Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) therapy
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) therapy: Definition and Characteristics
What is Interferon-gamma therapy?
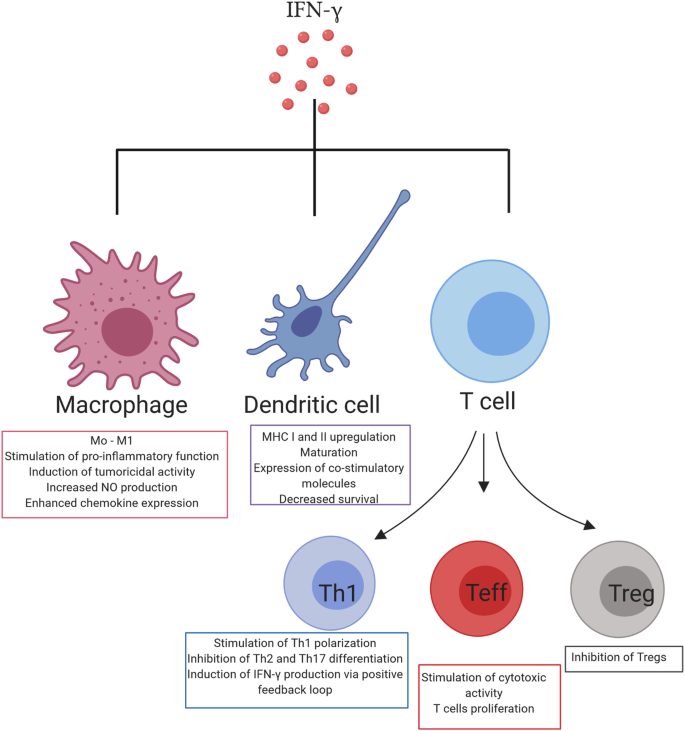
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) therapy involves using a cytokine, a protein that modulates the immune response, to enhance the body’s ability to fight infections. It is used particularly in patients with Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD), a rare inherited immune disorder where phagocytes lose the ability to produce reactive oxygen species needed to kill certain bacteria and fungi. IFN-γ boosts the immune response by activating macrophages and enhancing microbial killing, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of infections in CGD patients.
Characteristics
Mechanism: IFN-γ activates macrophages and other immune cells, promoting the production of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species that help kill pathogens. It also enhances antigen presentation and the development of an effective immune response, counteracting the defective oxidative burst in CGD. This cytokine modulates immune pathways, reducing inflammation and granuloma formation, and improving pathogen clearance.
Symptoms and Benefits: Patients receiving IFN-γ often experience fewer severe infections, along with decreased hospitalizations and absences from work or school. It has been shown to reduce bacterial and fungal infections significantly, especially when used as prophylaxis alongside antibiotics and antifungal medications.
Risks and Side Effects: Common side effects include flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, and muscle aches. Some patients may experience injection site reactions, headache, or nausea. Serious adverse events are rare, but long-term therapy requires monitoring for potential immune dysregulation or other complications.
Clinical Significance
IFN-γ therapy is a critical adjunct in managing CGD, especially for preventing life-threatening infections. Long-term use, often three times weekly subcutaneously, has demonstrated safety and efficacy over years of follow-up. This treatment improves quality of life and survival outcomes in affected patients, but it requires careful patient selection and monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Key Points
- Interferon-gamma boosts immune function in patients with CGD.
- It activates macrophages, reduces infections, and modulates inflammation.
- Common side effects are flu-like, with rare serious adverse events.
- Long-term therapy has proven safety and clinical benefits.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For personalized guidance on interferon-gamma therapy and management of CGD, contact our immunology and infectious disease specialists for comprehensive care including Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells and monitoring.
References:
- Liese J, et al. Gamma interferon treatment of patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1999 Apr 30;28(4):920-6. doi:10.1086/514202. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1086/514202
- Lee PY, et al. Interferon gamma rebalances immunopathological signatures in chronic granulomatous disease. Blood Adv. 2025 Oct 28;9(20):5306-5319. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2025016213. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2025016213
- Bemiller LS, et al. Safety and effectiveness of long-term interferon gamma therapy in CGD patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995;14(4):345-349. doi:10.1097/00006454-199504000-00010. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1097/00006454-199504000-00010
- Jyonouchi S, et al. Interferon Gamma Therapy for Recurrent Infections in Patients with CGD. J Infect Dis. 2001 Dec;184(12):1584-90. doi:10.1086/324232. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1086/324232
- Allen A, Jaffe J, Curnutte J. Interferon-Gamma Treatment of Chronic Granulomatous Disease. In: J. J. Howard, A. Jaffe, J. Curnutte, A. Ezekowitz. editors. Immunotherapy in Primary Immunodeficiency. 2020. DOI:10.1201/9781003066903-2. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003066903-2















