Ammonia (AMN)
Ammonia (AMN) Toxicity and Neurological Impact
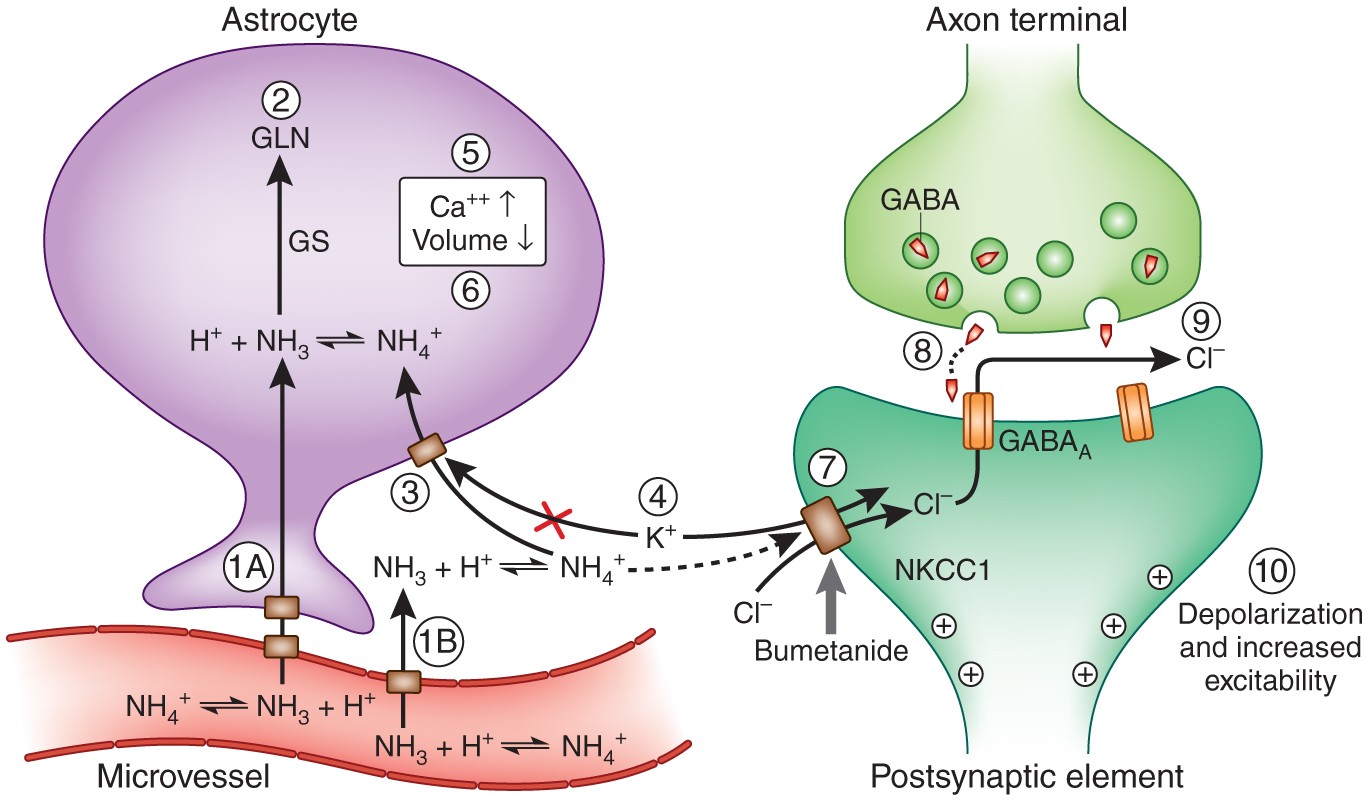
Ammonia (AMN)(NH₃/NH₄⁺) is a potent neurotoxin that disrupts brain function through multiple mechanisms, contributing to conditions like hepatic encephalopathy, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and hyperammonemia. Its effects range from mild cognitive impairment to life-threatening cerebral edema.
Mechanisms of Ammonia Toxicity
- Energy Metabolism Disruption:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction: Ammonia inhibits enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (e.g., α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) and pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), reducing ATP production and increasing oxidative stress12.
- Impaired glucose metabolism: Dysregulation of glycolysis and the malate-aspartate shuttle in astrocytes, exacerbating energy deficits1.
- Neurotransmission Imbalance:
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:
- Membrane Potential Disruption:
Clinical Implications
- Hepatic Encephalopathy:
- Alzheimer’s Disease (AD):
- Hyperammonemia:
- Causes: Inherited urea cycle disorders, liver disease, or medications (e.g., valproate).
- Symptoms: Confusion, seizures, coma, and brain swelling35.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges
- Detection:
- Treatment:
- Acute hyperammonemia: IV sodium benzoate/phenylacetate, hemodialysis3.
- AD: Experimental strategies targeting ammonia transport (e.g., RhAG inhibitors) or mitochondrial function1.
Conclusion
Ammonia’s neurotoxicity is multifaceted, involving energy failure, neurotransmitter imbalance, and inflammation. While its role in AD remains under investigation, managing ammonia levels is critical in hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia to prevent irreversible brain damage.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Ammonia (AMN) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















