Malignant Disease
Malignant Disease: Definition and Characteristics
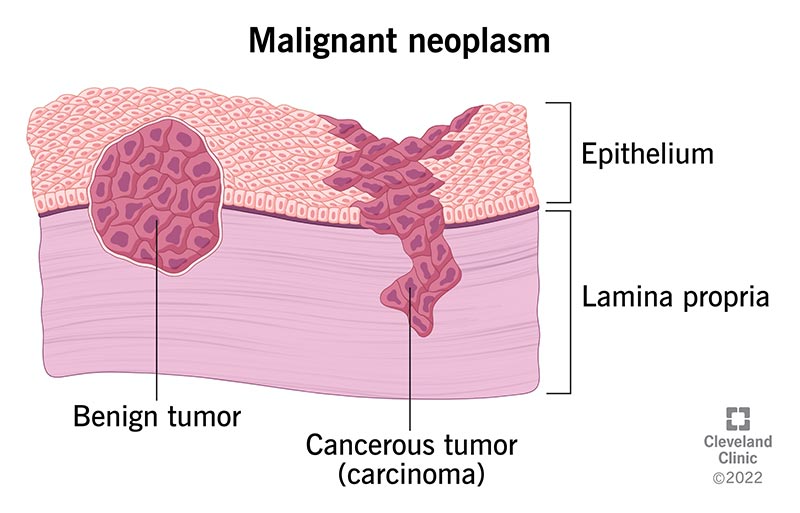
What is Malignant Disease?
Malignant disease refers to a condition characterized by cancerous growth, where cells proliferate uncontrollably and invade surrounding tissues. These abnormal cells have the ability to metastasize, spreading to distant parts of the body through blood or lymphatic systems. Malignant diseases can affect various organs and systems, disrupting normal function and potentially leading to life-threatening complications.
Characteristics
Mechanism
Malignant cells exhibit uncontrolled growth due to genetic mutations that enable them to bypass normal regulatory mechanisms for cell division, apoptosis, and DNA repair. They acquire invasive properties, allowing penetration into neighboring tissues and blood vessels. Metastasis involves detachment of cancer cells, intravasation, survival in circulation, extravasation at distant sites, and colonization of new tissues.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary widely depending on the tumor location, size, and metastasis. Common manifestations include painless masses or lumps, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, pain, organ dysfunction, and bleeding. Advanced disease can cause systemic effects like cachexia and paraneoplastic syndromes.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for malignant disease include genetic predisposition, exposure to carcinogens (tobacco, radiation, chemicals), chronic inflammation, infections with oncogenic viruses, lifestyle factors (diet, physical inactivity), and certain medical conditions.
Clinical Significance
Malignant diseases require early diagnosis and prompt treatment to improve prognosis. Treatment modalities include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Multidisciplinary care is often essential for optimal outcomes.
Key Points
- Malignant disease involves uncontrolled, invasive growth of cancer cells.
- Cells have the ability to metastasize to distant sites.
- Symptoms depend on location and extent of disease.
- Early detection and multimodal treatment improve survival and quality of life.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For personalized evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment options for malignant diseases, consult with our oncology specialists who provide comprehensive multidisciplinary care using Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells .
References:
- NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. Malignant. National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/malignant
- World Health Organization. Cancer Fact Sheet. 2025. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
- Brown JS, et al. Updating the Definition of Cancer: Cancer as a Disease of Uncontrolled Proliferation and Natural Selection. Cancer Cell. 2023 Jul 5;41(7):928-935. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2023.06.012. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2023.06.012
- Cleveland Clinic. What Is Cancer? Symptoms, Causes & Types. 2025. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12194-cancer
- National Cancer Institute. What Is Cancer? 2007. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer















