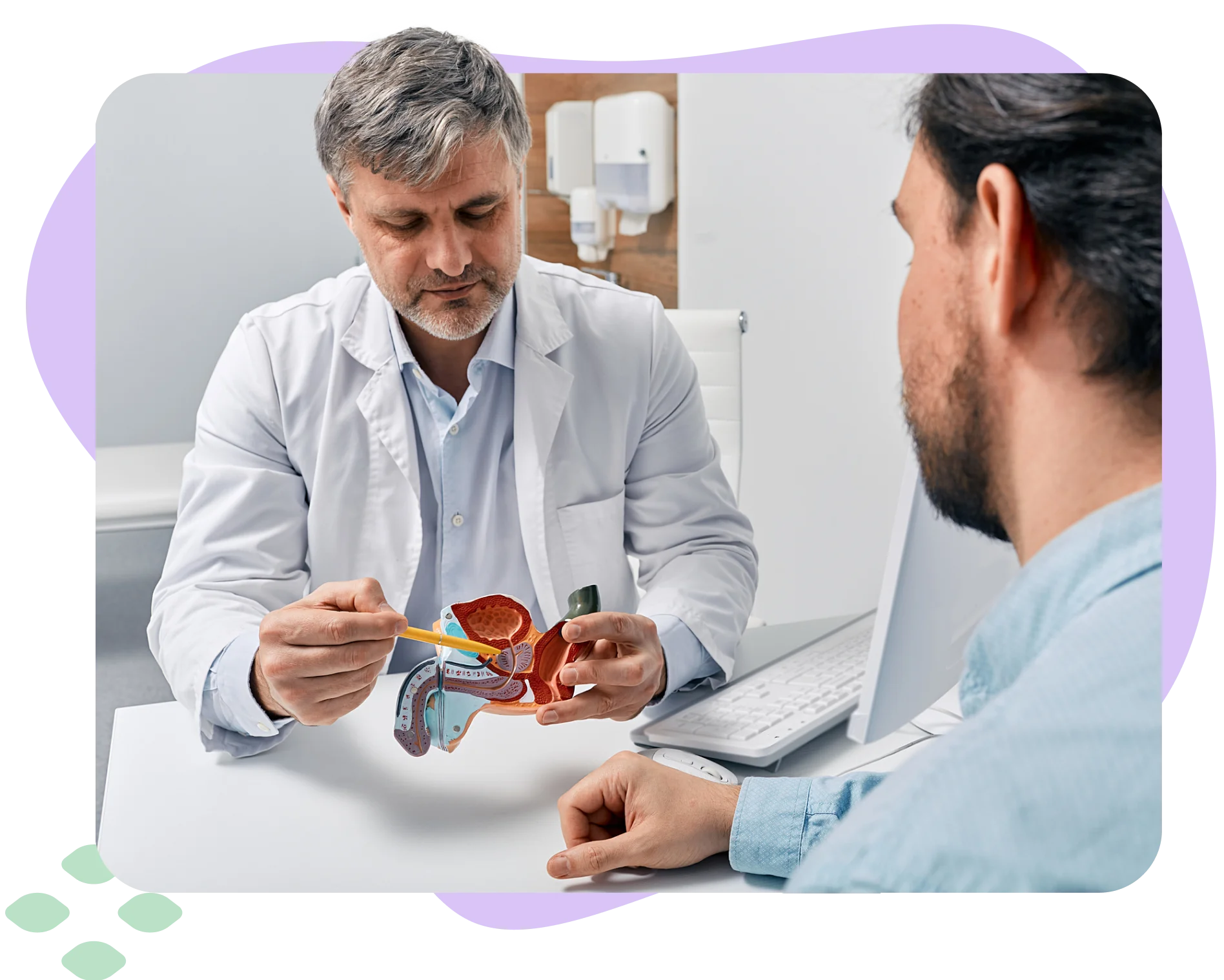
Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) represent a groundbreaking advancement in regenerative medicine, offering innovative therapeutic strategies for this prevalent male condition. ED is characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance, often due to vascular insufficiency, neuropathic damage, endothelial dysfunction, or hormonal imbalances. Conventional treatments, such as phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is), vacuum erection devices, and penile implants, provide symptomatic relief but fail to address the underlying causes of ED. This introduction will explore the potential of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for ED to regenerate penile tissues, restore endothelial integrity, enhance neurovascular function, and promote sustained erectile responses. Recent scientific advancements and future directions in this evolving field will be highlighted [1-5].
Despite progress in urology and sexual medicine, conventional treatments for Erectile Dysfunction remain limited in their ability to restore natural erectile function. Pharmacological interventions, such as PDE5Is (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil), enhance nitric oxide signaling but require continuous administration and may become ineffective in cases of severe vascular dysfunction. Additionally, surgical implants and vascular interventions carry risks of mechanical failure and complications. These limitations underscore the urgent need for regenerative therapies that go beyond symptomatic management to actively restore penile tissue integrity, vascular perfusion, and nerve function.
