Brain and Spinal Cord
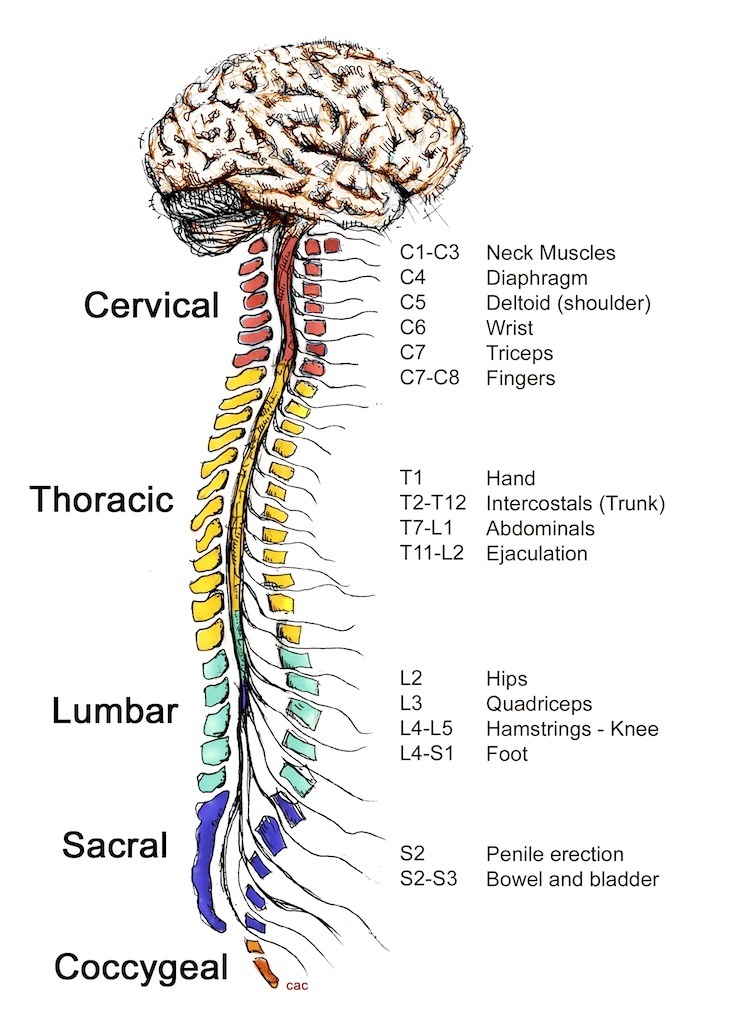
Brain and Spinal Cord: Understanding the Central Nervous System
Definition:
The brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system (CNS), a complex network responsible for analyzing, integrating, and coordinating bodily functions. The brain, housed within the skull, acts as the control center for movement, speech, memory, and emotions. The spinal cord, an extension of the brain, transmits motor commands and sensory information between the brain and the rest of the body, ensuring seamless communication and response to stimuli.
Functions:
The brain and spinal cord perform several critical functions:
- Sensory Processing: Receiving and interpreting sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
- Motor Control: Initiating and coordinating voluntary muscle movements.
- Reflex Actions: Facilitating quick, involuntary responses to stimuli.
- Communication: Transmitting messages between the brain and the body to regulate bodily functions.
Anatomy:
The spinal cord features distinct regions:
- Gray Matter: Located centrally, containing nerve cell bodies responsible for processing sensory information and controlling motor functions.
- White Matter: Surrounding the gray matter, composed of nerve fiber bundles (tracts) that transmit signals up and down the spinal cord.
- Spinal Nerves: Sensory nerve fibers enter via the posterior (dorsal) root, while motor fibers exit via the anterior (ventral) root.
Clinical Implications:
Damage to the CNS can result in significant functional changes:
- Motor Impairment: Injuries can lead to movement disorders or paralysis.
- Sensory Deficits: Damage may affect sensations such as touch or pain perception.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Spinal cord injuries can disrupt autonomic functions like blood pressure regulation or bladder control.
Diagnosis and Management:
Neurological assessments, imaging studies (e.g., MRI or CT scans), and specialized treatments are essential for managing CNS conditions.
- Rehabilitation: Physical and occupational therapy help restore motor and sensory functions.
- Medications: Various drugs can manage pain, inflammation, or other symptoms associated with CNS damage.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we offer cutting-edge regenerative therapies to support brain and spinal cord health. Our personalized treatment plans leverage advanced Cellular Therapy and Stem Cell technologies to promote neural repair, reduce inflammation, and improve overall neurological function. If you or a loved one is seeking innovative solutions for neurological conditions or injuries, consult with our experts today to explore how our comprehensive care can enhance your quality of life!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Central Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure & Function – Kenhub
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110188
This article provides an in-depth overview of CNS anatomy, focusing on its structure and functional roles in coordinating bodily activities. - Central Nervous System (CNS): What It Is & Function – Cleveland Clinic
DOI: 10.1007/s13311-011-0068-7
This resource outlines how the CNS regulates thoughts, feelings, movements, and autonomic functions through its intricate network of neurons. - The Brain and Spinal Cord | Canadian Cancer Society
DOI: 10.1016/j.cancercare.2020.01.001
This publication discusses CNS anatomy in detail while highlighting its role in neurological health and disease management. - Central Nervous System: Structure & Function – Medical News Today
DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2020.110188
This article explores CNS functionality while addressing common conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord. - Physiology of the Spinal Cord – StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf)
DOI: 10.1007/s00702-020-02238-x
This detailed review focuses on spinal cord physiology, including its role in motor commands, sensory input processing, and reflex actions.















