Lymphedema (Lpdm)
Lymphedema (Lpdm)
Lymphedema (Lpdm) is a chronic condition characterized by swelling caused by the accumulation of protein-rich lymphatic fluid in the tissues due to impaired drainage by the lymphatic system. It most commonly affects the arms or legs but can also occur in other areas such as the chest wall, abdomen, neck, genitals, face, and oral cavity.
Causes
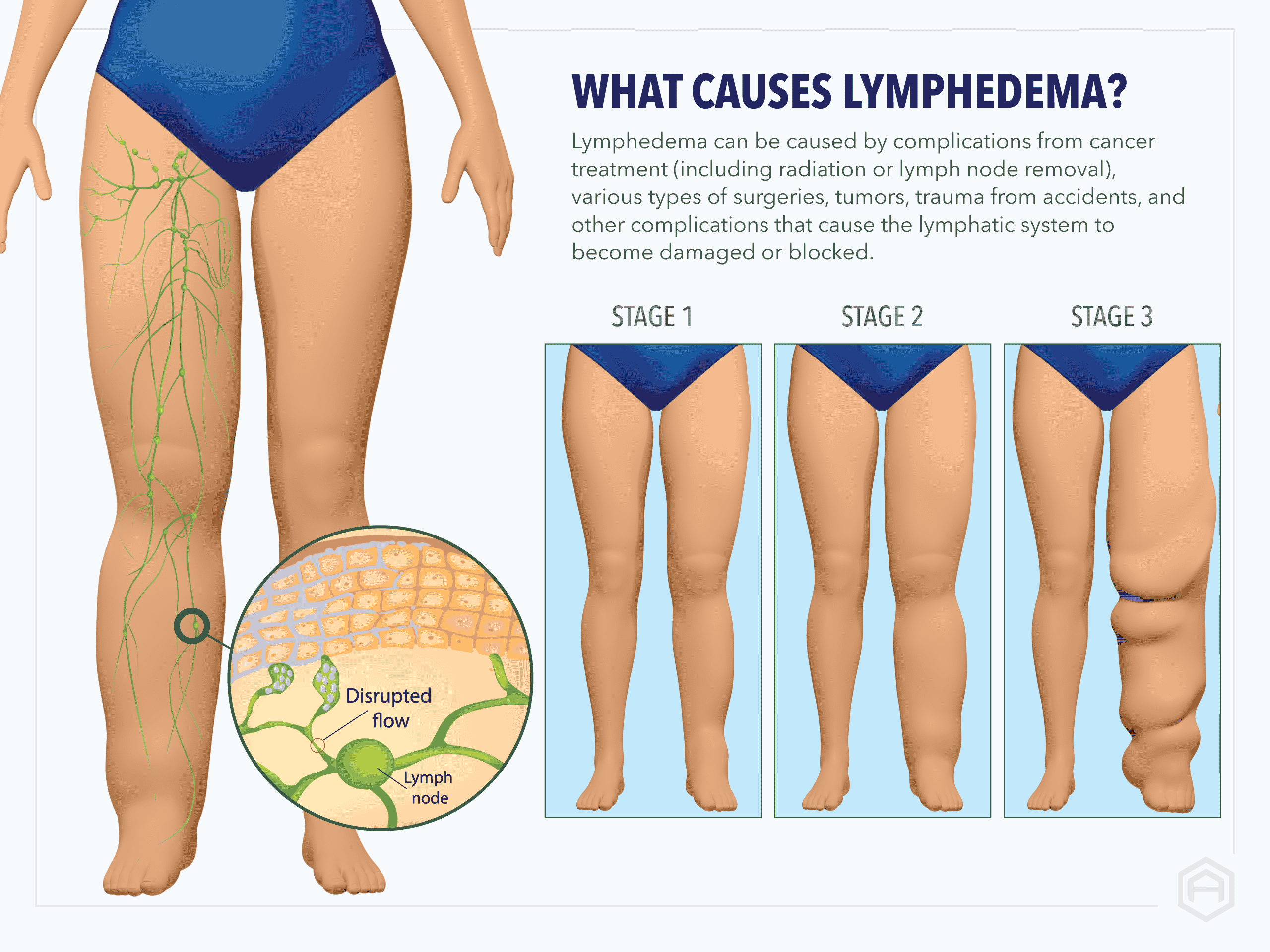
Lymphedema arises when the lymphatic system is damaged or blocked, preventing normal lymph fluid drainage. It is classified into two main types:
- Primary Lymphedema:
Caused by congenital or genetic abnormalities affecting lymphatic vessel development or function. It can present at birth (congenital), during adolescence (lymphedema praecox), or later in life (lymphedema tarda). - Secondary Lymphedema:
Results from damage to the lymphatic system due to:- Cancer treatments (surgical removal of lymph nodes, radiation therapy)
- Infections (e.g., cellulitis, parasitic infections like filariasis)
- Trauma or injury
- Inflammatory conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, eczema)
- Vascular diseases (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, varicose veins)
- Obesity and inactivity, which impair lymph circulation
Symptoms
- Swelling of part or all of an arm or leg, including fingers or toes
- Feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected limb
- Restricted range of motion
- Recurring infections in the affected area
- Hardening and thickening of the skin (fibrosis)
- Skin changes, including discoloration and breakdown in severe cases
- Swelling may develop gradually or suddenly and can range from mild to severe
Complications
- Increased risk of skin infections such as cellulitis and lymphangitis due to impaired immune function
- Reduced mobility and limb function
- Psychological and social impacts due to chronic swelling and disfigurement
Diagnosis
- Clinical evaluation of swelling and history of lymphatic injury or risk factors
- Imaging studies (e.g., lymphoscintigraphy) may be used to assess lymphatic function
- Rule out other causes of swelling such as venous insufficiency or heart failure
Treatment
While lymphedema is incurable, it can be managed effectively to reduce swelling and prevent complications:
- Compression therapy: Use of compression bandages or stockings to encourage lymph flow
- Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD): Specialized massage techniques to stimulate lymphatic drainage
- Sequential pneumatic compression devices: Mechanical pumps to assist lymph movement
- Skin care: Prevent infections by maintaining skin hygiene and treating wounds promptly
- Exercise: To improve lymph circulation and maintain limb function
- Surgery: Rarely, procedures to remove excess tissue or create new drainage pathways may be considered in severe cases
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you notice persistent swelling in an arm or leg, especially following cancer treatment, injury, or infection.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic swelling due to lymphatic fluid accumulation caused by impaired lymph drainage |
| Types | Primary (genetic/congenital) and Secondary (acquired due to damage or blockage) |
| Common Causes | Cancer treatment, infections, trauma, inflammation, vascular disease, obesity, inactivity |
| Symptoms | Limb swelling, heaviness, restricted motion, skin changes, recurrent infections |
| Complications | Skin infections, fibrosis, reduced mobility, psychological impact |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, imaging studies |
| Treatment | Compression, manual drainage, skin care, exercise, sometimes surgery |
| Prognosis | Chronic but manageable with proper care |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Lymphedema (Lpdm) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References:
- Rockson SG. “Lymphedema.” New England Journal of Medicine. 2021;385(6):556-565.
DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra2011564
Lymphedema is a lifelong condition requiring ongoing management to control swelling and reduce complications. Early diagnosis and treatment improve quality of life and limb function.