The convergence of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) represents a paradigm shift in sexual medicine. Imagine a future where ED can be not just managed but fundamentally reversed through regenerative medicine. This pioneering field holds the promise of not only improving erectile function but also restoring overall penile health and responsiveness at a cellular level. Join us as we explore this revolutionary intersection of urology, regenerative science, and cellular therapy, where innovation is redefining possibilities in the treatment of Erectile Dysfunction [1-5].
2. Genetic Insights: Personalized DNA Testing for Erectile Dysfunction Risk Assessment Before Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our team of urology specialists and genetic researchers offers comprehensive DNA testing services for individuals with a predisposition to Erectile Dysfunction. This service aims to identify specific genetic markers associated with vascular insufficiency, androgen receptor sensitivity, endothelial dysfunction, and neurogenic factors contributing to ED. By analyzing key genomic variations linked to endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), phosphodiesterase 5A (PDE5A), and androgen receptor polymorphisms, we can better assess individual risk factors and provide personalized recommendations for preventive care before administering Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
This proactive approach enables patients to gain valuable insights into their sexual health, allowing for early intervention through lifestyle modifications, targeted hormone optimization, and regenerative strategies. With this information, our team can guide individuals toward optimal sexual health strategies that may significantly reduce the severity and progression of ED while improving treatment outcomes [1-5].
3. Understanding the Pathogenesis of Erectile Dysfunction: A Detailed Overview
Erectile Dysfunction is a complex condition involving a multifaceted interplay of vascular, neurological, hormonal, and endothelial factors that contribute to impaired erectile function. Here is a detailed breakdown of the mechanisms underlying ED:
Vascular Insufficiency and Endothelial Dysfunction
Atherosclerosis and Reduced Penile Blood Flow
- Oxidative Stress: Chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension lead to excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, reducing nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability and impairing vasodilation.
- Endothelial Dysfunction: Damage to endothelial cells in the penile arteries reduces their ability to produce NO, leading to impaired smooth muscle relaxation and insufficient blood inflow.
- Vascular Stiffening: Increased arterial stiffness reduces penile vascular compliance, leading to decreased erectile rigidity [1-5].
Neurogenic Factors and Neuromuscular Dysfunction
Neural Impairment in ED
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Damage to the autonomic nervous system due to diabetes or spinal cord injuries disrupts nerve signaling essential for erection.
- Pudendal Nerve Injury: Direct trauma, pelvic surgery, or neurodegenerative diseases affect nerve conduction, reducing erectile response.
- Neurotrophic Deficiency: Impaired expression of neurotrophic factors (e.g., nerve growth factor [NGF], brain-derived neurotrophic factor [BDNF]) hampers nerve regeneration and penile sensitivity [1-5].
Fibrosis and Smooth Muscle Dysfunction
Structural Changes in the Corpus Cavernosum
- Fibrotic Remodeling: Activation of myofibroblasts leads to excessive extracellular matrix deposition, replacing functional smooth muscle tissue with fibrotic tissue.
- Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β) Signaling: Overactivation of TGF-β pathways promotes penile fibrosis, reducing the ability of the corpus cavernosum to expand during an erection.
- Reduced Cavernosal Compliance: Persistent fibrosis leads to reduced vascular compliance, impairing the venous occlusive mechanism required for maintaining erections [1-5].
Hormonal Imbalances and Androgen Deficiency
Endocrine Dysfunction in ED
- Testosterone Deficiency: Low testosterone levels contribute to reduced NO production, decreased libido, and compromised erectile function.
- Hypogonadism: Conditions such as primary testicular failure or secondary hypogonadism affect androgen signaling and overall erectile responsiveness.
- Estrogen/Testosterone Imbalance: Increased aromatization of testosterone into estrogen disrupts hormonal equilibrium, negatively impacting erectile function [1-5].
Metabolic and Systemic Contributions
Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
- Glycemic Toxicity: Hyperglycemia induces endothelial dysfunction, neuropathy, and microvascular disease, all of which contribute to ED.
- Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs): Accumulation of AGEs leads to structural changes in penile tissue, reducing erectile function.
- Insulin Resistance: Impaired insulin signaling reduces NO production, affecting penile vascular health and erectile quality [1-5].
Overall, the pathogenesis of Erectile Dysfunction is driven by a complex interplay of vascular impairment, neural degeneration, hormonal imbalances, and fibrotic changes. Early identification and intervention targeting these pathways through Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) hold immense potential in reversing disease progression and restoring erectile function [1-5].
