Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Understanding Their Mechanism and Effects
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications widely used for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. They work by inhibiting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are crucial in the synthesis of prostaglandins and thromboxanes.
Mechanism of Action
- COX Enzymes:
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit the activity of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. COX-1 is constitutively expressed and involved in maintaining normal physiological processes, such as protecting the stomach lining and promoting platelet aggregation. COX-2 is induced by inflammatory stimuli and primarily responsible for the synthesis of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain13. - Prostaglandins and Thromboxanes:
Prostaglandins are key mediators of inflammation and pain, while thromboxanes are involved in blood clotting. By inhibiting COX enzymes, NSAIDs reduce the production of these eicosanoids, thereby exerting their therapeutic effects7.
Types of NSAIDs
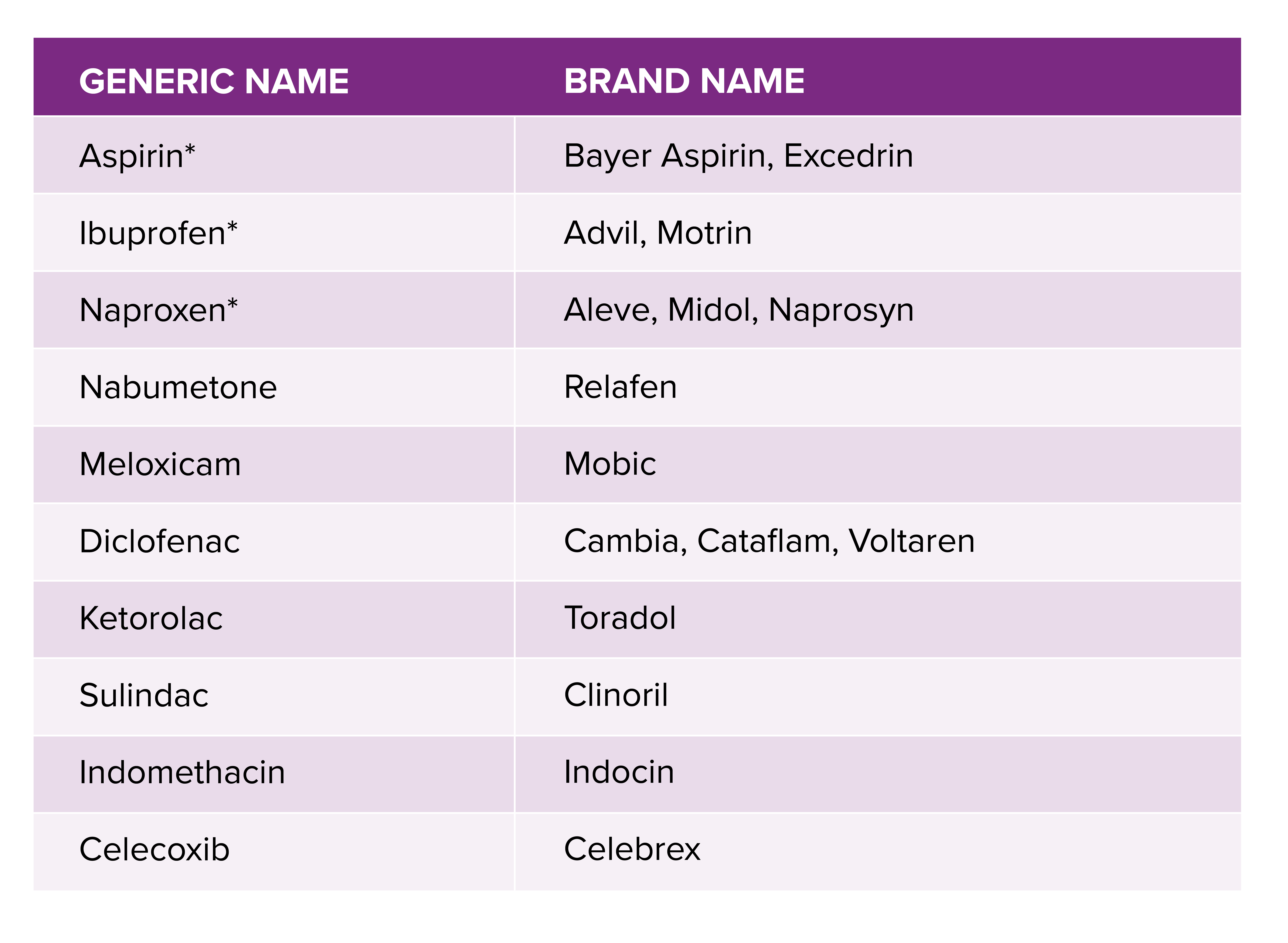
- Non-Selective NSAIDs:
These drugs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. While they effectively reduce inflammation, they can cause gastrointestinal side effects due to COX-1 inhibition24. - Selective COX-2 Inhibitors:
Drugs like celecoxib selectively inhibit COX-2, reducing gastrointestinal risks but potentially increasing cardiovascular risks due to the lack of COX-1 inhibition13.
Conclusion
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are effective for managing pain and inflammation but carry risks such as gastrointestinal complications and cardiovascular issues. Understanding their mechanism of action is crucial for safe and effective use.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatment plans of Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells for managing pain and inflammation. If you have questions about NSAIDs or would like more information on our services related to pain management, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Wikipedia: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug
Discusses the mechanism of action of NSAIDs, including COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition. - YouTube: Pharmacology – Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Explains how NSAIDs inhibit COX enzymes to reduce inflammation and pain. - PubMed: Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action
Highlights the role of COX-1 and COX-2 in NSAID action. - DrugBank: Ibuprofen
Details ibuprofen’s mechanism as a non-selective COX inhibitor. - MDPI: Mechanisms of Action of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Discusses COX-dependent mechanisms in cancer chemoprevention. - Physiopedia: NSAIDs
Explains how NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandin synthesis. - StatPearls: Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Summarizes the therapeutic effects of NSAIDs through COX inhibition.















