Thymosin β4 Analogs (Tβ4)
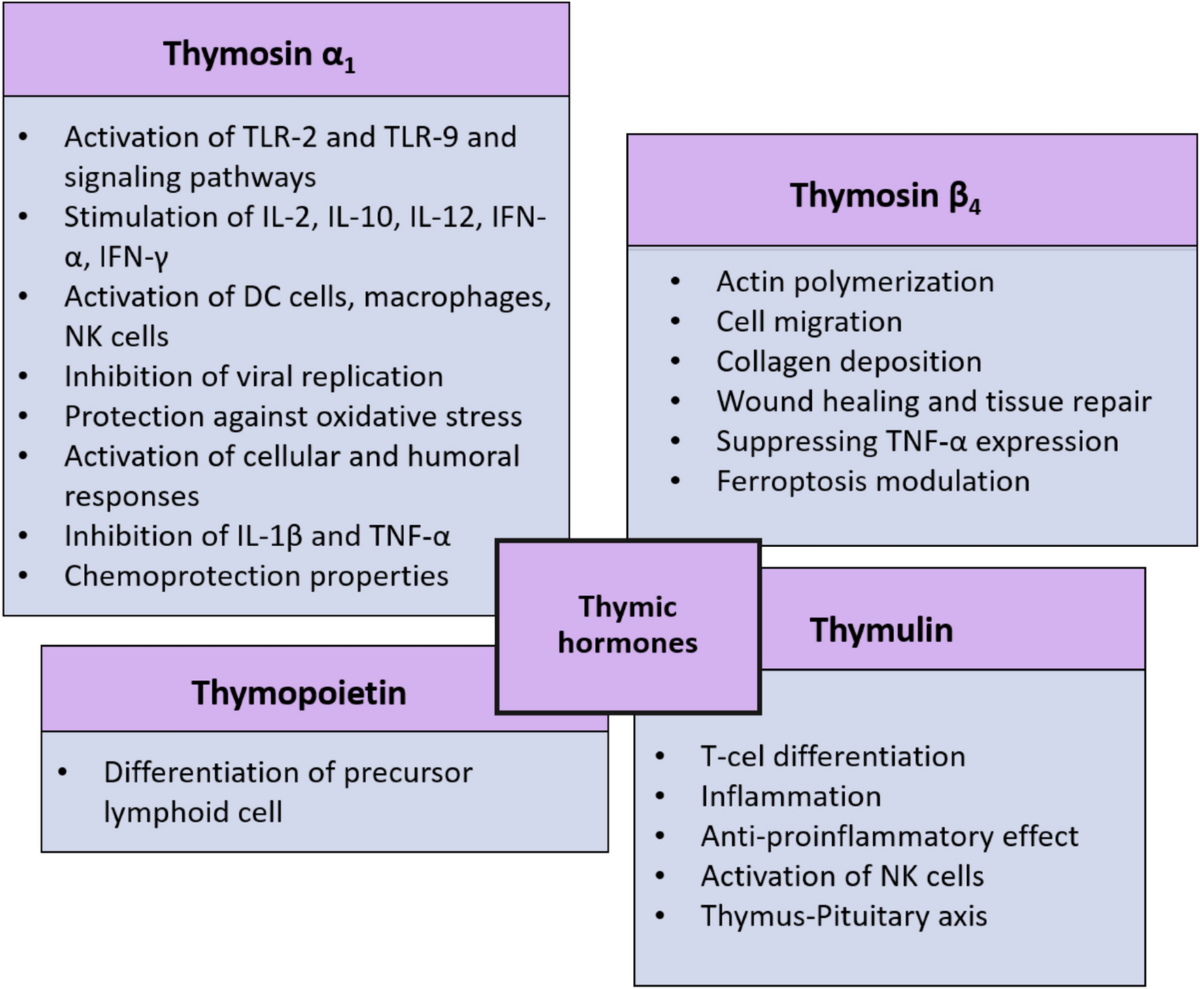
Thymosin β4 Analogs (Tβ4): Structure, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Potential
Thymosin β4 (Tβ4) is a 43-amino acid peptide with diverse roles in actin dynamics, tissue repair, and inflammation modulation. TMBA refers to synthetic or modified analogs designed to enhance or mimic Tβ4’s biological activities. Below is a structured overview of TMBA based on current research:
Structural Features and Analogs
- Native Tβ4: Sequence SDKPDMAEIEKFDKSKLKKTETQEKNPLPSKETIEQEKQAGES, with actin-binding motif LKKTET (residues 17–22).
- Key Analogs:
- Ac-SDKP: A tetrapeptide (N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline) derived from Tβ4’s N-terminus. It inhibits hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and reduces fibrosis13.
- Oxidized Tβ4: Modifies cysteine residues, altering bioactivity (e.g., immunomodulatory effects)3.
- Synthetic Peptides: Shorter sequences or modified residues to improve stability, bioavailability, or target specificity8.
Mechanisms of Action
- Actin Sequestration:
Tβ4 binds G-actin, regulating cytoskeletal dynamics critical for cell migration and tissue repair13. TMBA may enhance actin polymerization or stability in damaged tissues. - Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrotic Effects:
- Angiogenesis and Stem Cell Mobilization:
Promotes endothelial cell migration and vascular growth via VEGF and integrin pathways28. - Cell Survival:
Inhibits apoptosis by upregulating survival signals (e.g., Akt)27.
Therapeutic Applications
- Wound Healing: Enhances keratinocyte migration, collagen deposition, and reduces scarring (clinical trials in dermal and corneal injuries)28.
- Cardiac Repair: Controversial role-preclinical studies suggest benefits post-myocardial infarction, but Tβ4-knockout mice show normal cardiac development4.
- Neuroprotection: Promotes neurite outgrowth and reduces neuronal apoptosis in stroke models27.
- Anti-Fibrotic Therapy: Ac-SDKP analogs show promise in reducing renal and pulmonary fibrosis13.
Controversies and Challenges
- Knockout Studies: Global Tβ4 deletion in mice did not impair embryonic development or adult cardiac function, suggesting redundancy or context-dependent roles4.
- Delivery and Stability: Short half-life and rapid clearance of native Tβ4 necessitate engineered analogs (e.g., PEGylation, nanoparticle encapsulation)8.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Key Analogs | Ac-SDKP, oxidized Tβ4, synthetic peptides with improved stability |
| Mechanisms | Actin sequestration, anti-inflammatory signaling, angiogenesis, anti-apoptosis |
| Applications | Wound healing, cardiac/neuro repair, fibrosis reduction |
| Limitations | Redundancy in knockout models, bioavailability challenges |
| Clinical Status | Phase II trials for wound healing; preclinical research in other areas28 |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Thymosin β4 Analogs (Tβ4) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Thymosin beta-4: Moonlighting roles in tissue repair
- Thymosin β4: Multi-functional regenerative peptide
- Beta-thymosins and their diverse functions
- Tβ4 knockout mice study
- Tβ4 and Tβ10 expression in development
- Tβ4’s role in cytoskeletal dynamics
- TMBA modulators and mechanisms
Conclusion: TMBA holds therapeutic potential in regenerative medicine, particularly for wounds and fibrosis. However, conflicting knockout data and delivery challenges highlight the need for further research to optimize analogs and clarify mechanisms.