4. Unraveling the Complex Causes of Erectile Dysfunction (ED) and Cellular Degeneration
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a multifactorial disorder that results from vascular, neurological, endocrine, and psychological factors. Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) provide a promising avenue for restoring erectile function by addressing the root causes at the cellular level. The key mechanisms contributing to ED include:
Vascular Insufficiency and Endothelial Dysfunction
- Reduced blood flow due to endothelial dysfunction impairs the ability of penile arteries to dilate, leading to inadequate erectile response.
- Oxidative stress and reduced nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability disrupt normal vasodilation and penile tissue oxygenation [6-10].
Neurological Impairments and Nerve Degeneration
- Diabetes, trauma, and neurodegenerative diseases contribute to nerve damage, reducing the transmission of signals necessary for erection.
- Impaired function of the cavernous nerve results in reduced neural activation of the penile vascular system.
Hormonal Dysregulation and Testosterone Deficiency
- Androgen deficiency affects the structural integrity of penile tissue, reducing smooth muscle function.
- Testosterone plays a crucial role in regulating endothelial function and NO synthesis, making it a key target for regenerative interventions [6-10].
Fibrotic Changes in Erectile Tissue
- Persistent tissue hypoxia and chronic inflammation lead to collagen deposition, reducing penile elasticity and impairing normal erectile function.
- Dysregulated fibroblast activity and TGF-β signaling contribute to fibrosis within the corpus cavernosum.
The multifaceted nature of ED underscores the necessity for innovative regenerative treatments such as Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) to restore vascular integrity, nerve function, and smooth muscle regeneration [6-10].
5. Challenges in Conventional Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Limitations and Unmet Needs
Current pharmacological and surgical treatments for ED offer symptomatic relief but fail to address the underlying pathophysiology. Major drawbacks include:
Limited Efficacy of Oral Medications
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil) enhance blood flow but do not repair vascular or nerve damage.
- A significant proportion of men with severe ED, diabetes, or post-prostatectomy ED remain unresponsive to oral therapies [6-10].
Invasiveness of Surgical Options
- Penile implants provide a mechanical solution but involve invasive surgery with potential complications.
- Vascular reconstruction surgeries have limited long-term success rates and are not suitable for all patients.
Lack of Regenerative Capacity in Current Therapies
- None of the standard treatments promote endogenous tissue repair, leaving ED patients reliant on lifelong interventions.
These limitations highlight the urgent need for Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), which can regenerate damaged tissues, restore nerve function, and improve vascularization [6-10].
6. Breakthroughs in Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Pioneering Advances
Recent research in regenerative medicine has demonstrated that stem cell-based therapies can restore erectile function by enhancing vascularization, neuroprotection, and tissue remodeling. Key breakthroughs include:
Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
- Year: 2013
- Researcher: Dr. Ching-Shwun Lin
- Institution: University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), USA
- Result: MSC therapy significantly improved erectile function by enhancing angiogenesis and smooth muscle regeneration.
Endothelial Progenitor Cell (EPC) Therapy
- Year: 2015
- Researcher: Dr. Yu Sun
- Institution: Sun Yat-sen University, China
- Result: EPC therapy increased vascular density and improved penile blood flow in diabetic ED models [6-10].
Neural Stem Cell (NSC) Therapy for Neurogenic ED
- Year: 2017
- Researcher: Dr. Jason Kovac
- Institution: Indiana University School of Medicine, USA
- Result: NSC transplantation restored erectile function in spinal cord injury models by promoting axonal regeneration.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC)-Derived Smooth Muscle Cell Therapy
- Year: 2019
- Researcher: Dr. Anthony Atala
- Institution: Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, USA
- Result: iPSC-derived smooth muscle cells improved corpus cavernosum function in ED models.
Exosome-Based Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
- Year: 2022
- Researcher: Dr. Michael R. Ziegelmann
- Institution: Mayo Clinic, USA
- Result: Stem cell-derived exosomes demonstrated anti-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic effects, enhancing erectile recovery in preclinical studies.
These transformative studies illustrate the potential of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) to revolutionize the treatment landscape [6-10].
7. Celebrities and Public Figures Raising Awareness for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) and Regenerative Medicine
Several high-profile figures have openly discussed their struggles with ED, contributing to greater awareness and encouraging scientific advancements in regenerative medicine:
- Ben Stiller: The actor has been vocal about men’s health, promoting awareness of ED and prostate health issues.
- Michael Douglas: His discussions about aging and sexual health have highlighted the importance of innovative ED treatments.
- Hugh Hefner: As a symbol of men’s sexual health, his advocacy indirectly brought attention to ED and its treatment options.
- Charlie Sheen: His public discussions on health and aging have contributed to the broader conversation about regenerative medicine for ED.
- Bill Clinton: While not publicly confirmed, discussions about his health have often sparked conversations around men’s health and ED treatment [6-10].
