Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR)
Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR): Understanding Its Role in Diagnosing Kidney Disease
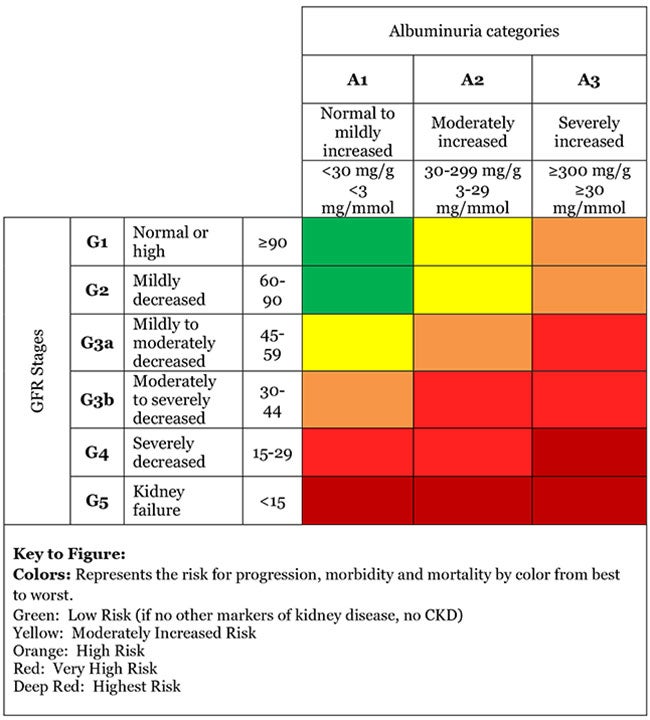
The Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR) is a critical marker used to diagnose and monitor kidney disease, particularly in patients with diabetes. It measures the amount of albumin (a protein) in relation to creatinine in urine, providing insights into kidney damage and function.
What is UACR?
- Definition:
UACR is calculated by dividing the concentration of albumin in urine (mg/dL) by the concentration of creatinine (g/dL), resulting in a ratio expressed in mg/g. - Normal Values:
A UACR of less than 30 mg/g is considered normal. Values above 30 mg/g indicate albuminuria, which is a marker for chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Importance of UACR in Diagnosing Kidney Disease
- Early Detection:
UACR is an early indicator of kidney damage, even when the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is normal. It helps identify patients at risk of progressive kidney disease. - Monitoring Disease Progression:
Changes in UACR levels can reflect the effectiveness of treatments and predict the risk of kidney disease progression. A decrease in UACR is associated with improved renal and cardiovascular outcomes. - Comparison with eGFR:
While eGFR measures kidney function, UACR assesses kidney damage. Both are essential for a comprehensive evaluation of CKD.
Conclusion
UACR is a vital tool for diagnosing and managing kidney disease, offering insights into kidney damage and the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing kidney health. If you have questions about UACR or would like more information on our services related to kidney disease management, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- NIDDK: Quick Reference on UACR & GFR
Discusses the role of UACR in diagnosing and monitoring kidney disease, emphasizing its independence from urine concentration. - NIDDK: UACR Quick Reference Sheet
Highlights UACR as a marker for CKD and its utility in monitoring treatment response. - Diabetes Spectrum: Laboratory Assessment of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Emphasizes UACR as a measure of kidney damage, crucial for identifying CKD. - National Kidney Foundation: Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio (uACR)
Explains how UACR indicates kidney disease even with normal eGFR. - Diabetes on the Net: Testing for Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes
Recommends UACR for identifying and monitoring kidney damage in diabetic patients. - National Kidney Foundation: Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratio
Discusses UACR as a measure of albuminuria, which is a marker for kidney disease. - MDPI: UACR in Random Urine Samples
Highlights UACR as the gold standard for diagnosing nephropathy. - Check Kidneys: UACR Testing
Emphasizes UACR’s role in detecting early signs of CKD and cardiovascular risk in diabetic patients.















