Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV): Clinical Overview and Management
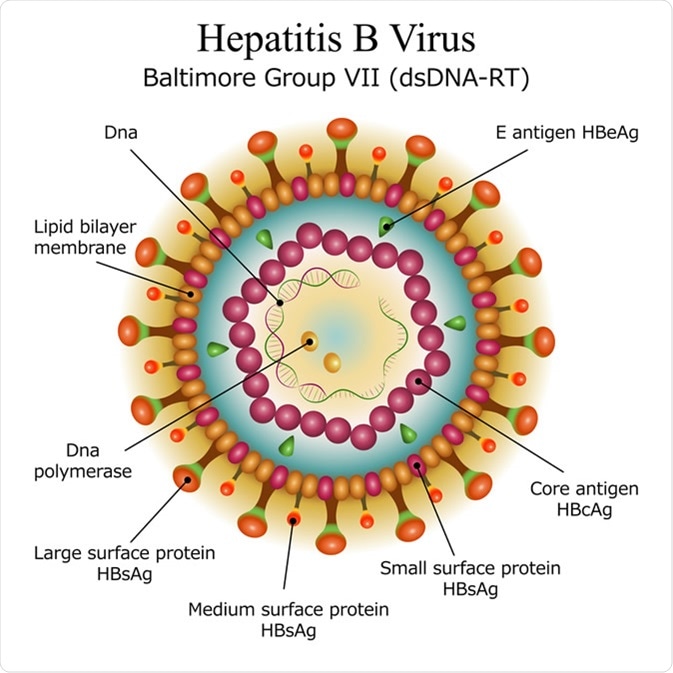
Overview
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a DNA virus causing infection of the liver, presenting as acute or chronic hepatitis. It remains a significant global public health problem, transmitted primarily through exposure to infected blood and bodily fluids.
Pathogenesis and Transmission
- HBV infects hepatocytes, releasing viral antigens (HBsAg, HBeAg) into the bloodstream, triggering immune-mediated liver injury.
- Transmission occurs via percutaneous or mucosal exposure to infectious secretions including blood, semen, and vaginal fluids. Common routes include sexual contact, needle sharing, mother-to-child transmission during childbirth, and unsafe medical practices.
Clinical Presentation
- Acute HBV: Incubation 1 to 6 months; symptoms range from asymptomatic to severe. Typical manifestations include fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice, and arthralgia.
- Chronic HBV: Defined by persistence of HBsAg >6 months. Many patients are asymptomatic; others develop progressive liver inflammation leading to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Diagnosis
- Serologic testing for HBsAg, anti-HBc, and HBV DNA quantification confirms infection and stage. Liver enzyme assays (ALT, AST) assess hepatic injury.
- Imaging and biopsy may be needed to evaluate liver damage.
Management Principles
- Acute infection often resolves spontaneously; supportive care is primary.
- Antiviral therapy indicated in chronic infection to suppress viral replication and reduce disease progression risk.
- Regular monitoring of liver function and cancer screening is essential for chronic HBV patients.
Prevention
- Universal vaccination is the most effective preventive measure and is recommended globally.
- Blood screening, safe injection practices, and safe sex education are critical components of transmission control.
Summary
HBV infection ranges from silent to life-threatening liver disease. Timely diagnosis, antiviral treatment, and preventive vaccination reduce morbidity and mortality associated with this infection.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For comprehensive HBV evaluation, management, and vaccination, consult infectious disease specialists and hepatologists.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Hepatitis B – Symptoms and Causes. 2024.mayoclinic
- CDC. Clinical Overview of Hepatitis B. 2025.cdc
- WHO. Hepatitis B Fact Sheet. 2025.who
- StatPearls. Hepatitis B – Diagnosis and Treatment. 2023.ncbi.nlm.nih
- Cleveland Clinic. Hepatitis B – Clinical Features. 2025.clevelandclinic