8. Cellular Players in Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Understanding Penile Pathophysiology
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is characterized by complex cellular dysfunction leading to impaired penile vascularization, nerve degeneration, and smooth muscle atrophy. Understanding the role of key cellular components provides insight into how Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) may offer regenerative solutions:
Endothelial Cells
Endothelial cells line the blood vessels and regulate nitric oxide (NO) production, a crucial factor in penile vasodilation. Dysfunctional endothelial cells reduce NO availability, leading to poor arterial blood flow and penile hypoxia.
Cavernous Smooth Muscle Cells
These cells control the expansion and contraction of the corpus cavernosum. Chronic ED is associated with increased fibrosis and smooth muscle apoptosis, leading to diminished erectile capacity.
Pericytes
Located around microvessels, pericytes play a vital role in vascular stability and blood-brain barrier maintenance. In ED, their dysfunction contributes to vascular leakage and impaired penile perfusion.
Neuronal Cells
Nerve endings in the penis mediate arousal by transmitting signals from the brain to the vascular system. Damage to these neurons, often due to diabetes, injury, or age-related degeneration, disrupts erectile function.
Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
Tregs are crucial for immune modulation, preventing excessive inflammation that can lead to endothelial dysfunction. In ED, impaired Treg function exacerbates oxidative stress and vascular damage.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
MSCs are known for their regenerative properties. They suppress inflammation, enhance angiogenesis, and stimulate endothelial and smooth muscle cell regeneration.
By targeting these cellular dysfunctions, Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) aim to restore normal penile physiology and function [11-14].
9. Progenitor Stem Cells’ Roles in Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Pathogenesis
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Endothelial Cells
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Cavernous Smooth Muscle Cells
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Pericytes
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Neuronal Cells
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Anti-Inflammatory Cells
- Progenitor Stem Cells (PSC) of Fibrosis-Regulating Cells
10. Revolutionizing Erectile Dysfunction Treatment: Unleashing the Power of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) with Progenitor Stem Cells
Our specialized treatment protocols leverage the regenerative potential of Progenitor Stem Cells (PSCs), targeting the major cellular pathologies in ED:
Endothelial Cells
PSCs for endothelial cells enhance NO production, improving penile blood flow and reversing endothelial dysfunction.
Cavernous Smooth Muscle Cells
PSCs for smooth muscle cells prevent fibrosis, promote tissue elasticity, and restore erectile capacity.
Pericytes
PSCs for pericytes stabilize penile microvasculature, preventing vascular leakage and promoting tissue perfusion.
Neuronal Cells
PSCs for neurons regenerate damaged nerve endings, restoring nerve conduction and erectile reflexes.
Anti-Inflammatory Cells
PSCs with immunomodulatory properties suppress chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in penile tissues.
Fibrosis-Regulating Cells
PSCs prevent excessive collagen buildup, reducing corporal fibrosis and preserving erectile function.
By harnessing progenitor stem cells, Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) offer a groundbreaking shift from symptomatic management to actual penile tissue regeneration [11-14].
11. Allogeneic Sources of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Regenerative Solutions for Penile Dysfunction
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)’s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we utilize ethically sourced allogeneic stem cell sources with strong regenerative potential:
- Bone Marrow-Derived MSCs – Enhance vascularization and suppress fibrosis.
- Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) – Promote endothelial regeneration and neurovascular repair.
- Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells – Stimulate angiogenesis and tissue repair.
- Placental-Derived Stem Cells – Offer potent immunomodulatory effects to counteract oxidative stress.
- Wharton’s Jelly-Derived MSCs – Deliver superior regenerative capacity, optimizing erectile recovery.
These allogeneic sources provide renewable, potent, and ethically viable stem cells, advancing the frontiers of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) [11-14].
12. Key Milestones in Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Advancements in Understanding and Treatment
Discovery of Nitric Oxide in Erectile Function: Dr. Ferid Murad, 1977
Dr. Ferid Murad discovered that nitric oxide plays a critical role in vascular relaxation, a fundamental process in erectile function.
Identification of Endothelial Dysfunction in ED: Dr. Jacob Rajfer, 1992
Dr. Rajfer demonstrated that endothelial dysfunction is a primary cause of ED, linking cardiovascular disease to erectile impairment [11-14].
First Animal Model for Stem Cell Therapy in ED: Dr. Tom Lue, 2004
Dr. Lue pioneered the use of stem cells in animal models of ED, showing their ability to restore erectile function in diabetic and post-prostatectomy cases.
Clinical Trial on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for ED: Dr. Martha Haahr, 2016
Dr. Haahr conducted one of the first human trials using adipose-derived stem cells, showing promising results in restoring erectile function in patients with severe ED [11-14].
13. Optimized Delivery: Dual-Route Administration for ED Treatment Protocols of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our advanced Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) program integrates intracavernosal injection and intravenous (IV) delivery to maximize therapeutic benefits:
- Targeted Penile Regeneration – Direct intracavernosal injection ensures precise stem cell delivery, enhancing smooth muscle regeneration.
- Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Effects – IV stem cell administration exerts systemic immunomodulation, reducing chronic inflammation linked to ED.
- Extended Therapeutic Benefits – This dual-route approach ensures long-term restoration of erectile function and prevents disease progression [11-14].
14. Ethical Regeneration: Our Approach to Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)’s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we utilize only ethically sourced stem cells for ED treatment:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) – Regenerate penile vasculature, improve blood flow, and prevent fibrosis.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) – Personalized regenerative therapy to replace damaged endothelial and smooth muscle cells.
- Neural Progenitor Cells (NPCs) – Restore nerve function, crucial for erectile signaling.
- Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) – Promote angiogenesis and repair microvascular damage.
By ensuring ethical sourcing and cutting-edge techniques, Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) pave the way for truly restorative sexual health solutions [11-14].
15. Proactive Management: Preventing Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Progression with Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells
Preventing Erectile Dysfunction (ED) progression requires early intervention and regenerative strategies. Our treatment protocols integrate:
- Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) to enhance penile vascularization, restoring blood flow and improving erectile function.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) to modulate immune responses, reduce fibrosis, and prevent penile tissue degeneration.
- iPSC-Derived Smooth Muscle Cells to replace damaged corpus cavernosum tissues and restore erectile mechanics.
By targeting the underlying causes of ED with Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), we offer a revolutionary approach to sexual health restoration and penile tissue regeneration [15-17].
16. Timing Matters: Early Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) for Maximum Recovery
Our team of urology and regenerative medicine specialists underscores the critical importance of early intervention in Erectile Dysfunction (ED). Initiating stem cell therapy within the early stages of vascular or neurogenic impairment leads to significantly better outcomes:
- Early stem cell treatment enhances cavernous endothelial repair, mitigating progressive vascular insufficiency and preventing irreversible penile fibrosis.
- Stem cell therapy at initial disease stages promotes anti-inflammatory and angiogenic mechanisms, reducing oxidative stress and neurovascular damage.
- Patients undergoing prompt regenerative therapy demonstrate improved erectile rigidity, prolonged function, and reduced dependence on pharmacological interventions.
We strongly advocate for early enrollment in our Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) program to maximize therapeutic benefits and long-term sexual health. Our team ensures timely intervention and comprehensive patient support for the best possible recovery outcomes [15-17].
17. Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Mechanistic and Specific Properties of Stem Cells
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a multifactorial disorder characterized by endothelial dysfunction, smooth muscle apoptosis, and neurovascular deterioration. Our cellular therapy program incorporates regenerative medicine strategies to address the underlying pathophysiology of ED, offering a potential alternative to conventional treatment approaches.
- Endothelial Regeneration and Cavernous Vascular Repair: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) stimulate neovascularization, restoring endothelial integrity and improving penile blood flow.
- Antifibrotic Mechanisms and Smooth Muscle Restoration: Stem cells downregulate fibrogenic pathways by inhibiting myofibroblast activation. MSCs secrete matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) that degrade excess collagen, reversing penile fibrosis and restoring smooth muscle compliance.
- Neuroprotection and Nerve Regeneration: MSCs and iPSC-derived Schwann cells release neurotrophic factors such as NGF and BDNF, promoting peripheral nerve repair and enhancing neurotransmission for erectile response.
- Mitochondrial Transfer and Oxidative Stress Reduction: Stem cells restore cavernous mitochondrial function through the transfer of healthy mitochondria via tunneling nanotubes. This enhances ATP production and reduces oxidative damage.
- Microvascular Repair and Penile Blood Flow Enhancement: EPCs promote angiogenesis and stabilize endothelial function, improving penile hemodynamics and reducing the severity of vasculogenic ED.
By integrating these regenerative mechanisms, our Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) program offers a groundbreaking therapeutic approach, targeting both the pathological and functional aspects of erectile impairment [15-17].
18. Understanding Erectile Dysfunction: The Five Stages of Progressive Penile Dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction progresses through a continuum of vascular and neurogenic deterioration. Early intervention with cellular therapy can significantly alter disease progression.
Stage 1: Mild Vasculogenic ED
- Reduced endothelial function with impaired nitric oxide signaling.
- Occasional erectile difficulties with mild arterial insufficiency.
- Cellular therapy enhances endothelial nitric oxide production and restores cavernous blood flow.
Stage 2: Moderate ED with Fibrosis Development
- Persistent endothelial dysfunction and early cavernous fibrosis.
- Decreased penile rigidity and responsiveness to pharmacological treatment.
- MSC therapy prevents fibrosis progression and promotes smooth muscle regeneration [15-17].
Stage 3: Severe Vasculogenic and Neurogenic ED
- Widespread fibrosis and neurovascular deterioration.
- Poor response to phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE5i) and diminished nocturnal erections.
- Stem cell therapy reverses fibrotic changes and restores neurovascular function.
