DNA Methylation (DNM)

DNA Methylation (DNM): Understanding the Epigenetic Mechanism
DNA Methylation (DNM) is a fundamental epigenetic mechanism that regulates gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence1378. It involves the addition of a methyl group (CH3) to a DNA molecule, typically to a cytosine base, forming 5-methylcytosine (5-mC)3. This process is crucial for various cellular functions, including genomic imprinting, genomic stability, and cellular differentiation3.
The Process of DNA Methylation
- Mechanism: DNA methylation involves the addition of a methyl group to the cytosine base in DNA3. This modification plays a key role in regulating gene activity3.
- Enzymes Involved: DNA methylation is catalyzed by a family of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs)24. Key enzymes include1:
- Targeting: How de novo DNMTs target specific genetic regions is still unclear; however, it is suggested that transcription factors regulate de novo DNA methylation by binding to specific DNA sequences to either recruit DNMTs for methylation or protect from DNA methylation2.
- Crosstalk: DNA methylation interacts with histone modifications and microRNA (miRNA) to regulate transcription2. DNMTs directly interact with enzymes that regulate histone modifications involved in gene repression2.
Basic Function of DNA Methylation
- Gene Expression Regulation: DNA methylation is crucial in regulating gene activity, where specific genes are activated or silenced based on the methylation pattern3.
- Genomic Imprinting: Genes are marked to reflect their parental origin, leading to differential expression based on whether the gene is inherited from the maternal or paternal lineage3.
- DNA Demethylation: 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine (5hmC) serves as an intermediate in the DNA demethylation pathway2.
Importance of DNA Methylation
Understanding DNA methylation is paramount in the life sciences because it influences gene expression patterns, genomic stability, and cellular differentiation3. As such, it is a central player in molecular biology and genetics3.
DNA Methylation and Anti-Aging: Understanding the Connection
DNA methylation, an epigenetic modification, plays a significant role in aging, age-related diseases, and longevity. It represents a link between genetic and environmental signals by regulating gene transcription1. Aberrant epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation, occur throughout the aging process at both cellular and organismal levels1.
DNA Methylation Changes During Aging
- Global Hypomethylation and Local Hypermethylation: Aging is associated with a general decrease in DNA methylation (hypomethylation) across the genome and an increase in methylation at specific sites, particularly CpG islands (hypermethylation)4.
- Sexually Divergent Changes: Age-related changes in DNA methylation can differ significantly between males and females. For example, in mice and humans, over 95% of age-related changes in DNA methylation in the hippocampus are sexually divergent2.
- Influence on Gene Expression: Changes in DNA methylation patterns can affect gene regulation, potentially leading to less efficient gene regulation due to global hypomethylation or inappropriate silencing of specific genes due to CpG island hypermethylation4.
Role of DNA Methylation in Aging
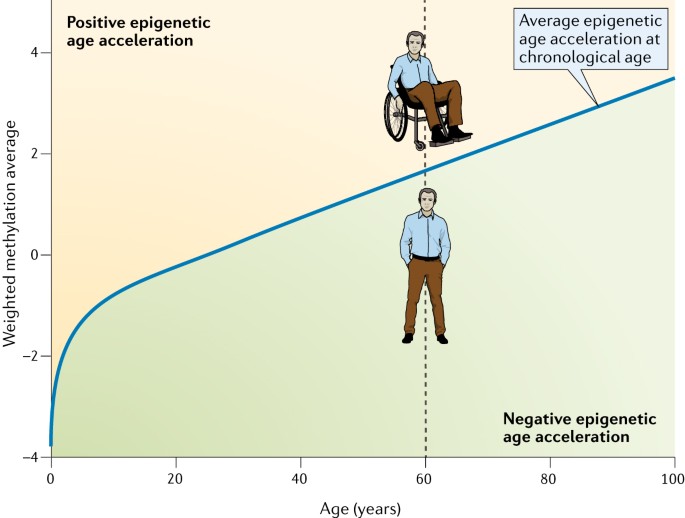
- Epigenetic Clocks: DNA methylation changes at specific CpG sites can be used to create epigenetic clocks that accurately predict chronological age in various species, including humans2. These clocks are also considered reliable biomarkers for predicting mortality5.
- Age-Related Diseases: Aberrant DNA methylation patterns are implicated in the pathogenesis of age-related diseases1. Mutations in genes like TET2 or DNMT3A, which are involved in DNA methylation, can increase the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chronic inflammation, associated with cardiovascular disease3.
- Genome Stability: DNA methylation is crucial for maintaining genome stability, and age-related changes in methylation patterns may contribute to genome instability and aging phenotypes4.
Interventions Targeting DNA Methylation for Anti-Aging
- Caloric Restriction (CR): CR is a proven intervention strategy to prevent or delay age-related diseases and extend lifespan. It can reverse aberrant methylation status, suggesting that changing DNA methylation is an underlying mechanism involved in CR response1.
- NAD+ Precursors: Supplementation with NAD+ precursors like nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) and nicotinamide riboside (NR) can prevent the decline in NAD+ levels, exhibiting beneficial effects against aging and aging-related diseases. NAD+ plays a role in DNA repair and epigenetic regulation3.
- Dietary Supplementation and Chemical Drugs: Emerging evidence suggests that certain interventions, such as dietary supplementation and chemical drugs, can prevent age-related diseases and promote longevity, at least in part, through reversing the aberrant age-associated changes in DNA methylation1.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHM): can reduce the DNA methylation age of primary human keratinocytes6.
- CALERIE intervention: Slowed the pace of aging, as measured by the DunedinPACE DNAm algorithm7.
Conclusion
DNA methylation plays a crucial role in aging and longevity. Age-related changes in DNA methylation patterns can influence gene expression, genome stability, and the development of age-related diseases. Interventions like caloric restriction and NAD+ supplementation may promote healthy aging by modulating DNA methylation patterns. Further research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of targeting DNA methylation to prevent age-related diseases and promote healthy longevity.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing genomic, cellular health and various health conditions. If you have questions about DNA methylation or would like more information on our services related to molecular biology, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References:
- DNA Methylation As an Epigenetic Mechanism in the Development of Multiple Sclerosis: Discusses how DNA methylation functions as a key epigenetic mechanism in regulating gene expression and summarizes data on MS risk factors that can affect the DNA methylation profile DOI: https://doi.org/10.32607/actanaturae.11043
- Roles and Mechanisms of DNA Methylation in Vascular Aging and Related Diseases: This article describes how DNA methylation regulates gene expression by recruiting proteins involved in gene repression or by inhibiting the binding of transcription factor(s) to DNA. DOI:https://www.nature.com/articles/npp2012112
- DNA methylation: The epigenetic mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease: This study dives into how DNA methylation is a major epigenetic mechanism that normally represses gene expression, whereas demethylation induces gene reactivation. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ibra.12121















