Adenocarcinoma (ADC)
Adenocarcinoma (ADC): Overview, Types, and Clinical Implications
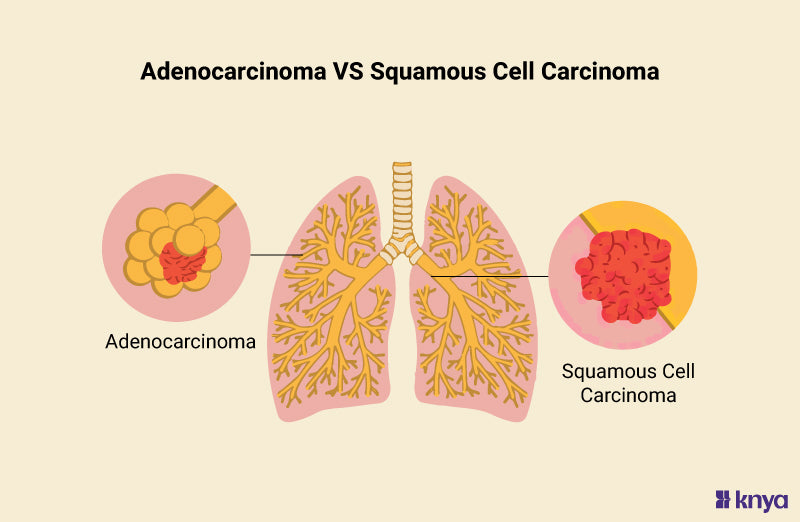
Adenocarcinoma (ADC) is a type of cancer that originates in glandular epithelial cells, which are responsible for secreting mucus, digestive juices, or other fluids. It is one of the most common forms of cancer and can occur in various organs, including the breast, lung, colon, prostate, and pancreas. Below is a detailed overview of adenocarcinoma, including its types, clinical implications, and treatment options.
Definition and Characteristics
Origin:
- Develops from glandular epithelial cells, which are found in the linings of organs and ducts.
Glandular Differentiation:
- Characterized by the presence of glandular structures or mucin production.
Variability:
- Adenocarcinomas vary significantly in their histological appearance and clinical behavior depending on the organ involved.
Types of Adenocarcinoma
Organ-Specific Adenocarcinomas:
- Breast Adenocarcinoma: Most breast cancers are adenocarcinomas, specifically invasive ductal carcinoma.
- Lung Adenocarcinoma: The most common type of non-small cell lung cancer, often found in the outer parts of the lungs.
- Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: Accounts for about 90% of bowel cancers, arising from glandular tissue in the colon or rectum.
- Prostate Adenocarcinoma: Almost all prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, originating in the glandular tissue of the prostate.
- Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: The most common type of pancreatic cancer, typically arising from the ductal epithelium.
- Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: Commonly linked to Barrett’s esophagus, a condition involving abnormal cell changes in the esophagus.
Histological Subtypes:
- Acinar, Papillary, Micropapillary, Lepidic, and Solid Patterns are seen in lung adenocarcinoma, each with distinct microscopic features.
- Mucinous and Nonmucinous subtypes are recognized based on the presence or absence of mucin.
Clinical Implications and Treatment
Symptoms:
- Vary depending on the organ affected but often include localized pain, weight loss, and changes in organ function (e.g., bowel obstruction in colon cancer).
Diagnosis:
- Typically involves imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, MRI) and biopsy to confirm glandular differentiation.
Treatment Options:
- Surgery: Often the primary treatment for localized adenocarcinomas.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: Used alone or in combination with surgery, depending on cancer stage and location.
- Targeted Therapies: For specific molecular subtypes, such as those with EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma.
Staging and Prognosis
Staging:
- Adenocarcinoma staging varies by organ but generally includes stages from 0 (in situ) to IV (metastatic).
- Accurate staging is crucial for determining prognosis and guiding treatment decisions.
- Varies significantly based on the organ involved, stage at diagnosis, and response to treatment.
- Early detection and treatment improve survival rates.
Conclusion
Adenocarcinoma is a diverse group of cancers with varying clinical behaviors and outcomes. Understanding its types and characteristics is essential for effective diagnosis and management. Advances in targeted therapies have improved treatment options for certain adenocarcinomas, particularly those with specific molecular markers.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Adenocarcinoma or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