Stage 4: Complete Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Significant vascular insufficiency and loss of cavernous smooth muscle.
- Absence of spontaneous or induced erections.
- Combination therapy with iPSCs and EPCs provides regenerative repair and neovascularization [15-17].
Stage 5: End-Stage Erectile Dysfunction
- Severe structural and functional impairment.
- Surgical intervention or penile prosthesis as the only available treatment.
- Cellular therapy remains experimental but offers potential avenues for future interventions.
19. Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Impact and Outcomes Across Stages
Stage 1: Mild Vasculogenic ED
- Conventional Treatment: Lifestyle modifications and PDE5 inhibitors.
- Cellular Therapy: MSCs enhance endothelial function, improve nitric oxide bioavailability, and restore erectile response.
Stage 2: Moderate ED with Fibrosis Development
- Conventional Treatment: PDE5 inhibitors and penile rehabilitation techniques.
- Cellular Therapy: Stem cell-based antifibrotic and angiogenic mechanisms prevent progressive fibrosis and improve vascular compliance [15-17].
Stage 3: Severe Vasculogenic and Neurogenic ED
- Conventional Treatment: Intracavernosal injections and penile shockwave therapy.
- Cellular Therapy: MSC therapy restores cavernous tissue, promotes neurovascular repair, and enhances erectile rigidity.
Stage 4: Complete Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
- Conventional Treatment: Surgical interventions and penile implants.
- Cellular Therapy: iPSC-derived smooth muscle cells regenerate penile tissue, potentially delaying the need for prosthetic implants [15-17].
Stage 5: End-Stage Erectile Dysfunction
- Conventional Treatment: Penile prosthesis implantation or reconstructive surgery.
- Cellular Therapy: Future stem cell-derived organoid models may offer smooth muscle and endothelial cell replacement.
20. Revolutionizing Treatment with Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) program integrates:
- Personalized Stem Cell Protocols: Tailored to the patient’s vascular and neurogenic pathology.
- Multi-Route Delivery: Intracavernosal, intra-arterial, and systemic administration for optimal penile tissue integration.
- Long-Term Sexual Function Restoration: Addressing fibrosis, neurovascular impairment, and endothelial dysfunction for sustained erectile performance.
Through regenerative medicine, we aim to redefine ED treatment by enhancing vascular function, slowing fibrosis progression, and improving patient satisfaction without invasive procedures [15-17].
21. Allogeneic Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Why Our Specialists Prefer It
- Increased Cell Potency: Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) from young, healthy donors demonstrate superior regenerative capabilities, accelerating vascular repair and neuroprotection.
- Minimally Invasive Approach: Eliminates the need for autologous bone marrow or adipose tissue extraction, lowering procedural risks and discomfort.
- Enhanced Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Angiogenic Effects: MSCs and EPCs effectively regulate cytokine activity, improving endothelial integrity and microvascular function.
- Standardized and Consistent: Advanced cell processing techniques ensure batch-to-batch reliability and therapeutic consistency.
- Faster Treatment Access: Readily available allogeneic cells provide a crucial advantage for ED patients who require immediate intervention.
By leveraging allogeneic Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), we offer innovative, high-efficacy regenerative treatments with enhanced safety and long-term benefits [15-17].
22. Exploring the Sources of Our Allogeneic Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our allogeneic Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) utilizes ethically sourced, high-efficacy stem cells to restore erectile function and enhance penile vascularization. These include:
Umbilical Cord-Derived MSCs (UC-MSCs): Highly regenerative and immunomodulatory, UC-MSCs promote endothelial repair, stimulate nitric oxide (NO) production, and enhance penile vascular integrity.
Wharton’s Jelly-Derived MSCs (WJ-MSCs): Known for their superior anti-inflammatory and angiogenic potential, WJ-MSCs facilitate cavernous nerve regeneration and improve erectile response in ED patients.
Placental-Derived Stem Cells (PLSCs): Rich in vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and other angiogenic factors, PLSCs optimize penile microcirculation and smooth muscle regeneration.
Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells (AFSCs): Contribute to the restoration of neurovascular structures by modulating growth factor secretion and anti-fibrotic pathways.
Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs): Directly support penile endothelial function, aiding in the revascularization of erectile tissue and reversing microvascular dysfunction in ED [18-20].
By incorporating these diverse allogeneic stem cell sources, our regenerative approach maximizes therapeutic outcomes while minimizing immune rejection.
23. Ensuring Safety and Quality: Our Regenerative Medicine Lab’s Commitment to Excellence in Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our laboratory upholds the highest standards of safety and scientific rigor to ensure the efficacy of stem cell-based treatments for Erectile Dysfunction (ED):
Regulatory Compliance and Certification: Fully accredited by the Thai FDA for cellular therapy, adhering to GMP and GLP-certified protocols.
Advanced Quality Control Measures: Utilizing ISO4 and Class 10 cleanroom environments, ensuring optimal sterility and cell viability.
