Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test: A Comprehensive Overview
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test is a crucial diagnostic procedure used to measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood, as well as the blood’s pH balance[1][4][2]. Unlike a blood gas analysis that can use blood from any part of the circulatory system, an ABG specifically requires a sample drawn from an artery[4]. This test provides valuable information about a patient’s ventilation, gas exchange, and acid-base status[5]. ABGs are commonly performed in intensive care units and emergency settings to quickly assess and manage critical illnesses[1][4].
What ABG Measures
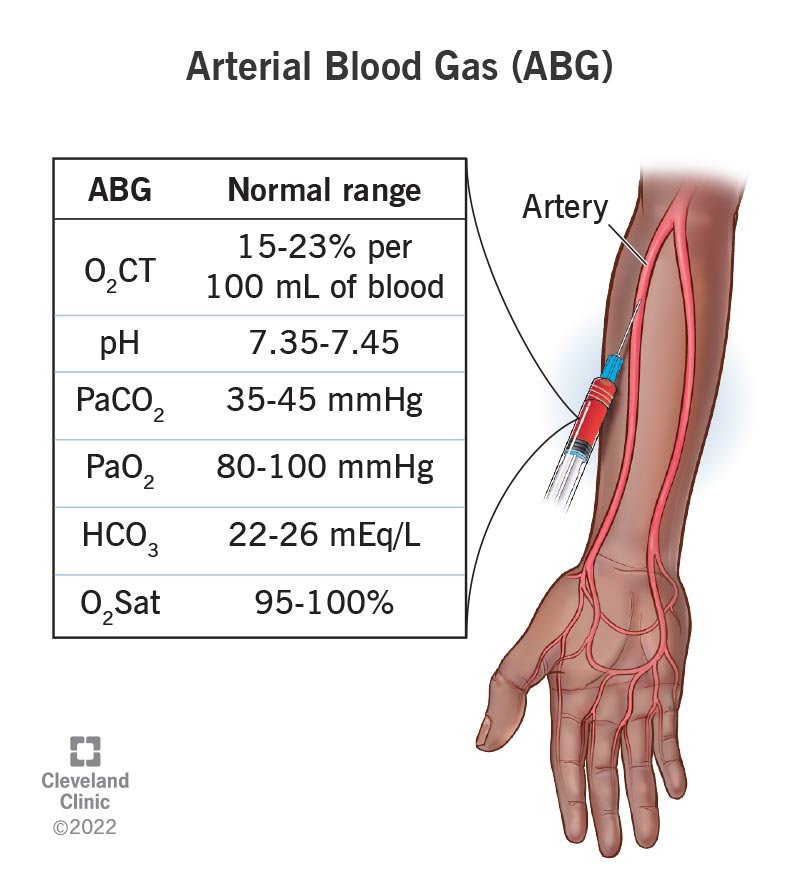
An ABG test typically includes the following measurements[4]:
- pH: Reflects the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in the blood, indicating acidity or alkalinity. Normal range is 7.35 to 7.45[3].
- Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PaO2): Measures the amount of oxygen gas dissolved in the blood.
- Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide (PaCO2): Measures the amount of carbon dioxide gas dissolved in the blood.
- Arterial Oxygen Saturation (SaO2): Indicates the percentage of hemoglobin saturated with oxygen[1].
- Bicarbonate (HCO3-): A base that helps regulate the pH of the blood. Normal range is 21 to 28 mEq/L[3].
Why is an ABG Test Performed?
ABG tests are used in a variety of clinical settings to[4]:
- Evaluate lung conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia[4][5].
- Diagnose serious breathing problems and respiratory failure[2][5].
- Check the acid-base balance in the blood[2].
- Assess the effectiveness of treatments for lung conditions and other conditions that affect acid-base balance[2][5].
- Diagnose kidney disorders[2].
- Detect conditions causing respiratory failure, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and drug overdose[5].
How is an ABG Test Performed?
- Sampling: Blood is typically drawn from the radial artery in the wrist because it is easily accessible and has less risk for vascular occlusion[1][5]. The brachial artery or femoral artery may also be used, especially in emergency situations or with children[1]. An Allen’s test is often performed to assess the adequacy of collateral circulation in the hand before radial artery puncture[1].
- Procedure: A respiratory therapist, phlebotomist, nurse, paramedic, or doctor usually performs the test[1]. The site is cleaned with an antiseptic solution, and a small needle is inserted into the artery to draw the blood sample[1][5].
- Sample Handling: The blood sample is collected in a syringe pre-packaged with heparin to prevent coagulation[1]. Any air bubbles are removed to ensure accurate results[1]. The sample should be analyzed within 30 minutes if a plastic syringe is used and kept at room temperature, or immediately placed on ice if a glass syringe is used and analysis will be delayed[1].
- Analysis: The sample is taken to a blood gas analyzer, which measures the pH, PaO2, and PaCO2[1]. Bicarbonate concentration and SaO2 are calculated from these measured values[1].
Interpretation of Results
ABG test results can help healthcare providers assess various conditions, including[4][5]:
- Acidosis: A condition in which the blood has too much acid (pH < 7.35)[3].
- Alkalosis: A condition in which the blood has too much base (pH > 7.45)[3].
- Hypoxemia: Low blood oxygen levels, which can lead to serious conditions and organ damage[4].
- Hypercapnia: Elevated carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
ABG results can also indicate problems with the lungs, kidneys, or metabolic processes[4][5].
DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand and ABG Testing
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, ABG testing may be utilized as part of our comprehensive patient evaluation to:
- Assess respiratory and metabolic function before and after Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells.
- Monitor the effectiveness of treatments aimed at improving overall health and well-being.
- Provide a baseline assessment for patients undergoing regenerative medicine procedures.
While ABG testing is not directly Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells, it provides crucial data to ensure patient safety and optimize treatment strategies.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Arterial blood gas test – Wikipedia. Link
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test – MedlinePlus. Link
- Arterial blood gas (ABG) – Overview: Nursing: Video & Causes. Link
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG): What It Is, Purpose, Procedure & Levels. Link
- Arterial Blood Gases – Physiopedia. Link
- Arterial Blood Gas – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf. Link
- Arterial Blood Gases – Clinical Methods – NCBI Bookshelf. Link









![An arterial blood gas (ABG) test is a crucial diagnostic procedure used to measure the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood, as well as the blood's pH balance[1][4][2]. Unlike a blood gas analysis that can use blood from any part of the circulatory system, an ABG specifically requires a sample drawn from an artery[4]. This test provides valuable information about a patient's ventilation, gas exchange, and acid-base status[5]. ABGs are commonly performed in intensive care units and emergency settings to quickly assess and manage critical illnesses[1][4].](https://cdn.drstemcellsthailand.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/image-48.png)





