Leptin (Lpt)
Leptin (Lpt): Role, Function, and Clinical Implications
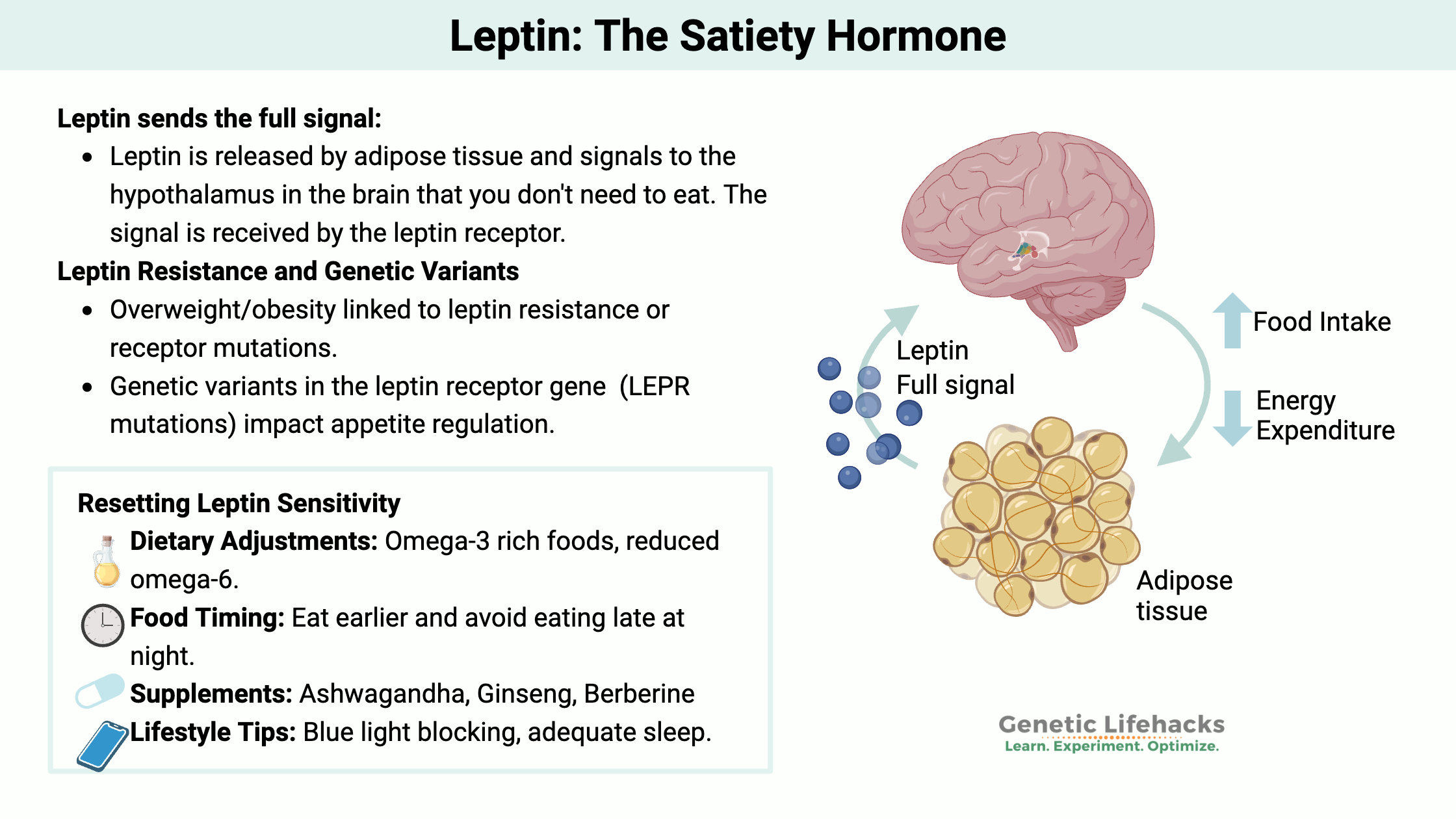
Leptin (Lpt) is a peptide hormone secreted by adipose tissue that plays a critical role in regulating food intake, energy expenditure, and body weight. It acts as an appetite suppressant and signals the brain about the body’s energy reserves. Below is a detailed overview of leptin, including its mechanisms, clinical implications, and challenges in obesity management.
Role and Mechanism of Leptin
Production and Function:
- Leptin is produced by fat cells in white adipose tissue and released into the bloodstream.
- It binds to leptin receptors (LEP-R), primarily located in the hypothalamus, to regulate hunger and energy balance through a negative feedback mechanism[1][2][3].
Regulation of Energy Balance:
- High leptin levels signal sufficient fat stores, suppressing appetite and promoting energy expenditure.
- Low leptin levels occur during fasting or weight loss, triggering hunger and conserving energy[4][6].
Other Functions:
- Involved in reproductive health, fetal growth, angiogenesis, lipolysis, and immune responses[1][2].
Leptin Resistance in Obesity
Definition:
- Leptin resistance occurs when the brain fails to respond to high levels of circulating leptin, leading to reduced satiety signals despite adequate fat stores[1][5][6].
Mechanisms:
- Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
- Saturation or dysfunction of leptin receptors in the hypothalamus[5].
Impact:
- Promotes overeating and reduced energy expenditure, contributing to obesity.
- Limits the effectiveness of exogenous leptin as a therapeutic agent for weight loss[1][5][6].
Clinical Implications and Therapeutic Strategies
Obesity Management:
- Leptin therapies combined with leptin sensitizers are being explored to overcome resistance and improve weight loss outcomes[1][3].
Other Applications:
- Research into leptin’s role in Alzheimer’s disease, reproductive health, infertility, and metabolic disorders is ongoing[4][6].
Challenges:
- Leptin resistance remains a major obstacle for therapeutic use in obesity treatment. Understanding its molecular mechanisms is crucial for developing effective interventions[5].
Conclusion
Leptin is a vital hormone for maintaining energy balance by regulating hunger and fat storage. While it holds promise as a therapeutic target for obesity management, leptin resistance significantly limits its effectiveness. Continued research into overcoming this resistance may pave the way for improved treatments.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Leptin or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Title: Leptin and Its Role in Energy Balance: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential
DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1008321
Summary: Explores leptin’s mechanisms in regulating energy balance and its therapeutic potential in obesity management, focusing on overcoming leptin resistance. - Title: Leptin Resistance and Obesity: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms
DOI: 10.1016/j.cellmet.2023.03.004
Summary: Reviews molecular pathways involved in leptin resistance and their implications for obesity treatment, highlighting strategies to enhance leptin sensitivity. - Title: Clinical Applications of Leptin in Metabolic Disorders
DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01734-2
Summary: Discusses the use of leptin therapies in metabolic disorders, including obesity and diabetes, emphasizing clinical trial outcomes and future directions.















