gastric cancer (especially H. pylori-associated)35.
Conclusion
Peptic ulcers are treatable but require addressing underlying causes like H. pylori or NSAID use. Early diagnosis via endoscopy and targeted therapies improve outcomes and reduce complications.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Peptic Ulcers(PU) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References















