Encephalopathy (ECP)
Encephalopathy (ECP): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Encephalopathy (ECP) is a brain disorder characterized by altered mental status due to structural, metabolic, or infectious insults. It manifests as confusion, cognitive decline, or behavioral changes, ranging from mild to life-threatening.
Causes of Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy arises from diverse etiologies, categorized as reversible or irreversible:
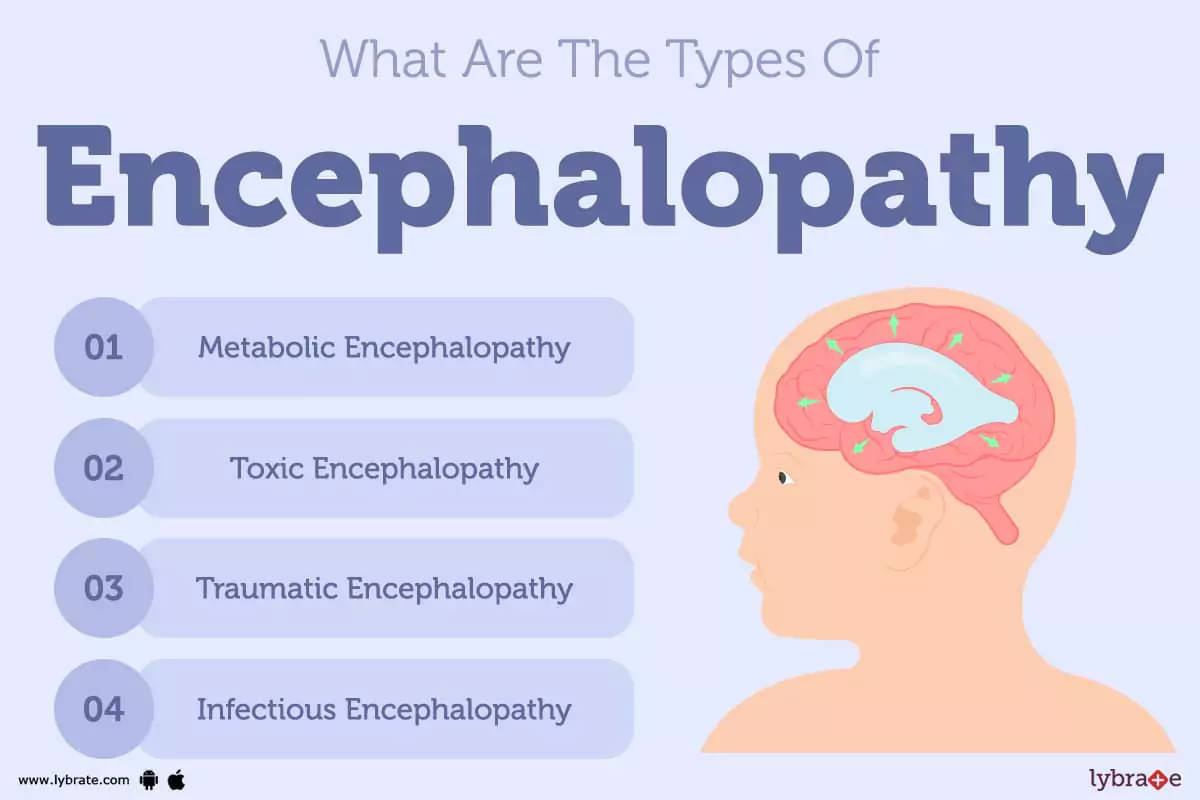
- Metabolic Disorders:
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Liver failure (e.g., cirrhosis) leads to ammonia accumulation, causing confusion and asterixis (flapping tremor)17.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis/hyperglycemia: Severe hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia disrupts brain function18.
- Uremic encephalopathy: Kidney failure causes toxin buildup (e.g., urea)26.
- Infections:
- Toxins/Drugs:
- Autoimmune/Neurodegenerative:
- Hashimoto’s encephalopathy: Autoimmune thyroid disorder linked to brain inflammation12.
- Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE): Repeated head trauma (e.g., contact sports)16.
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury:
- Cardiac arrest, drowning, or stroke12.
Symptoms of Encephalopathy
Symptoms vary by severity and cause:
| Mild | Severe |
|---|---|
| Confusion, disorientation | Coma, seizures, or death13 |
| Fatigue, memory loss | Cheyne-Stokes respiration23 |
| Slurred speech, tremors | Myoclonus (muscle twitching)3 |
| Sleep disturbances | Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES)2 |
Special Cases:
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome: Confabulations (false memories) and anterograde amnesia3.
- Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: Psychosis, hallucinations, and autonomic instability3.
Diagnosis
- Clinical Evaluation:
- Neurological exam: Assess consciousness, reflexes, and focal deficits.
- Mental status testing: Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE).
- Imaging:
- Blood/Urine Tests:
- Specialized Tests:
- Lumbar puncture: CSF analysis for infections or inflammation23.
- EEG: Rule out seizures or status epilepticus3.
Treatment
Treatment targets the underlying cause:
- Metabolic Disorders:
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Lactulose, rifaximin, and dietary protein restriction7.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis: Insulin, fluids, and electrolyte correction18.
- Infections:
- Toxins/Drugs:
- Thiamine: For Wernicke encephalopathy13.
- Chelation therapy: For heavy metal poisoning26.
- Autoimmune/Neurodegenerative:
- Supportive Care:
Complications
- Permanent brain damage: From hypoxia or untreated infections16.
- Coma or death: In severe metabolic or infectious cases23.
- Secondary infections: Pneumonia or UTIs in immobile patients16.
Prevention
- Metabolic control: Manage diabetes, liver/kidney disease17.
- Vaccinations: Prevent infections (e.g., meningitis, hepatitis)16.
- Avoid toxins: Limit alcohol, industrial chemicals, or drug misuse26.
Conclusion
Encephalopathy is a medical emergency requiring rapid diagnosis and cause-specific treatment. Early intervention can reverse symptoms in reversible cases (e.g., hepatic encephalopathy), while irreversible forms (e.g., CTE) demand supportive care.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing various health conditions. If you have questions about Encephalopathy or would like more information on our services, consult with our experts today!















