Topical Agents for Skin Conditions: Overview and Treatment Uses
Definition and Importance
Topical agents are medications applied directly to the skin to treat various dermatologic conditions. They allow targeted treatment of affected areas, minimizing systemic absorption and side effects.
Common Types of Topical Agents and Their Uses
| Type | Common Examples | Indications | Mechanism/Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Corticosteroids | Hydrocortisone, Betamethasone, Clobetasol | Eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, lichen planus | Reduce inflammation, itching, and immune response |
| Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors | Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus | Atopic dermatitis, vitiligo | Immunomodulation without steroid side effects |
| Antibiotics | Mupirocin, Clindamycin | Bacterial skin infections | Eliminate pathogenic bacteria |
| Antifungals | Clotrimazole, Ketoconazole, Terbinafine | Fungal infections (tinea, candidiasis) | Kill or inhibit fungal growth |
| Retinoids | Tretinoin, Adapalene | Acne, photoaging, fine wrinkles | Promote epidermal turnover, collagen production |
| Keratolytics | Salicylic acid, Urea | Psoriasis, acne, hyperkeratosis | Remove dead skin cells, soften skin |
| Moisturizers/Emollients | Petrolatum, Dimethicone | Dry skin, eczema | Hydrate and protect skin barrier |
| Topical Immunomodulators | Imiquimod | Actinic keratosis, superficial skin cancers | Stimulate local immune response |
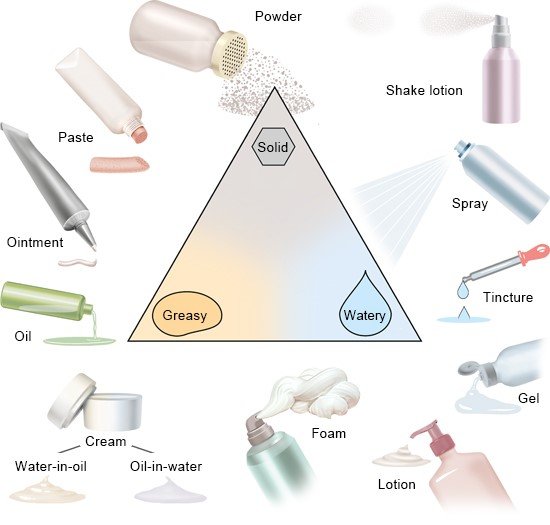
Mode of Application and Forms
- Available as creams, ointments, lotions, gels, foams, solutions, and tapes depending on condition and body area.
- The choice of vehicle influences absorption and suitability for different skin types or lesion locations.
Treatment Considerations
- Potency and concentration must correspond to the severity and location of the disease (e.g., low potency for face, higher potency for thick plaques on soles).
- Prolonged or inappropriate use of some topicals (like corticosteroids) may cause side effects like skin thinning, pigmentation changes, or irritation.
- Some conditions require combination treatments or adjunctive systemic therapy.
Clinical Applications
- Inflammatory conditions: Corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are mainstays in diseases such as eczema and psoriasis.
- Infectious conditions: Topical antibiotics and antifungals treat localized infections effectively.
- Pigmentation disorders and photoaging: Retinoids and other skin-lightening agents improve pigmentation and skin texture.
- Precancerous lesions: Imiquimod or fluorouracil creams for actinic keratosis prevention and management.
Summary
Topical agents are central to dermatologic care, efficiently addressing a wide range of skin disorders through diverse mechanisms. Safe and effective use requires tailored selection based on diagnosis, lesion characteristics, and patient factors.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
For precise diagnosis and personalized topical treatment plans for your specific skin condition, consult our dermatology specialists who specialize in advanced and evidence-based skin therapies.
References:
- National Eczema Association. Topical Steroids and Non-Steroid Topicals. 2025.nationaleczema
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Topical Corticosteroids: Choice and Application. 2021.aafp
- Merck Manuals. Treatment of Skin Disorders. 2024.merckmanuals
- DermNet NZ. Topical Medications for Skin Conditions. 2024.dermnetnz
- WebMD. Medications for Skin Conditions. 2025.webmd















