Cachexia (CCX)
Cachexia (CCX): Definition and Characteristics
What is Cachexia?
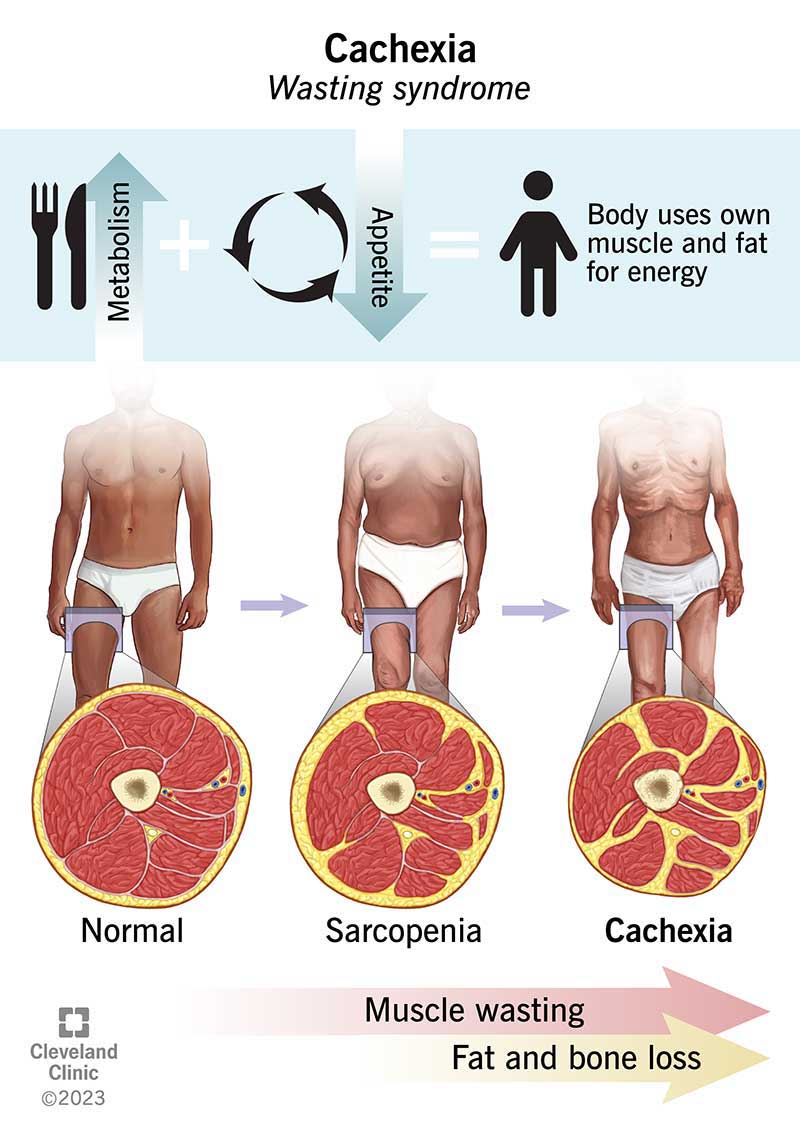
Cachexia (CCX) is a complex metabolic syndrome characterized by severe muscle wasting (sarcopenia) and fat loss that cannot be fully reversed by conventional nutritional support. It is commonly seen in patients with chronic illnesses, especially advanced cancers. Cachexia leads to weakness, fatigue, reduced functional ability, and worsened prognosis.
Characteristics
Mechanism
Cachexia results from a combination of reduced food intake and an abnormal metabolism driven by inflammation, increased catabolism, insulin resistance, and hormonal changes. Tumor-derived factors and host inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and interferon-gamma contribute to muscle protein degradation and fat breakdown. Unlike starvation, cachexia involves persistent muscle loss despite adequate nutrition.
Symptoms
- Significant unintended weight loss involving both fat and skeletal muscle.
- Loss of appetite and early satiety
- Fatigue and reduced strength
- Anemia
- Physical weakness and impaired mobility
These symptoms are usually progressive and worsen as the underlying illness advances.
Stages
- Pre-cachexia: Early weight loss less than 5%, appetite changes, mild inflammation.
- Cachexia: Weight loss more than 5%, muscle wasting, fatigue, and systemic inflammation.
- Refractory cachexia: Severe, unresponsive to treatment, with ongoing weight and muscle loss, often in terminal stages.
Clinical Significance
Cachexia negatively impacts quality of life, reduces effectiveness of chemotherapy, increases treatment toxicity, and is responsible for up to 20% of cancer-related deaths. Early recognition and a multidisciplinary treatment approach involving nutrition, pharmacological agents, and symptom management are essential. Currently, no single treatment can fully reverse cachexia, but interventions may slow progression and improve patient outcomes.
Key Points
- Cachexia is a wasting syndrome with irreversible muscle and fat loss.
- Driven by inflammation, metabolic disturbances, and reduced intake.
- Significantly worsens prognosis in cancer and other chronic diseases.
- Requires early identification and integrated management.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plans in cachexia, consult with our oncology, nutrition, and palliative care specialists to optimize quality of life and clinical outcomes utilizing Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells .
References:
- Argilés JM, et al. Cancer cachexia: understanding the molecular basis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Nov;14(11):754-62. doi:10.1038/nrc3829. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3829
- Takaoka T, et al. Prevalence of and survival with cachexia among patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer. 2024 Apr;32(4):2345-2356. doi:10.1007/s00520-023-07896-8. Available at: ttps://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-023-07896-8[]
- en H, et al. Efficacy and safety of pharmacotherapy for cancer cachexia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2024 Mar;13(3):517-528. doi:10.1002/cam4.70166. Available at: htps://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.70166[6] 4.
- O, et al. Prognostic significance of the cachexia index in cancer patients: a systematic review. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2025 Apr;55:102-110. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.03.023. Available at: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.03.023[7]















