Thyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland: Understanding Its Role in Metabolism and Overall Health
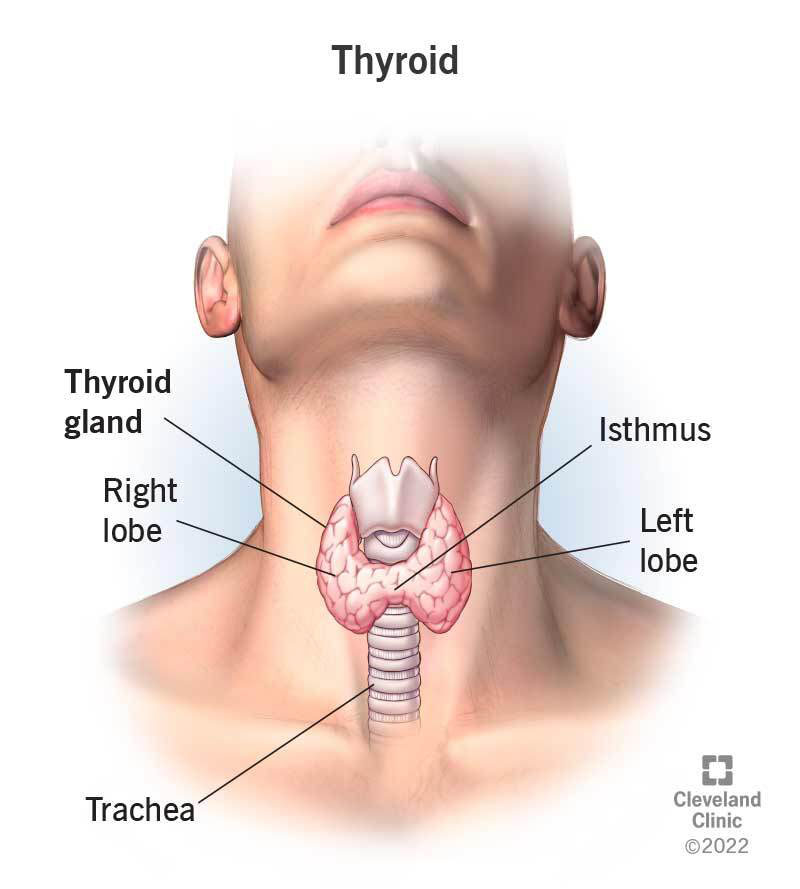
The thyroid gland is a vital endocrine organ located in the front of the neck, shaped like a butterfly. It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions by producing hormones that influence metabolism, energy levels, and overall health.
Key Components of the Thyroid Gland
- Hormone Production:
- The primary hormones produced by the thyroid are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is the prohormone that is converted into the more active T3 in peripheral tissues, primarily the liver and kidneys.
- Calcitonin is another hormone secreted by the thyroid, which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood by inhibiting osteoclast activity, thus promoting bone formation.
- Iodine Dependency:
- Iodine is an essential trace element required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from dietary sources and incorporates it into T3 and T4 molecules.
- Regulatory Mechanisms:
- The production of thyroid hormones is regulated through a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The hypothalamus secretes thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating the pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then prompts the thyroid to produce T4 and T3.
- Elevated levels of T3 and T4 inhibit further release of TRH and TSH, maintaining hormonal balance.
Functions of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones have widespread effects on various body systems:
- Metabolic Regulation:
They increase basal metabolic rate, influencing how the body utilizes energy from food. This includes stimulating appetite, enhancing nutrient absorption, and promoting fat breakdown while reducing cholesterol levels. - Cardiovascular Effects:
Thyroid hormones increase heart rate and cardiac output, facilitating improved oxygen consumption and blood flow throughout the body. - Developmental Role:
These hormones are critical for normal growth and brain development, particularly during fetal development and early childhood. - Thermoregulation:
They play a significant role in maintaining body temperature by increasing heat production through metabolic processes.
Clinical Implications
Understanding thyroid function is essential for diagnosing and managing various disorders:
- Hypothyroidism: A condition where the thyroid does not produce sufficient hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression.
- Hyperthyroidism: Conversely, an overactive thyroid produces excessive hormones, causing symptoms like weight loss, rapid heart rate, anxiety, and heat intolerance.
- Thyroid Nodules and Thyroid Cancer: Abnormal growths in the thyroid can be benign or malignant; regular monitoring through ultrasound or biopsy may be necessary.
Conclusion
The thyroid gland plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism and maintaining overall health through its hormone production. Understanding its functions and regulatory mechanisms is crucial for recognizing potential disorders that can impact well-being.
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we emphasize comprehensive evaluations of thyroid function as part of our holistic approach to health management. If you have questions about your thyroid health or would like more information on our services related to hormonal balance and regenerative medicine, consult with our experts today!
Consult with Our Team of Experts Now!
References
- Wikipedia: Thyroid
Provides an overview of thyroid hormones’ production, regulation, and functions. - You and Your Hormones: Thyroid Gland
Discusses hormone production within the thyroid gland and its physiological roles. - Cleveland Clinic: Thyroid Hormone
Focuses on how thyroid hormones control metabolism and their regulatory mechanisms. - StatPearls: Physiology of Thyroid Hormone
Highlights the physiological roles of thyroid hormones in various bodily functions. - Healthdirect: Thyroid Gland
Outlines key functions of the thyroid gland in regulating metabolism and energy production. - MSD Manuals: Overview of the Thyroid Gland
Provides insights into disorders related to the thyroid gland and their implications for health.















