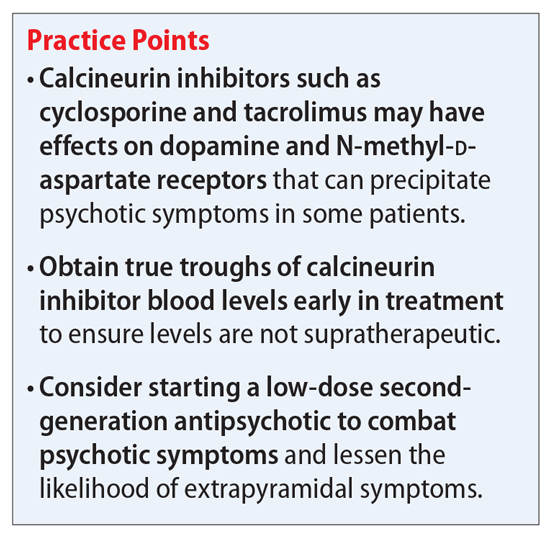
Calcineurin Inhibitors (CAI)
Calcineurin Inhibitors (CAI): Overview and Uses in Skin Conditions
What Are Calcineurin Inhibitors?
Calcineurin inhibitors (CAI) are immune-modulating medications used topically to treat various inflammatory skin conditions, especially atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, and sometimes other skin disorders. They work by suppressing the activation of T-lymphocytes, thereby reducing inflammation and immune response.
Common Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
- Tacrolimus (Protopic): Usually prescribed for moderate to severe eczema and vitiligo. Available as ointment in 0.1% and 0.03% strengths.
- Pimecrolimus (Elidel): Typically used for mild to moderate eczema, particularly facial and sensitive skin areas.
How Do They Work?
- Block calcineurin, a protein essential for T-cell activation.
- Reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha.
- Decrease skin inflammation, redness, itching, and immune-mediated pigmentary changes.
- Promote repigmentation in conditions like vitiligo, especially in small, localized areas.
Clinical Uses
- Atopic Dermatitis: Second-line therapy when corticosteroids are unsuitable or long-term management needed.
- Vitiligo: Off-label use to stimulate melanocyte activity and repigmentation.
- Other Applications: Potential off-label use for inflammatory skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and certain pigmentary disorders.
Advantages and Safety Profile
- Do not cause skin atrophy or telangiectasia, common side effects of topical steroids.
- Well-tolerated with transient side effects like mild burning, stinging, or erythema.
- Suitable for sensitive areas such as eyelids, face, and genitals.
- Can be used long-term safely, especially in areas prone to steroid side effects.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
- Mild transient irritation, redness, or burning.
- Rarely, induced lentiginosis or hyperpigmentation at application sites.
- Caution in immunocompromised patients; avoid use with certain vaccinations.
Summary
Calcineurin inhibitors are effective, steroid-sparing agents for inflammatory skin conditions and pigmentary disorders like vitiligo. They provide anti-inflammatory benefits while minimizing adverse effects associated with corticosteroids.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For personalized treatment plans involving calcineurin inhibitors for your skin condition, contact our dermatology specialists who tailor therapy to optimize outcomes and safety.
References:
- Wollina U. The Role of Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors for Skin Diseases Other Than Atopic Dermatitis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2007;8(3):157-73. doi:10.2165/00128071-200708030-00003. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17492844/
- Wang Y, Xu Y, Sheng S, et al. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors in Dermatology: A Comprehensive Review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013 Jun;68(6):1003-1020. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2012.11.023. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834721/
- Asgari MM, Tsai A, Avalos L, et al. Association Between Topical Calcineurin Inhibitor Use and Keratinocyte Carcinoma Risk Among Adults With Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Oct;156(10):1066-1073. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.2240. Available at: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamadermatology/fullarticle/2768937
- Primary Care Dermatology Society. Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors. 2024 Mar 2. Available at: https://www.pcds.org.uk/clinical-guidance/topical-calcineurin-inhibitors















