Nerve Trauma
Nerve Trauma (Peripheral Nerve Injury): Overview, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Nerve trauma refers to injury to peripheral nerves caused by physical damage such as cuts, compression, stretching, or blunt force. These injuries disrupt nerve function, leading to sensory, motor, and autonomic symptoms depending on the nerve involved and severity of damage.
Causes
- Direct trauma: lacerations, fractures, crush injuries
- Compression or entrapment (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Stretch injuries during accidents or surgery
- Ischemia or inflammation
- Surgical complications or radiation therapy
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the type of nerve fibers affected:
- Sensory nerve damage: Numbness, tingling, burning, pain, sensitivity changes, and loss of positional awareness
- Motor nerve damage: Muscle weakness, twitching (fasciculations), atrophy, paralysis
- Autonomic nerve damage: Abnormal sweating, dry eyes/mouth, bladder or bowel dysfunction, sexual dysfunction, orthostatic hypotension
Diagnosis
- Clinical history and physical examination: Assess symptoms, injury mechanism, and neurological deficits.
- Electrodiagnostic tests:
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures muscle electrical activity to detect denervation.
- Nerve conduction studies: Assess speed and strength of electrical signals in nerves.
- Imaging:
- MRI and ultrasound to visualize nerve structure and surrounding tissues.
- CT scan if bone injury or complex anatomy involved.
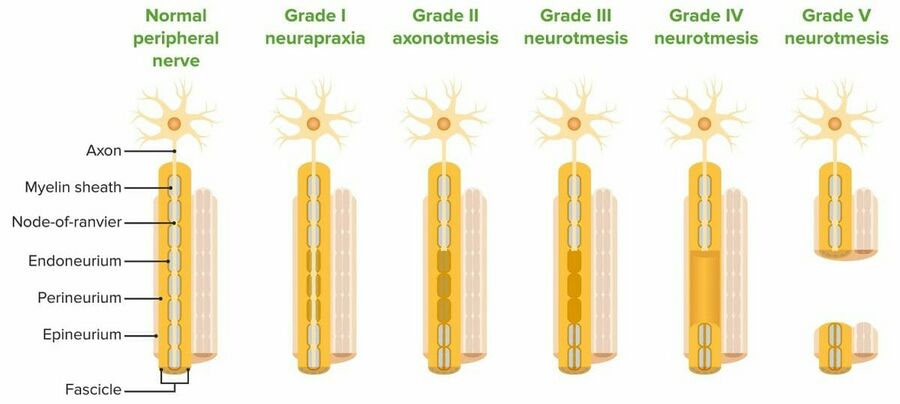
- Classification of nerve injury severity:
- Neuropraxia (first degree): Temporary conduction block, no axonal damage, usually recovers fully.
- Axonotmesis (second degree): Axonal damage with intact connective tissue, recovery possible but slower.
- Neurotmesis (third to fifth degree): Complete nerve disruption, scarring, or loss of continuity; often requires surgery.
Treatment
- Conservative management:
- Rest and protection of the injured area
- Pain control with NSAIDs or other analgesics
- Physical and occupational therapy to maintain muscle strength and joint mobility
- Desensitization techniques for hypersensitivity
- Medications:
- Neuropathic pain agents such as anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin), antidepressants (amitriptyline, duloxetine)
- Interventional procedures:
- Nerve blocks with anesthetics or steroids for pain relief
- Surgical treatment:
- Indicated for severe injuries with nerve transection or persistent dysfunction
- Procedures include nerve repair, grafting, neurolysis (removal of scar tissue), or nerve decompression
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), lifestyle modifications
Prognosis
- Recovery depends on injury severity, location, and timely treatment.
- Neuropraxia often resolves within weeks to months.
- More severe injuries may have incomplete recovery and require surgery.
- Early diagnosis and rehabilitation improve outcomes.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Injury to peripheral nerves causing sensory, motor, and autonomic dysfunction |
| Causes | Trauma, compression, stretch, ischemia, surgery |
| Symptoms | Numbness, tingling, pain, weakness, muscle atrophy, autonomic dysfunction |
| Diagnosis | History, physical exam, EMG, nerve conduction studies, MRI, ultrasound |
| Injury Types | Neuropraxia (mild), axonotmesis (moderate), neurotmesis (severe) |
| Treatment | Rest, medications, physical therapy, nerve blocks, surgery if needed |
| Prognosis | Variable; better with early treatment and less severe injury |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Nerve Trauma or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Mayo Clinic. Peripheral nerve injuries – Diagnosis and treatment. 2024.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-nerve-injuries/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355632 - Mayo Clinic. Peripheral nerve injuries – Symptoms and causes. 2024.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-nerve-injuries/symptoms-causes/syc-20355631 - WebMD. Nerve Pain and Nerve Damage: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments. 2024.
https://www.webmd.com/brain/nerve-pain-and-nerve-damage-symptoms-and-causes - Johns Hopkins Medicine. Peripheral Nerve Injury. 2022.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-nerve-injury - Cleveland Clinic. Neuropraxia: What It Is, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment. 2025.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22608-neuropraxia - Healthdirect Australia. Nerve pain (neuralgia) – causes, diagnosis and treatments. 2024.
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/nerve-pain
Nerve trauma can cause significant sensory and motor deficits but often improves with appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention and rehabilitation are key to optimizing recovery.















