EGFR Mutations (EGFRM)
EGFR Mutations (EGFRM): Overview, Types, and Clinical Implications
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mutations (EGFRM) are genetic alterations in the EGFR gene that lead to abnormal cell growth and division, often resulting in cancer. These mutations are particularly significant in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), where they serve as a biomarker for targeted therapies. Below is a detailed overview of EGFR mutations, including their types, clinical implications, and treatment options.
Role of EGFR in Cell Growth
Normal Function:
- EGFR is a protein on the cell surface that helps cells grow and divide by sending signals in response to epidermal growth factor (EGF) binding.
Abnormal Function:
- Mutations in the EGFR gene cause the protein to be overactive, leading to uncontrolled cell proliferation and cancer.
Types of EGFR Mutations
Common Mutations in Lung Cancer:
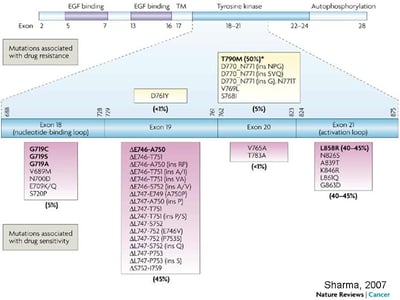
- Exon 19 Deletion: A deletion in the EGFR gene at Exon 19, leading to abnormal protein function.
- L858R Mutation: A point mutation in Exon 21, resulting in abnormal protein function[1][2][5].
Less Common Mutations:
- Exon 20 Insertions: Less responsive to standard EGFR inhibitors.
- T790M Mutation: Often associated with resistance to first-generation EGFR inhibitors[5][6].
Clinical Implications and Treatment
Prevalence in Lung Cancer:
- EGFR mutations are more common in non-smokers and light smokers, particularly in adenocarcinoma, a subtype of NSCLC[1][6].
- Approximately 10-15% of NSCLC cases in Western countries have EGFR mutations, with higher rates in Asian populations[6].
Targeted Therapies:
- EGFR inhibitors (e.g., gefitinib, erlotinib) are effective treatments for EGFR-positive NSCLC, offering improved outcomes compared to traditional chemotherapy[2][5].
- Resistance mutations, such as T790M, require newer generations of EGFR inhibitors like osimertinib[5].
Diagnosis and Testing
Tissue Biopsy:
- The most common method for detecting EGFR mutations, involving a sample of lung tissue analyzed for genetic alterations[6].
Liquid Biopsy:
- A less invasive technique using circulating tumor DNA in blood, becoming increasingly popular for monitoring and diagnosis[6].
Conclusion
EGFR mutations are critical biomarkers in lung cancer, guiding targeted therapies that have significantly improved treatment outcomes for patients with EGFR-positive NSCLC. Understanding these mutations is essential for personalized medicine approaches in oncology.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Bowel Obstruction (BO) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















