Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM): Overview, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly aggressive and malignant type of brain tumor classified as a grade IV astrocytoma by the World Health Organization (WHO). It is the most common primary malignant brain tumor in adults, arising from glial cells in the brain or spinal cord. Below is a detailed overview of GBM, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Symptoms of Glioblastoma Multiforme
GBM symptoms vary based on the tumor‘s location and size but often include:
- Headaches: Persistent and worsening over time, often more severe in the morning[1][3][5].
- Seizures: Common, especially in patients without a prior seizure history[3][5].
- Weakness or Numbness: In one side of the body or a limb[1][2].
- Cognitive Changes: Confusion, memory loss, difficulty with language (aphasia), and personality changes[1][5].
- Vision Changes: Blurred or double vision[5].
- Nausea and Vomiting: Due to increased intracranial pressure[3][5].
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Difficulty with movement and balance[5].
Causes and Risk Factors
Unknown Primary Cause:
- The exact cause of GBM is not well understood, but it is thought to arise from immature cells or stem cells that have suffered DNA damage[1].
Risk Factors:
- Ionizing Radiation: Previous exposure to radiation therapy increases the risk[4].
- Occupational Exposures: Certain chemicals used in synthetic rubber manufacturing, petroleum refining, and pesticides may be linked to GBM[4].
- Genetic Syndromes: Rare conditions like Turcot syndrome and Li-Fraumeni syndrome are associated with an increased risk[4].
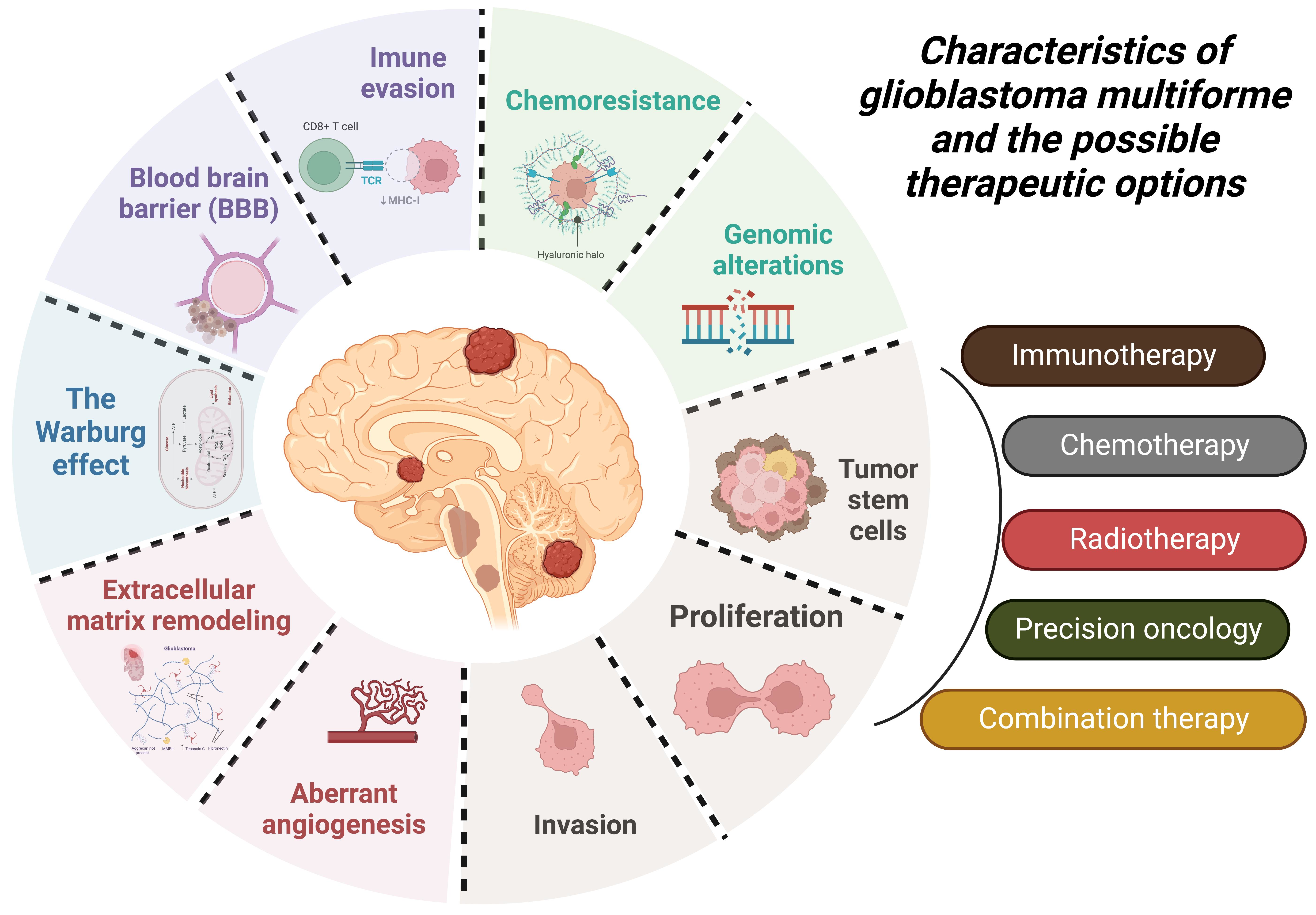
Treatment Options
Surgical Resection:
- The primary treatment involves removing as much of the tumor as possible while preserving brain function[4].
Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy:
- Adjuvant treatments to target remaining tumor cells. Commonly used is temozolomide chemotherapy combined with radiation[4].
Tumor Treating Fields (TTF):
- An innovative approach using alternating electric fields to disrupt cancer cell division[4].
Emerging Therapies:
- Research into targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and gene therapies is ongoing to improve outcomes[2][3].
Prognosis and Survival
- Despite aggressive treatment, the prognosis for GBM remains poor, with a median survival time of approximately 14.6 months after diagnosis[4].
- Factors like tumor location, patient age, and performance status influence survival outcomes.
Conclusion
Glioblastoma multiforme is a highly aggressive brain tumor with a poor prognosis. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment involving surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy are crucial for managing symptoms and extending survival. Ongoing research aims to improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients with GBM.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















