Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cell Therapy
Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cell Therapy: Overview and Clinical Applications
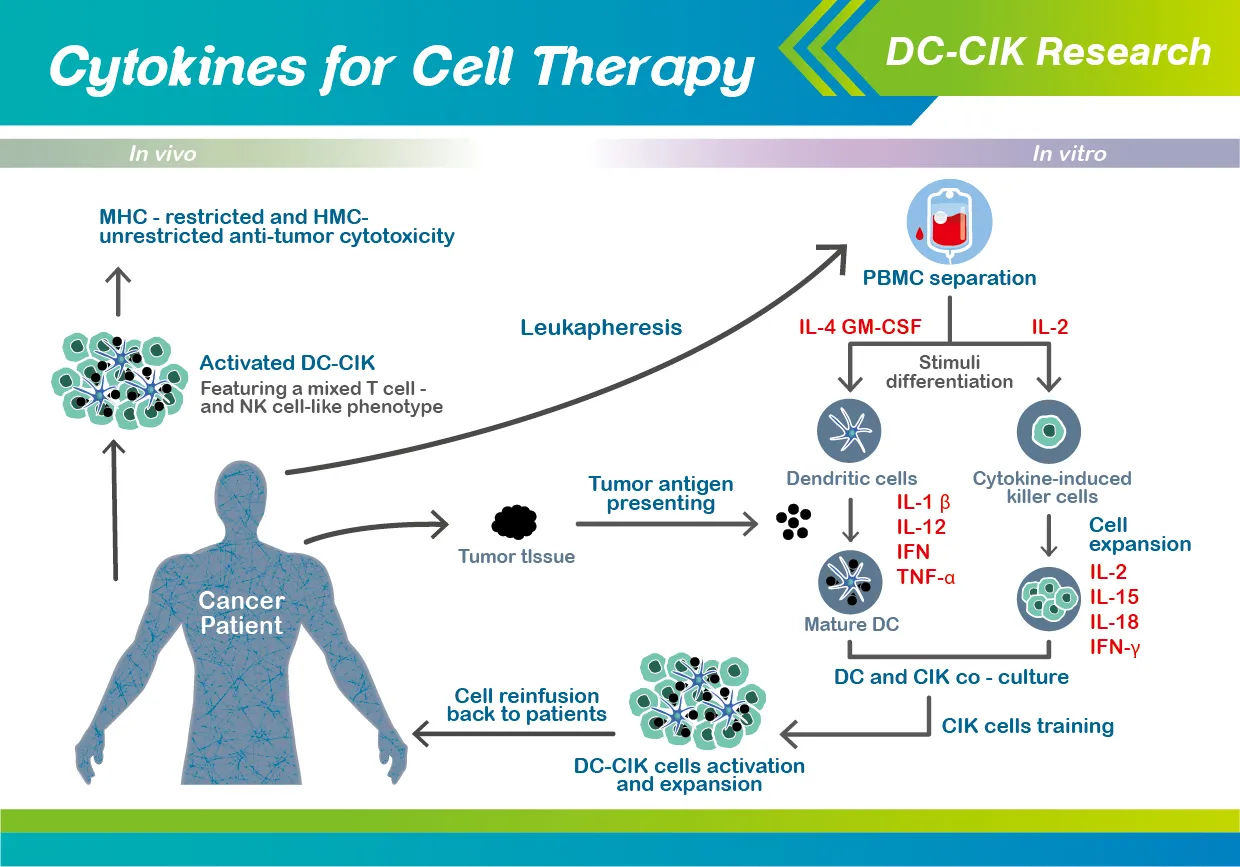
Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cell Therapy are heterogeneous immune effector cells with hybrid T-cell and natural killer (NK) cell properties. Generated ex vivo from peripheral or cord blood mononuclear cells using cytokines (interferon-γ, IL-2, anti-CD3 antibody), they exhibit potent MHC-unrestricted cytotoxicity against tumors. Below is a synthesis of their mechanisms, clinical utility, and challenges.
Mechanisms of Action
Tumor Recognition:
- NK-like receptors (NKG2D, DNAM-1, NKp30) target overexpressed ligands on cancer cells, enabling MHC-independent killing.
- T-cell receptors (TCRs) allow MHC-restricted cytotoxicity.
Cytolytic Activity:
- Direct lysis via perforin/granzyme release and Fas/FasL pathways.
- Secretion of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 to enhance immune responses.
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC):
- CD16a (FcγRIIIa) on CIK cells binds tumor-bound antibodies (e.g., cetuximab), improving targeting in cancers like triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)[1][2].
Clinical Applications
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Improved median overall survival (mOS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) when combined with surgery or chemotherapy[4][5].
- Colorectal cancer (CRC): Enhanced survival rates and reduced recurrence in meta-analyses[3][4].
- TNBC: CIK + cetuximab reduced tumor growth and metastasis in preclinical models[1].
- Post-allogeneic HSCT: CIK cells show graft-versus-leukemia effects with lower GVHD risk compared to donor lymphocyte infusions (DLI)[3][6].
Combination Therapies:
- DC-CIK: Dendritic cells enhance CIK activity via antigen presentation (e.g., improved survival in pancreatic and breast cancers)[3][4].
- Checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy: Synergistic effects observed in trials[2][5].
Advantages Over Other Therapies
- Safety: Minimal toxicity (e.g., low rates of cytokine release syndrome) and no severe graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)[2][4].
- Broad Targeting: Effective against MHC-negative and drug-resistant tumors[1][5].
- Ease of Production: Cost-effective expansion from peripheral blood[6].
Clinical Trial Outcomes
| Cancer Type | Key Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HCC | 14-month RFS benefit post-curative therapy; improved OS vs. controls[5]. | [4][5] |
| Metastatic TNBC | CIK + cetuximab reduced metastasis by 90% in murine models[1]. | [1] |
| Post-HSCT relapse | 28% complete remission rate with low GVHD incidence[3][6]. | [3][6] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | DC-CIK + S-1 chemotherapy improved 6-month OS (62.2% vs. 25% in chemotherapy)[3]. | [3] |
Challenges and Future Directions
Standardization:
- Variability in cell expansion protocols and quality control[4][6].
Combination Strategies:
- CAR-CIK: Engineering CIK cells with chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) for precision targeting[2][5].
- Bispecific antibodies: Redirect CIK cells to tumor-specific antigens[5].
Biomarker Development:
- Use of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) to monitor response[6].
Conclusion
CIK cell therapy offers a versatile, low-toxicity approach for diverse cancers, particularly in combination with conventional treatments. While challenges in standardization persist, ongoing innovations in CAR engineering and biomarker integration hold promise for broader clinical adoption.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Cytokine-Induced Killer (CIK) Cell Therapy or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References















