Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The Autonomic Nervous System: A Vital Regulator of Bodily Functions
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a crucial component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary bodily functions. It operates largely unconsciously, controlling essential processes such as heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, and the functioning of glands. Understanding the structure and function of the ANS is essential for recognizing its role in maintaining homeostasis and responding to stress.
Key Components of the Autonomic Nervous System
- Divisions of the ANS:
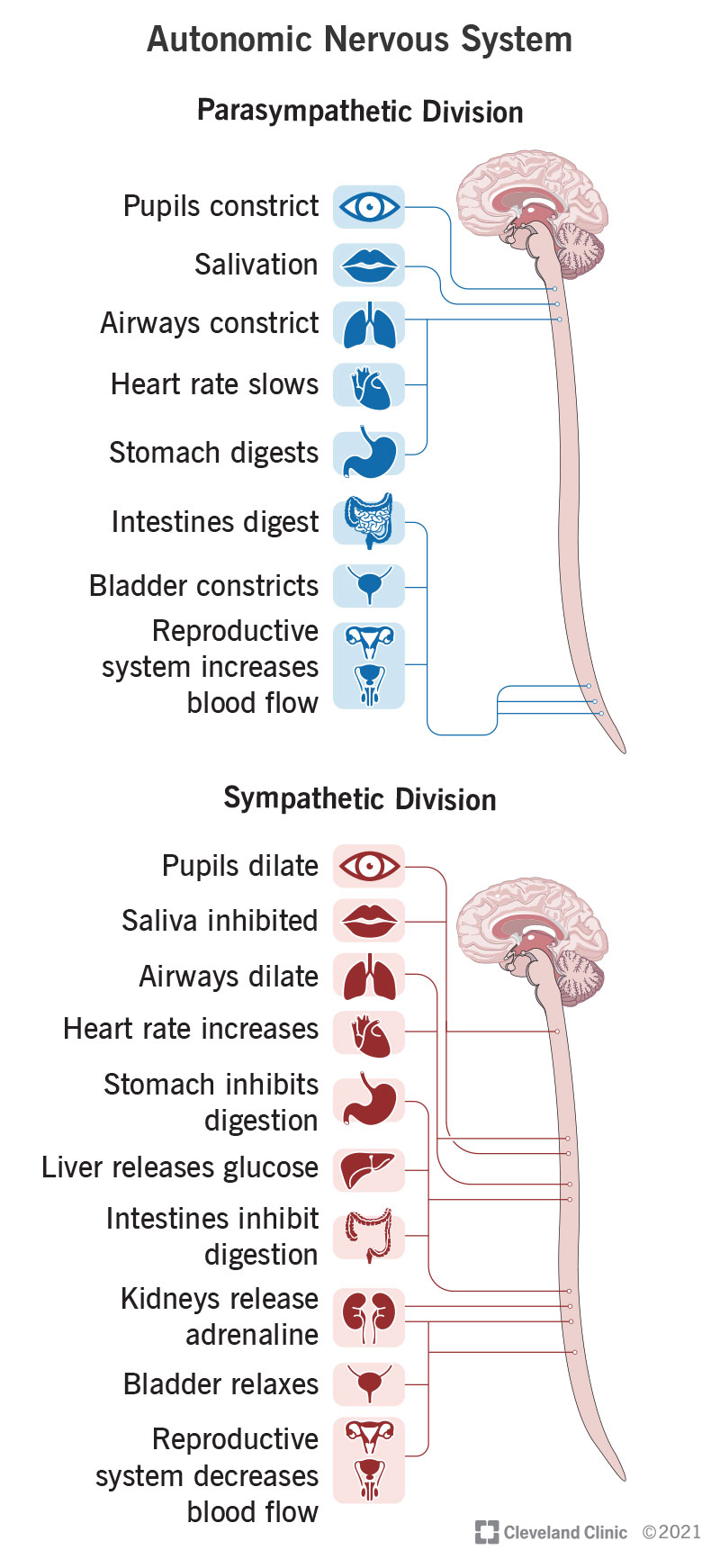
- Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS): Often referred to as the “fight or flight” system, the SNS prepares the body for stressful situations by increasing heart rate, dilating airways, and redirecting blood flow to muscles. It stimulates energy expenditure and inhibits non-essential functions like digestion.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS): Known as the “rest and digest” system, the PNS promotes relaxation and conservation of energy. It slows heart rate, enhances digestive processes, and facilitates recovery after stress.
- Enteric Nervous System (ENS): Sometimes considered a part of the ANS, the ENS governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract independently but can communicate with both the SNS and PNS.
- Neuronal Pathways:
The ANS operates through a two-neuron pathway:- Preganglionic Neuron: Originates in the central nervous system (CNS) and synapses in an autonomic ganglion.
- Postganglionic Neuron: Extends from the ganglion to target organs. This structure allows for complex reflexes and modulation of responses.
- Neurotransmitters:
- Preganglionic fibers in both SNS and PNS release acetylcholine (ACh).
- Postganglionic fibers release different neurotransmitters: norepinephrine for most sympathetic fibers and ACh for parasympathetic fibers.
Functions of the Autonomic Nervous System
The ANS plays a vital role in regulating various involuntary functions:
- Cardiovascular Regulation: Controls heart rate and blood pressure through sympathetic stimulation during stress and parasympathetic activity during rest.
- Respiratory Control: Adjusts breathing rates based on metabolic needs, increasing during exercise or stress while slowing during relaxation.
- Digestive Processes: The PNS stimulates digestive secretions and motility, while the SNS inhibits these functions during stress.
- Temperature Regulation: The ANS regulates sweating and blood flow to maintain body temperature.
- Urinary Function: Controls bladder contraction and relaxation through autonomic pathways.
Clinical Implications
Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system can lead to various disorders:
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Often seen in diabetes, it can affect heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder control.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: A condition where blood pressure drops significantly upon standing, leading to dizziness or fainting due to impaired autonomic regulation.
- Dysautonomia: A term for disorders that affect autonomic function, causing symptoms like abnormal heart rates, gastrointestinal issues, or temperature regulation problems.
Conclusion
The autonomic nervous system is essential for regulating involuntary bodily functions that maintain homeostasis. Its complex interactions between sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions allow for adaptive responses to various internal and external stimuli. Understanding its structure and function is crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions related to autonomic dysfunction.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations of nervous system health as part of our holistic approach to patient care. If you have questions about your autonomic nervous system function or would like more information on our services related to neurological health, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Wikipedia: Autonomic Nervous System
Overview of the structure and functions of the autonomic nervous system. - Kenhub: Anatomy of the Autonomic Nervous System
Discusses anatomical features and functional divisions within the ANS. - MSD Manuals: Overview of Autonomic Nervous System
Provides insights into disorders related to autonomic dysfunction. - Cleveland Clinic: Autonomic Nervous System
Highlights effects on various body systems regulated by the ANS. - Verywell Mind: Autonomic Nervous System
Overview of anatomy, function, and common disorders associated with the ANS. - Britannica: Autonomic Nervous System
Summary of structure and functions within the autonomic nervous system.















