Cardiomyopathy (CMP)
Cardiomyopathy (CMP): Understanding the Disease
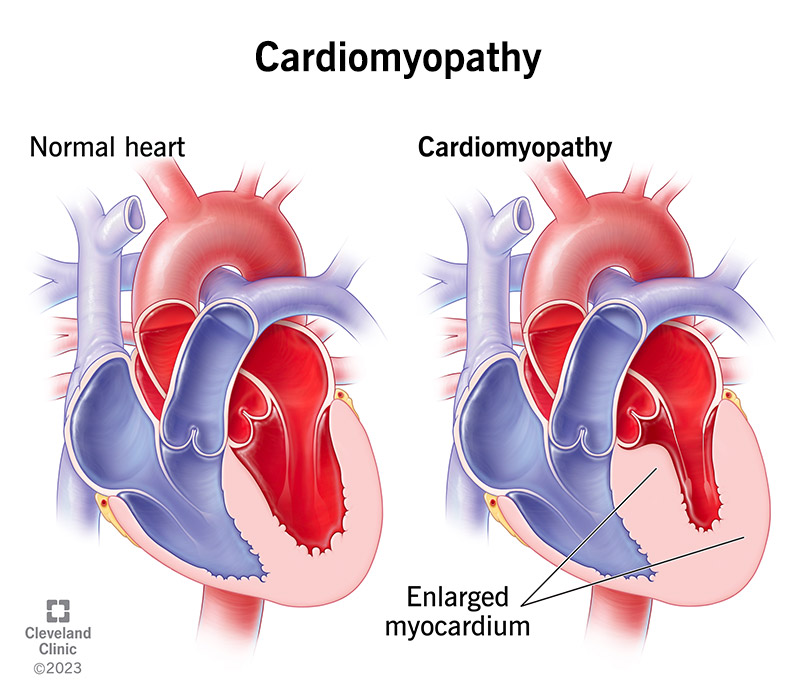
Cardiomyopathy (CMP) is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body1. It encompasses a collection of diverse conditions with many causes, symptoms, and treatments, affecting people of all ages and races2. In most cases, the heart muscle becomes enlarged, thick, or rigid1. In rare instances, diseased heart muscle tissue is replaced with scar tissue1.
Types of Cardiomyopathy
The main types of cardiomyopathy are:
- Dilated cardiomyopathy: One of the pumping chambers (ventricles) of the heart is enlarged2. It is the most common form of cardiomyopathy in children2.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The heart muscle is thickened2. It can cause sudden death in adolescents and young adult athletes2.
- Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: The disease causes irregular heartbeats or rhythms2.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy: Heart muscle is stiff or scarred, or both2.
- Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM)1.
Some other types of cardiomyopathy are called “unclassified cardiomyopathy”1. Another type, which usually follows acute emotional stress, is “stress-induced cardiomyopathy,” also known as broken heart syndrome1.
Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
Some people who have cardiomyopathy never have symptoms, while others may show signs as the disease progresses2. These might include the following27:
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially with physical exertion27
- Fatigue2
- Swelling in the ankles and legs2
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations2
- Dizziness37
- Fainting27
- Chest pain34
- Heart murmurs (extra or unusual sounds heard with heartbeats)7
Causes of Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy can be “acquired” when it develops due to another disease, condition, or factor12. Or cardiomyopathy can be “inherited” when the gene for the disease is passed on from a parent12. In many cases, the cause of cardiomyopathy isn’t known12. Certain diseases or conditions can lead to cardiomyopathy2:
- A family history of cardiomyopathy, heart failure, or sudden cardiac arrest2
- Connective tissue disease and other types of autoimmune disease2
- Coronary heart disease or a heart attack23
- Diseases that can damage the heart, such as hemochromatosis, sarcoidosis or amyloidosis2
- Endocrine diseases, including thyroid conditions and diabetes2
- Infections in the heart muscle23
- Long-term alcoholism or cocaine abuse2
- Muscle conditions such as muscular dystrophy2
- Pregnancy2
Diagnosis and Treatment
A cardiologist or pediatric cardiologist usually diagnoses and treats cardiomyopathy7. Your health care professional will diagnose cardiomyopathy based on your medical history, family history, a physical exam and diagnostic test results7. Treatment options for cardiomyopathy include lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery3.
Risks and Complications
As cardiomyopathy worsens, the heart becomes weaker1. The heart becomes less able to pump blood throughout the body and incapable of maintaining a normal electrical rhythm1. The result can be heart failure or irregular heartbeats called arrhythmias1. A weakened heart also can cause other complications, such as heart valve problems1.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing cardiovascular health. If you have questions about cardiomyopathy or would like more information on our services related to cardiovascular care, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- American Heart Association: What Is Cardiomyopathy?1
- CDC: About Cardiomyopathy2
- Healthline: Cardiomyopathy3
- WebMD: Cardiomyopathy4
- Cleveland Clinic: Cardiomyopathy5
- Johns Hopkins Medicine: Cardiomyopathy6
- American Heart Association: Symptoms and Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy7
- NHLBI: What Is Cardiomyopathy?8















