Myelopathy
Myelopathy (Cervical Myelopathy): Overview, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is Myelopathy?
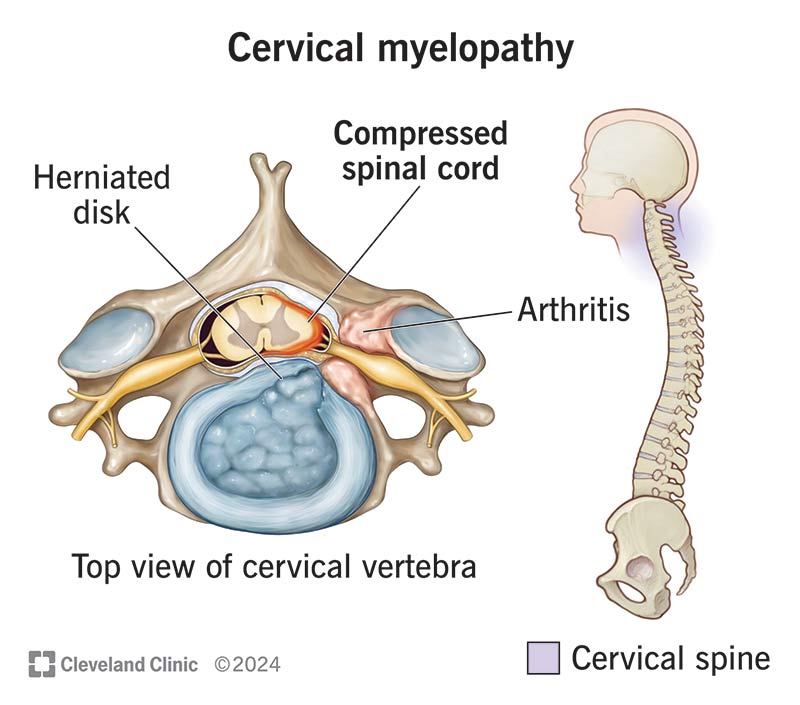
Myelopathy refers to spinal cord compression that leads to neurological deficits. When this compression occurs in the cervical spine (neck region), it is called cervical myelopathy, the most common type of myelopathy. It results from narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord, impairing nerve signal transmission to and from the brain.
Causes
- Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM): Age-related degenerative changes in the cervical spine (disc degeneration, bone spurs, ligament thickening) that narrow the spinal canal and compress the cord.
- Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL): Thickening and hardening of a spinal ligament causing cord compression.
- Congenital spinal canal narrowing: Some individuals have a naturally narrow canal, increasing risk.
- Other causes: Trauma, tumors, infections, inflammatory diseases.
Symptoms
Symptoms often develop insidiously and progressively, including:
- Motor symptoms:
- Clumsiness and weakness in the hands (difficulty with fine motor tasks like buttoning shirts)
- Weakness or stiffness in the legs leading to gait disturbances and balance problems
- Sensory symptoms:
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in arms, hands, legs, or feet
- Reflex changes:
- Hyperreflexia (exaggerated reflexes), pathological reflexes (e.g., Babinski sign)
- Other symptoms:
- Neck pain or stiffness (may or may not be present)
- Problems with bladder or bowel control in advanced cases
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation: Neurological exam assessing strength, sensation, reflexes, coordination, and gait.
- Imaging:
- MRI is the gold standard to visualize spinal cord compression and soft tissue changes.
- X-rays and CT scans assess bony structures and alignment.
Treatment
Non-Surgical
- Physical therapy and cervical collar bracing may provide symptomatic relief in mild or stable cases.
- Oral corticosteroids can offer transient symptom improvement but are not definitive treatment.
Surgical
- Surgery is the definitive treatment to decompress the spinal cord and prevent progression.
- Approaches vary (anterior, posterior, or combined) depending on the location and cause of compression and spinal alignment.
- Early surgery is recommended once progressive symptoms or significant cord compression are identified to optimize outcomes.
- Surgery may involve decompression (removal of bone spurs, discs, ligament) and sometimes spinal fusion.
Prognosis
- Without treatment, cervical myelopathy typically worsens, potentially leading to significant disability or paralysis.
- Early diagnosis and timely surgical intervention improve functional recovery.
- Prognosis is poorer with longer symptom duration (>18 months), reduced neck mobility, and in some demographic groups.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Spinal cord compression in the cervical spine causing neurological dysfunction |
| Common Causes | Cervical spondylosis, OPLL, congenital stenosis, trauma |
| Symptoms | Hand clumsiness, leg weakness, numbness, hyperreflexia, gait disturbances, bladder issues |
| Diagnosis | Clinical exam, MRI, X-ray, CT |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, corticosteroids (transient), surgical decompression and fusion |
| Prognosis | Progressive without treatment; better outcomes with early surgery |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Myelopathy or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References:
- Cleveland Clinic 14
- Johns Hopkins Medicine 25
- Orthobullets 3
- StatPearls 7
- Healthline 8
- DISCMD Group 6
Cervical myelopathy is a progressive condition caused primarily by degenerative changes compressing the spinal cord. Early recognition and surgical treatment are key to preventing permanent neurological damage and improving quality of life.















