Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC): Understanding Its Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
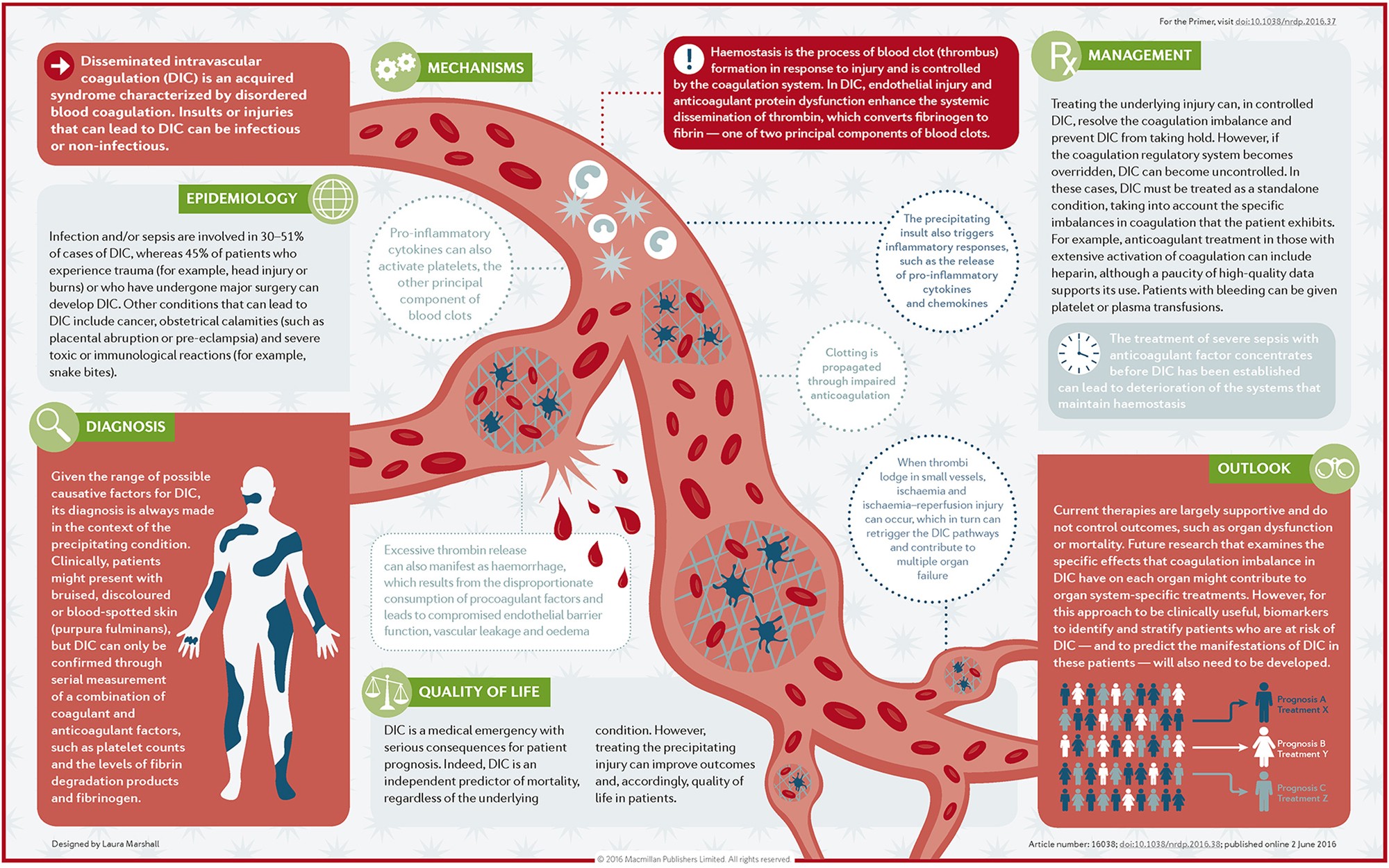
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) is a complex condition characterized by both widespread clotting and bleeding in the vascular system. It is often triggered by severe underlying diseases such as sepsis, trauma, or cancer.
Causes of DIC
- Sepsis:
Infections, particularly those caused by gram-negative bacteria, are a common trigger for DIC. - Trauma:
Severe injuries can initiate DIC due to tissue damage and release of pro-coagulant substances. - Cancer:
Malignant diseases, especially those involving the pancreas or prostate, can lead to DIC. - Obstetric Complications:
Conditions like abruptio placentae can cause DIC.
Diagnosis of DIC
- Clinical Presentation:
Symptoms include bleeding, thrombosis, and organ dysfunction. - Laboratory Tests:
- Platelet Count: Low levels indicate platelet consumption.
- Coagulation Tests: Prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
- Fibrinogen Levels: Decreased levels suggest consumption.
- D-Dimer: Elevated levels indicate fibrin degradation products.
- Scoring Systems:
The International Society for Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) scoring system helps diagnose DIC based on clinical and laboratory findings.
Treatment of DIC
- Underlying Cause:
The cornerstone of treatment is addressing the underlying condition, such as administering antibiotics for sepsis or surgery for trauma. - Supportive Care:
- Blood Transfusions: Platelets, fresh frozen plasma (FFP), and cryoprecipitate may be used to replace consumed clotting factors.
- Heparin: Used in cases with thrombosis, especially in slowly evolving DIC.
- Antifibrinolytic Agents:
Generally not recommended unless there is a primary hyperfibrinolytic state with severe bleeding.
Conclusion
DIC is a serious condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its causes and management strategies is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand (DRSCT)‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing complex medical conditions. If you have questions about DIC or would like more information on our services related to hematological care, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- PMC: Diagnosis and Treatment of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Discusses the importance of treating underlying conditions and using supportive therapies like blood transfusions and heparin. - MSD Manuals: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Highlights the role of correcting the underlying cause and replacing clotting factors. - PubMed: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of DIC
Emphasizes the ISTH scoring system for diagnosis and the use of transfusions in bleeding patients. - BSH: Diagnosis and Management of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Discusses the use of heparin in thrombotic DIC and transfusions in bleeding cases. - Cleveland Clinic: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Lists common causes and symptoms of DIC. - Medscape: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Treatment
Provides insights into treatment strategies, including supportive care and heparin use. - TSH: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Discusses treatment approaches based on DIC types. - Ramathibodi Hospital: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Highlights sepsis as a common cause of DIC and the need for early diagnosis and treatment guidelines.















