Regulatory T Cells
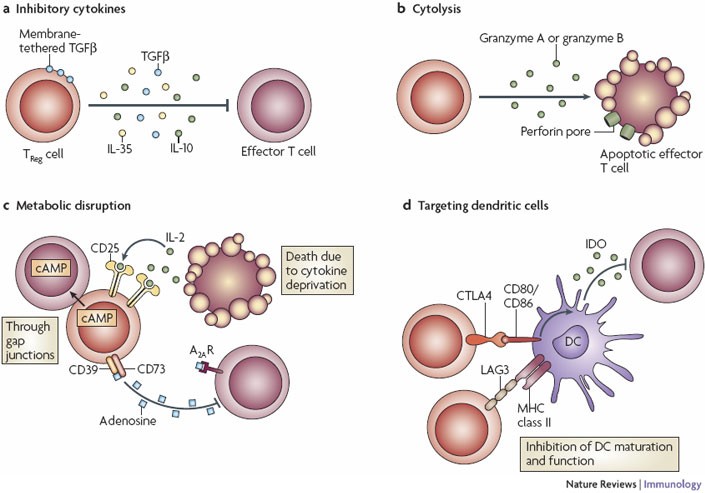
Regulatory T Cells
Definition:
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are a specialized subset of T lymphocytes essential for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmune diseases. Characterized by the expression of the transcription factor FoxP3, Tregs modulate the immune response by suppressing the activation and proliferation of other immune cells, thereby preventing excessive inflammation and tissue damage.
Symptoms:
While regulatory T cells themselves do not exhibit symptoms, their dysfunction or deficiency can lead to various clinical manifestations, including:
- Autoimmune Disease: An insufficient number or impaired function of Tregs can result in autoimmune conditions, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues.
- Chronic Inflammation: Overactive immune responses may lead to chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Allergic Reactions: Impaired Treg function can increase susceptibility to allergies and asthma.
- Increased Cancer Risk: A lack of effective Treg activity may allow unchecked immune responses against tumors, potentially leading to tumor progression.
Causes:
The development and function of regulatory T cells can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Genetic Factors: Mutations in genes associated with Treg development (e.g., FoxP3 mutations) can lead to severe autoimmune diseases.
- Environmental Influences: Factors such as infections, diet, and exposure to environmental toxins can impact Treg populations and their activity.
- Age: Aging is associated with changes in immune cell populations, including a decline in both the number and function of Tregs.
- Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammatory conditions can disrupt the balance between Tregs and effector T cells.
Clinical Significance:
Regulatory T cells are crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis. Their dysfunction can have significant health implications, leading to:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and lupus arise from a failure of Tregs to control self-reactive immune responses.
- Transplant Rejection: Insufficient Treg activity may result in the rejection of transplanted tissues or organs.
- Cancer Immunology: While Tregs can suppress anti-tumor immunity, they are also being studied as potential therapeutic targets to enhance cancer treatments.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing issues related to regulatory T cells typically involves:
- Immunophenotyping: Flow cytometry is used to identify and quantify Treg populations based on specific surface markers (e.g., CD4, CD25).
- Functional Assays: Evaluating the suppressive capacity of Tregs through co-culture experiments with effector T cells.
- Genetic Testing: In cases of suspected genetic disorders affecting Treg function, sequencing may be performed.
Treatment:
Management strategies for conditions related to regulatory T cell dysfunction include:
- Immunosuppressive Therapies: Medications such as corticosteroids or specific immunosuppressants can help modulate the immune response in autoimmune diseases.
- Biologics: Targeted therapies that inhibit specific pathways involved in inflammation may restore balance within the immune system.
- Treg Therapy: Emerging treatments involve expanding or infusing autologous Tregs to enhance tolerance in autoimmune diseases or improve transplant outcomes.
How DrStemCellsThailand Can Help:
At DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand, we offer cutting-edge cellular therapies designed to address issues related to regulatory T cell dysfunction using NK-T Therapy. Our specialized treatments aim to enhance immune regulation and restore balance within the immune system.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: We develop tailored treatment plans that focus on improving the function of regulatory T cells through advanced Cellular Therapy and Stem Cells as well as immunotherapies.
- Innovative Cellular Therapies: Utilizing Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) and other regenerative techniques, we aim to reduce chronic inflammation and enhance overall immune health.
- Comprehensive Follow-Up Care: Our center provides thorough post-treatment monitoring to ensure optimal recovery and assess improvements in symptoms related to autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammation.
By addressing the root causes of regulatory T cell dysfunction, DrStemCellsThailand‘s Anti-Aging and Regenerative Medicine Center of Thailand aims to significantly improve our patients’ quality of life and restore their health.















