Osteomyelitis (OM)
Osteomyelitis (OM)
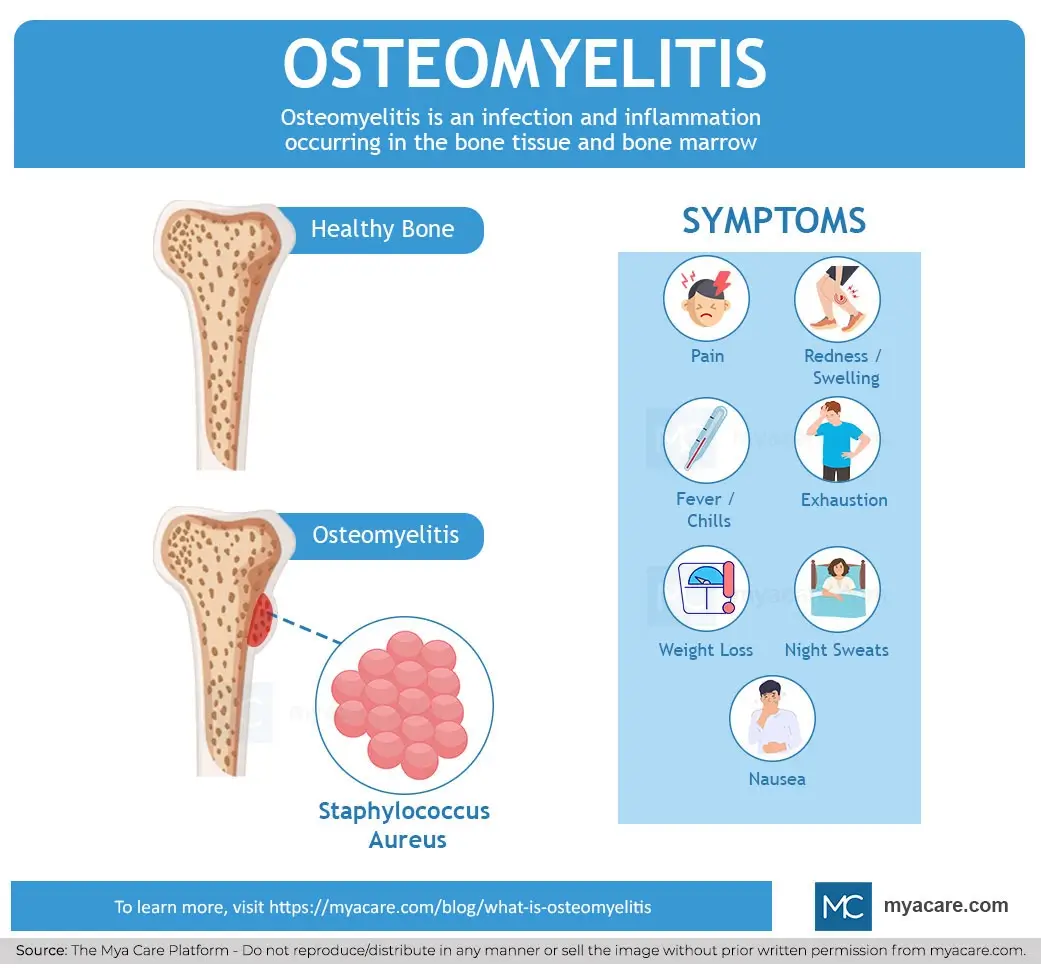
Osteomyelitis (OM) is a serious infection of the bone and bone marrow that can be acute or chronic. It involves inflammation caused by microbial invasion, most commonly bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. The infection can arise hematogenously, from contiguous spread, or by direct inoculation during trauma or surgery. Osteomyelitis is challenging to treat due to the formation of bacterial biofilms and the poor penetration of antibiotics into bone tissue.
Pathophysiology
- Bacteria invade bone tissue, often forming biofilms that protect them from immune responses and antibiotics.
- Infection leads to inflammation, bone necrosis, and sequestrum formation (dead bone).
- Chronic infection may cause involucrum (new bone formation) and sinus tract development.
- Host immune response and bacterial virulence factors determine disease progression.
Clinical Presentation
- Localized bone pain and tenderness
- Swelling, redness, and warmth over the affected area
- Fever and systemic signs in acute cases
- Chronic osteomyelitis may present with draining sinuses and intermittent pain
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation and history (including recent infections, trauma, surgery)
- Imaging: X-rays (may lag behind clinical signs), MRI (gold standard for early detection), CT, bone scans
- Laboratory tests: elevated inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP), blood cultures
- Bone biopsy and culture remain the definitive diagnostic method
Treatment
- Prolonged antibiotic therapy, often guided by culture and sensitivity
- Surgical debridement to remove necrotic bone and infected tissue
- Novel therapies targeting biofilms and local antibiotic delivery systems are under investigation
- Supportive care includes pain management and addressing underlying conditions
Recent Advances
- Improved understanding of biofilm biology has led to new therapeutic strategies, including biofilm disruptors and immunotherapies.
- Development of local delivery materials with controlled antibiotic release and scaffolding for bone regeneration.
- Enhanced diagnostic methods for early detection of low-grade infections.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Infection and inflammation of bone and bone marrow |
| Common Pathogen | Staphylococcus aureus (most frequent) |
| Clinical Signs | Bone pain, swelling, redness, fever, draining sinuses (chronic) |
| Diagnosis | Clinical assessment, imaging (MRI preferred), lab tests, bone biopsy |
| Treatment | Long-term antibiotics, surgical debridement, novel therapies targeting biofilms |
| Challenges | Biofilm formation, antibiotic penetration, chronicity |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Osteomyelitis or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References with DOI links
- Lew DP, Waldvogel FA. Osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2004;364(9431):369-379.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16727-5 - Masters EA, et al. Osteomyelitis: Recent advances in pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. J Orthop Res. 2016 Oct 26.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23255
PMC article - Arciola CR, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis: Bone, Bugs, and Surgery. Infect Immun. 2020 Feb 24;88(3):e00932-19.
https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00932-19 - Zimmerli W, Sendi P. Orthopedic biofilm infections. APMIS. 2017 Apr;125(4):353-364.
https://doi.org/10.1111/apm.12673 - Lew DP, Waldvogel FA. Osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2004;364(9431):369-379.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16727-5 - Lipsky BA, et al. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(12):e132-e173.
https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cis346
Osteomyelitis remains a complex disease requiring early diagnosis and combined medical-surgical treatment. Advances in understanding biofilms and local antibiotic delivery promise improved outcomes in the future.














