Fat Grafting
Fat Grafting: Clinical Overview and Techniques
Overview
Fat grafting, also called fat transfer or autologous fat transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which fat is removed from one area of the body and injected into another to restore volume, improve contour, or repair defects. This technique is popular in both reconstructive and cosmetic procedures due to its natural, biocompatible results and low risk of rejection.
Indications
Fat grafting is used for:
- Facial rejuvenation to restore volume in the cheeks, lips, temples, tear troughs, and periorbital regions.
- Breast and buttock augmentation or correction of asymmetry.
- Hand rejuvenation to camouflage tendons and veins.
- Repair of trauma, congenital defects, and post-operative defects.
Technique
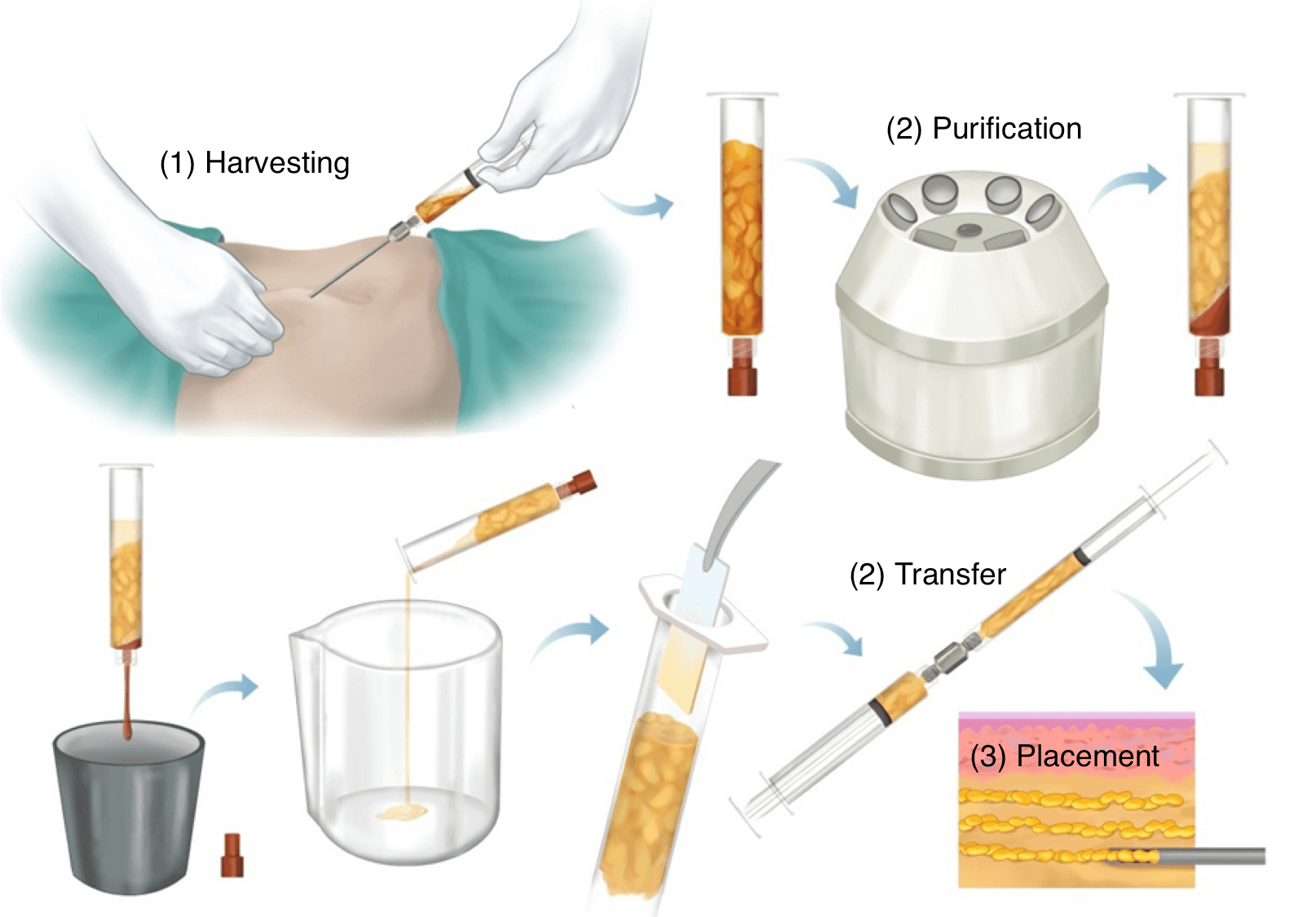
Donor Site Selection and Harvesting
- Fat is harvested using liposuction or syringe aspiration from areas with excess fat (abdomen, thighs, buttocks, flanks).
- Donor area is chosen based on accessibility, patient preference, and desired body contour.
Fat Processing
- Extracted fat is processed to remove blood, oil, and debris.
- Common methods include centrifugation and filtration to maximize cell viability.
Fat Injection and Placement
- Processed fat is injected into the recipient area through small cannulas and incisions.
- Fat is placed in small aliquots or droplets, using multi-layer, crosshatch techniques to maximize survival and integration.
- Digital manipulation or gentle massage may be used to ensure smooth contour and optimal distribution.
Postoperative Care
- Compression garments or dressings may be used on donor sites to minimize swelling and promote healing.
- Mild swelling, bruising, or temporary numbness at the recipient site is common.
Clinical Considerations
- A portion of fat is reabsorbed over time, making touch-up or staged treatments sometimes necessary for lasting results.
- Longevity depends on technique, vascularity of the site, and patient-specific factors.
Advantages and Risks
- Uses autologous tissue, minimizing allergy and immunogenic risk.
- Can improve donor area contour in the process.
- Risks include infection, contour irregularities, fat necrosis, calcification, and variable resorption.
Summary
Fat grafting is a versatile approach for soft-tissue augmentation and reconstruction. With careful technique and patient selection, it provides durable, natural, and aesthetically favorable results.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For personalized fat grafting strategies, including donor selection and planning for optimal outcomes, consult with board-certified plastic surgeons specializing in autologous tissue transfer.
References
- PMC. Principles and Applications of Fat Grafting in Plastic Surgery. 2019.pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih
- The Aesthetic Society. Fat Transfer Procedure Information. 2021.theaestheticsociety
- Cleveland Clinic. Fat Transfer: Surgeries, Risks & Results. 2025.clevelandclinic
- UCSF OHNS. Fat Grafting for Facial Rejuvenation. 2023.ohns.ucsf
- Breastcancer.org. Fat Grafting to the Breast. 2023.breastcancer