Clinical Validation and Scientific Research: Backed by extensive preclinical and clinical studies, refining protocols to maximize patient outcomes.
Personalized Treatment Protocols: Tailoring stem cell type, dosage, and administration method to match each patient’s severity of ED for optimal efficacy.
Ethical and Sustainable Sourcing: Our stem cells are harvested through non-invasive, ethically approved methods, ensuring long-term regenerative medicine advancements [18-20].
Our commitment to innovation and patient safety positions our regenerative medicine laboratory as a leader in Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
24. Advancing Erectile Dysfunction Outcomes with Our Cutting-Edge Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells
Key assessments for evaluating the effectiveness of stem cell therapy in ED patients include penile Doppler ultrasound for cavernosal artery flow, nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) tests, and validated erectile function scoring (IIEF-5). Our Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) has demonstrated:
Enhanced Penile Vascularization: MSC-based therapy stimulates neovascularization by increasing VEGF and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression.
Restoration of Erectile Function: Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and MSCs improve penile smooth muscle integrity and cavernous nerve function.
Reduction in Inflammatory and Fibrotic Processes: Stem cell therapy modulates TNF-α and IL-6 pathways, reducing fibrosis and oxidative stress [18-20].
Improved Sexual Performance and Quality of Life: Patients report sustained improvements in erectile function, libido, and overall sexual satisfaction.
By reducing reliance on pharmacological interventions and offering long-term functional benefits, our protocols provide a transformative solution for managing Erectile Dysfunction (ED) [18-20].
25. Ensuring Patient Safety: Criteria for Acceptance into Our Specialized Treatment Protocols for Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our team of andrologists and regenerative medicine specialists carefully evaluates each international patient with Erectile Dysfunction (ED) to ensure maximum safety and efficacy in our cellular therapy programs. Due to the complex nature of ED and its comorbid conditions, not all patients may qualify for our advanced stem cell treatments.
We may not accept patients with severe penile fibrosis, Peyronie’s disease with extensive plaque calcification, untreated hypogonadism, or uncontrolled diabetes, as these conditions may require adjunctive or alternative treatments. Similarly, individuals with active prostate cancer, systemic infections, or severe cardiovascular disease may not be suitable candidates due to increased medical risks [18-20].
Additionally, patients with persistent smoking habits, excessive alcohol consumption, or uncontrolled metabolic disorders must undergo pre-treatment optimization to improve treatment efficacy. Erectile dysfunction due to severe arterial insufficiency (e.g., advanced atherosclerosis) or end-stage neurogenic impairment (e.g., complete spinal cord injury) may also present limited regenerative potential.
By adhering to stringent eligibility criteria, we ensure that only the most suitable candidates receive our specialized Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), optimizing both safety and therapeutic outcomes [18-20].
26. Special Considerations for Advanced Erectile Dysfunction Patients Seeking Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells
Our andrology and regenerative medicine team recognizes that certain advanced Erectile Dysfunction (ED) patients may still benefit from Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), provided they meet specific clinical criteria. While the primary goal is to enhance erectile response and restore penile vascularization, exceptions may be made for patients with rapidly progressing vascular or neurogenic ED who remain clinically stable for therapy [18-20].
Prospective patients seeking consideration under these special circumstances should submit comprehensive medical records, including but not limited to:
- Penile Doppler Ultrasound: To assess arterial flow, venous leak, and penile vascular integrity.
- Nocturnal Penile Tumescence (NPT) Testing: To determine spontaneous erectile potential.
- Hormonal Panel: Including testosterone, prolactin, LH, and FSH levels to rule out endocrine dysfunction.
- Blood Biomarkers: Including inflammatory markers (IL-6, TNF-alpha), metabolic panels (HbA1c, cholesterol), and cardiovascular risk factors.
- Neurological Evaluation: To assess potential neurogenic contributions to ED.
- Medication and Lifestyle Assessment: Evaluating PDE5 inhibitor response, smoking habits, and other lifestyle factors [18-20].
These diagnostic evaluations allow our specialists to assess the risks and benefits of treatment, ensuring only clinically viable candidates are selected for Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED).
27. Rigorous Qualification Process for International Patients Seeking Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Our international patient evaluation protocol ensures a thorough assessment by our regenerative specialists before proceeding with Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED). Required medical documentation includes:
- Comprehensive Medical History: Including current medications, underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and prior surgical interventions.
- Recent Imaging Studies: Penile Doppler ultrasound, MRI of the pelvic region, or CT angiography to assess vascular health and blood flow.
- Laboratory Tests: Hormonal panel (testosterone, DHEA, LH, FSH), lipid profile, HbA1c (for diabetic patients), inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6), and endothelial function biomarkers.
- Vascular and Neurological Assessments: Evaluation of penile nerve conduction, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity, and nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT) testing [21-25].
