Brain (B)
Brain (B): Anatomy and Function
Definition:
The brain is the central organ of the nervous system, housed within the protective structure of the skull. It is responsible for processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and facilitating cognitive abilities such as thought, memory, and emotion. The brain is composed of various specialized regions that work together to control both voluntary and involuntary actions.
Anatomy:
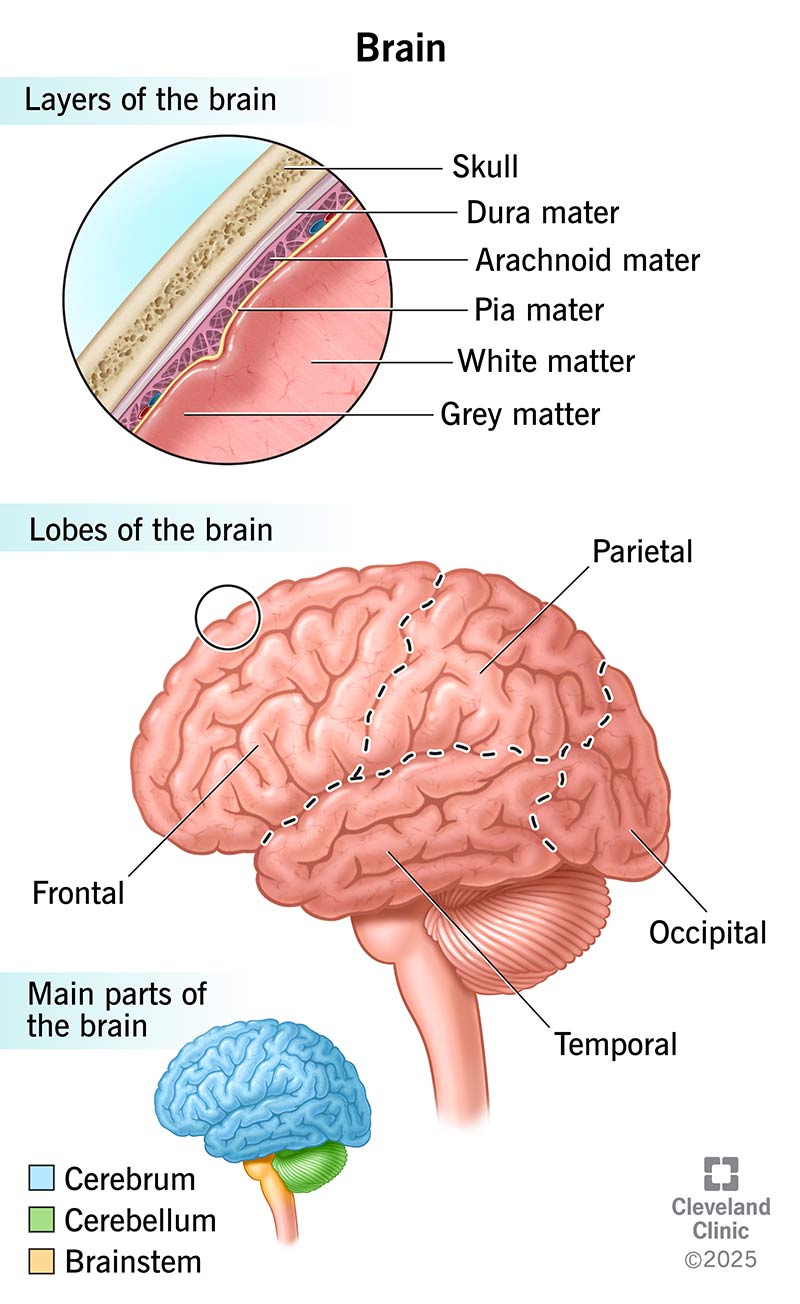
The brain can be divided into several key components:
- Cerebral Cortex: The outer layer of the brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, language, and decision-making. It is divided into four lobes:
- Frontal Lobe: Involved in motor function, language, memory, and executive functions.
- Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information related to touch, temperature, and pain.
- Temporal Lobe: Responsible for auditory processing and memory formation.
- Occipital Lobe: Primarily involved in visual processing.
- Brainstem: Comprising the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, the brainstem controls basic life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It acts as a relay station for signals between the brain and spinal cord.
- Cerebellum: Located at the back of the brain, the cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements and maintains posture and balance.
- Limbic System: Often referred to as the “emotional brain,” this system includes structures such as the amygdala and hippocampus, which are crucial for emotion regulation and memory processing.
Functions:
The brain performs numerous essential functions:
- Sensory Processing: Interpreting signals from the five senses (sight, sound, touch, taste, smell) to create a coherent understanding of the environment.
- Motor Control: Sending signals to muscles to facilitate movement.
- Cognitive Functions: Enabling reasoning, problem-solving, planning, and emotional responses.
- Homeostasis Regulation: Maintaining internal balance by regulating bodily functions such as temperature and hunger.
Clinical Implications:
Damage or disease affecting the brain can lead to various neurological disorders:
- Cognitive Impairments: Conditions like Alzheimer’s disease can affect memory and reasoning abilities.
- Motor Disorders: Diseases such as Parkinson’s can impair movement control due to degeneration of specific neuron populations in the brain.
- Emotional Dysregulation: Mental health disorders can arise from imbalances in neurotransmitter systems within the brain.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we focus on innovative therapies aimed at enhancing brain health. Our advanced regenerative treatments utilize Cellular Therapy and Stem Cell technology to promote neural repair, improve cognitive function, and support emotional well-being. If you or a loved one is seeking cutting-edge solutions for neurological conditions or cognitive enhancement, consult with our experts today to explore personalized treatment options!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Anatomy of the Brain – AANS
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110188
This article provides a comprehensive overview of brain anatomy including its protective layers and major structures. - Brain Anatomy – Physiopedia
DOI: 10.1007/s00702-020-02238-x
This resource discusses various aspects of brain anatomy along with its functional significance in health. - The Human Brain: Parts, Function, Diagram – Medical News Today
DOI: 10.1016/j.cancercare.2020.01.001
This publication outlines the different parts of the human brain while explaining their specific roles in processing information. - Brain Anatomy and How It Works – Johns Hopkins Medicine
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110188
This article explores how various parts of the brain interact to regulate bodily functions and maintain homeostasis. - Structure of Human Brain – BYJU’S
DOI: 10.1007/s00702-020-02238-x
This educational piece covers key structural components of the human brain along with their respective functions in daily life activities.















