Gangrene (Gg)
Gangrene (Gg)
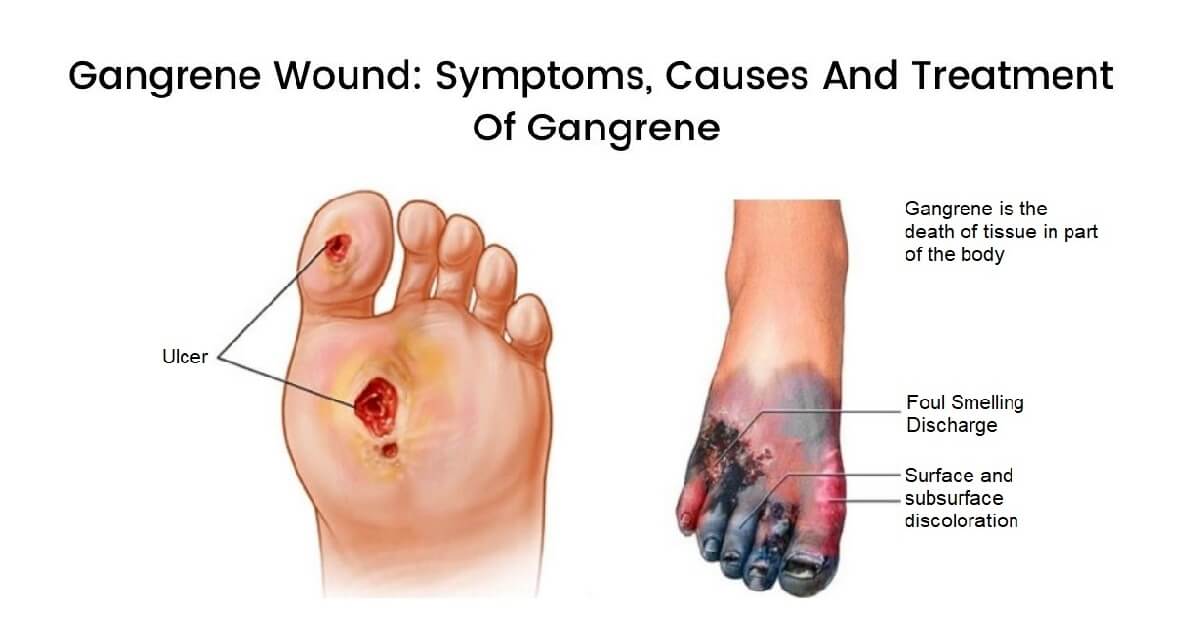
Gangrene (Gg) is the death of body tissue resulting from a lack of blood supply or a severe bacterial infection. It most commonly affects the extremities such as the fingers, toes, hands, and feet but can also involve internal organs.
Causes
- Lack of blood flow: Blood delivers oxygen, nutrients, and immune cells to tissues. When blood flow is blocked or severely reduced (due to conditions like diabetes, peripheral artery disease, atherosclerosis, or blood clots), tissues begin to die.
- Infection: Untreated bacterial infections, especially with bacteria like Clostridium perfringens, can cause gas gangrene, producing toxins and gas that destroy tissue rapidly.
- Traumatic injury: Severe injuries such as crushing wounds or gunshot wounds can introduce bacteria and disrupt blood supply, leading to gangrene.
Types of Gangrene
- Dry gangrene: Caused by poor blood flow without infection. Tissue becomes dry, shriveled, and changes color from pale to brown, purple, or black. Common in vascular diseases and diabetes.
- Wet gangrene: Involves bacterial infection causing swelling, blisters, pus, and rapid tissue destruction. It can spread quickly and is life-threatening.
- Gas gangrene: A severe form of wet gangrene caused by Clostridium bacteria producing gas within tissues, leading to a crackling sensation and rapid progression.
- Internal gangrene: Affects internal organs like the intestines or gallbladder due to blocked blood flow or infection.
- Fournier’s gangrene: A rare, severe infection of the genital and perineal area, mostly in males.
Symptoms
- Skin discoloration: pale, gray, blue, purple, black, bronze, or red.
- Swelling and blisters, sometimes leaking foul-smelling discharge.
- Sudden, severe pain followed by numbness or loss of sensation.
- Thin, shiny, or hairless skin in the affected area.
- Cool or cold skin to the touch.
- In gas gangrene, a crackling sound may be felt under the skin due to gas bubbles.
- Fever, malaise, and signs of systemic infection if bacteria spread.
Complications
- Septic shock if infection spreads to the bloodstream, characterized by low blood pressure, rapid pulse, confusion, breathing difficulty, and can be fatal without urgent treatment.
- Tissue loss requiring surgical removal (debridement or amputation).
- Organ failure in internal gangrene.
Diagnosis
- Physical examination observing skin changes and symptoms.
- Imaging (X-ray, CT, MRI) may detect gas in tissues.
- Laboratory tests including blood cultures and wound cultures to identify infection.
- Vascular studies to assess blood flow.
Treatment
- Immediate medical emergency requiring prompt intervention.
- Surgical removal of dead tissue to prevent spread.
- Antibiotics to treat underlying bacterial infection.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be used to increase oxygen supply to tissues and inhibit anaerobic bacteria.
- Supportive care including fluids, pain management, and treatment of underlying conditions.
Prevention
- Managing chronic diseases like diabetes and vascular disorders.
- Prompt treatment of wounds and infections.
- Avoiding smoking and maintaining good circulation.
Summary Table
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Death of tissue due to loss of blood supply or infection |
| Common Sites | Toes, fingers, hands, feet, internal organs |
| Causes | Poor blood flow, bacterial infection, trauma |
| Types | Dry, wet, gas, internal, Fournier’s gangrene |
| Symptoms | Skin discoloration, swelling, blisters, pain, numbness, foul discharge, fever |
| Diagnosis | Clinical exam, imaging, cultures, vascular studies |
| Treatment | Surgery, antibiotics, hyperbaric oxygen, supportive care |
| Complications | Septic shock, tissue loss, organ failure |
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Gangrene or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Mayo Clinic: Gangrene – Symptoms & Causes [https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gangrene/symptoms-causes/syc-20352567][1]
- Cleveland Clinic: Gangrene – Symptoms, Causes & Treatment [https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21070-gangrene][2]
- WebMD: Gangrene Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments [https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/gangrene-causes-symptoms-treatments][3]
- NHS: Gangrene – Symptoms [https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gangrene/symptoms/][4]
- Healthline: Gangrene – Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Diagnosis [https://www.healthline.com/health/gangrene][7]
- NCBI Bookshelf: Gangrene – StatPearls [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560552/][9]
Gangrene is a serious medical condition requiring immediate treatment to prevent life-threatening complications and tissue loss. Early recognition and prompt management improve outcomes significantly.