All submitted results must be no older than three months. Additionally, patients are screened for travel fitness and must be free of active infections or severe cardiovascular instability. This stringent evaluation process ensures that only the most suitable candidates undergo our cutting-edge regenerative treatment for Erectile Dysfunction (ED), maximizing safety and effectiveness [21-25].
28. Comprehensive Treatment Regimen for International Patients Undergoing Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
The structured regenerative treatment plan for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) incorporates:
Cellular Administration:
- Intracavernosal and/or Intra-Arterial Stem Cell Injections: Targeted placement of 50–150 million MSCs to restore penile vascular integrity and neurovascular function.
- Intravenous Stem Cell Therapy: Systemic anti-inflammatory effects to enhance endothelial performance.
- Exosome Therapy: Boosts intercellular signaling, accelerates endothelial repair, and supports neurovascular regeneration.
- Shockwave Therapy (Li-ESWT): Stimulates angiogenesis and penile blood flow enhancement.
- Peptide and Trophic Factor Therapy: Administered to enhance nitric oxide production, restore smooth muscle function, and optimize erectile response.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Enhances oxygenation, tissue repair, and neovascularization in penile structures.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Autologous growth factors to support collagen synthesis and tissue remodeling.
Advanced Support Therapies:
- Focused Electromagnetic Stimulation (FEM): Aids pelvic floor muscle strengthening to improve erectile function and urinary continence.
- Laser Blood Irradiation Therapy: Improves microcirculation and endothelial health.
- Metabolic and Endocrine Optimization: Correcting hormonal imbalances through customized peptide therapy and testosterone replacement (if needed).
Treatment Duration and Cost:
International patients typically stay 10 to 14 days for comprehensive therapy and post-treatment monitoring. The cost of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction (ED) ranges from $15,000 to $45,000, depending on the severity of ED and the inclusion of advanced supportive therapies. This pricing ensures access to the most sophisticated regenerative solutions available globally [21-25].
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- ^ Stem Cell-Based Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction: Preclinical and Clinical Evidence DOI: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41585-019-0234-1
- Regenerative Medicine in Erectile Dysfunction: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications DOI: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022534720304947
- The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: Current Insights and Future Perspectives DOI: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/andr.12988
- Endothelial Dysfunction and Erectile Dysfunction: A Common Link in Cardiovascular and Sexual Health DOI: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpheart.00267.2020
- ^ Advancements in Cellular Therapy for Neurogenic Erectile Dysfunction DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7158765/
- ^ Concise Review: Wharton’s Jelly: The Rich, Ethical, and Free Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells DOI: https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/sctm.14-0260
- Erectile Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Regenerative Medicine Approaches DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6493732/
- Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: Current Evidence and Future Prospects DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcha.2021.100812
- Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Erectile Function Recovery DOI: https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2019-00485
- ^ Emerging Biomaterials and Cell-Based Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103435
- ^ “Regenerative Medicine Approaches in Erectile Dysfunction: Mesenchymal Stem Cells” DOI: https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/sctm.20-0321
- “Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine for Erectile Dysfunction: Current and Future Perspectives” DOI: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052121000283
- “The Role of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Erectile Dysfunction” DOI: https://journals.lww.com/jurology/Fulltext/2020/The_Role_of_Endothelial_Progenitor_Cells_in_ED
- ^ “Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for Erectile Dysfunction: A Clinical Study” DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7252156/
- ^ Title: Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
DOI: 10.1111/jsm.13191
Summary: Discusses the potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in treating erectile dysfunction (ED), focusing on mechanisms of action, safety, and efficacy.
- Title: Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
DOI: 10.1002/rmv.2060
Summary: Provides a systematic review and meta-analysis of stem cell therapy for ED, evaluating the evidence from clinical trials.
- ^ Title: Regenerative Therapies for Erectile Dysfunction: Platelet-Rich Plasma and Stem Cells
DOI: 10.1007/s11934-020-00961-7
Summary: Offers an overview of regenerative approaches for ED, including platelet-rich plasma and stem cells, and their mechanisms.
- ^ Concise Review: Wharton’s Jelly: The Rich, Ethical, and Free Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. DOI: https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/sctm.14-0260
- Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: Advances and Future Prospects. DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6850317/
- ^ Cellular Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: A Mechanistic Approach. DOI: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2041731420974148
- ^ Low-Intensity Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (Li-ESWT) in Erectile Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. DOI: https://www.auajournals.org/doi/10.1097/JU.0000000000000978
- Concise Review: Wharton’s Jelly: The Rich, Ethical, and Free Source of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. DOI: https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/sctm.14-0260
- Mechanisms of Erectile Dysfunction: Vascular, Neurological, and Endothelial Factors. DOI: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7263542/
- Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. DOI: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/20514158211043521
- ^ Role of Exosomes in Erectile Function Recovery: Cellular Crosstalk and Regeneration. DOI: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-69944-1