Osteogenesis
Osteogenesis
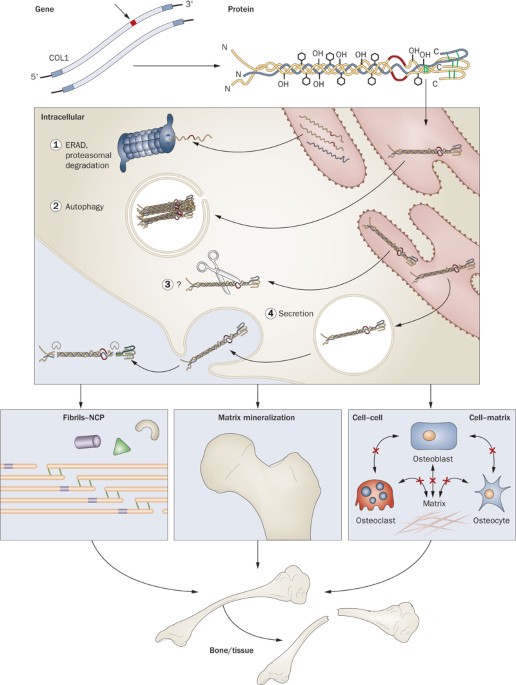
Osteogenesis, also known as ossification, is the biological process by which new bone is formed. This process is essential not only during embryonic development and childhood growth but also throughout life for bone remodeling and repair after injury234.
Types of Osteogenesis
There are two primary modes of bone formation:
- Intramembranous Ossification:
- Involves the direct transformation of mesenchymal tissue into bone without a cartilage intermediate.
- Responsible for forming flat bones such as those of the skull, facial bones, and parts of the clavicle and hip bone.
- Mesenchymal cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which secrete osteoid (an unmineralized collagen-proteoglycan matrix). Osteoid then mineralizes, trapping osteoblasts that become osteocytes-the mature bone cells123.
- Endochondral Ossification:
- Involves the replacement of a cartilage template with bone.
- Responsible for the formation of long bones (e.g., femur, humerus) and most bones of the body.
- Begins with the formation of a cartilage model, followed by the invasion of blood vessels and the development of primary and secondary ossification centers. Osteoblasts deposit bone tissue onto the cartilage matrix, which is gradually replaced by bone234.
Stages and Timeline
- Embryonic Development:
- Ossification begins between the sixth and seventh weeks of embryogenesis4.
- By the third month, ossification starts in the long bones; primary ossification centers appear in bone shafts (diaphyses).
- Secondary ossification centers appear in the ends (epiphyses) after birth and continue into adolescence2.
- Childhood to Adulthood:
- Bone Remodeling and Repair:
- Osteogenesis is ongoing throughout life, enabling bone remodeling and healing after fractures3.
Key Cellular Players
- Osteoblasts: Bone-forming cells that secrete osteoid.
- Osteocytes: Mature bone cells derived from osteoblasts, embedded in the bone matrix.
- Osteoclasts: Cells responsible for bone resorption, essential for bone remodeling23.
Clinical Relevance
- Abnormalities in osteogenesis can lead to bone disorders, such as osteogenesis imperfecta (a genetic disorder affecting collagen synthesis)5.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Osteogenesis or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- NCBI Bookshelf: Developmental Biology-Modes of Bone Formation
- Wikipedia: Ossification (Osteogenesis)
- Osteogenesis: The Science behind Bone Formation and Healing (PDF)
- NCBI Bookshelf: Embryology, Bone Ossification
- Orthobullets: Osteogenesis Imperfecta
In summary:
Osteogenesis is the process of bone formation via intramembranous or endochondral ossification, beginning in embryonic life and continuing through growth, remodeling, and repair. It is fundamental to skeletal development and health1234.














